A Journey Through Europe’s Peninsulas: Understanding the Shapes of History
Related Articles: A Journey Through Europe’s Peninsulas: Understanding the Shapes of History
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Europe’s Peninsulas: Understanding the Shapes of History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Europe’s Peninsulas: Understanding the Shapes of History

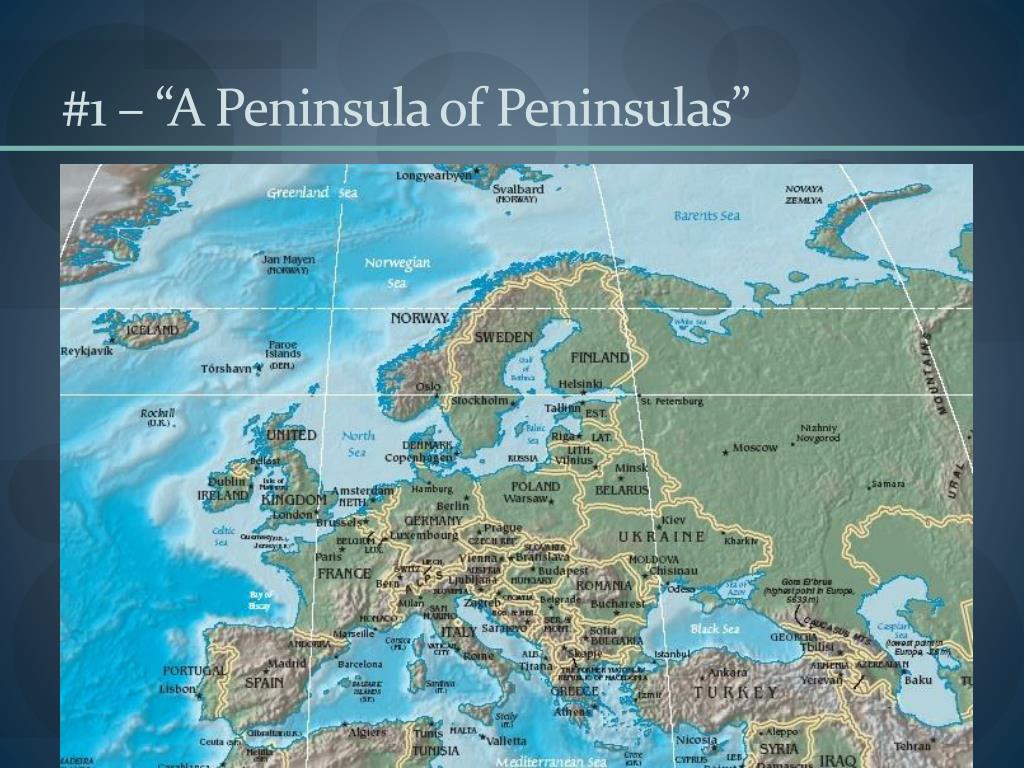
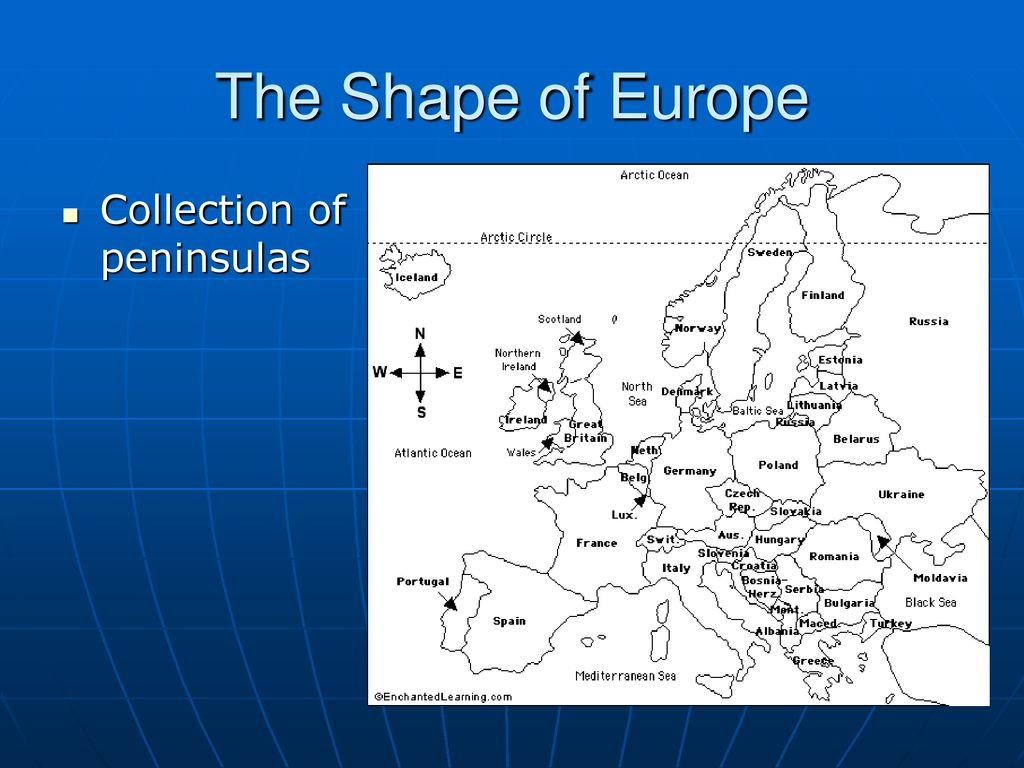
Europe, a continent known for its diverse landscapes, rich history, and vibrant cultures, is also defined by its distinctive peninsulas. These landmasses, jutting out into surrounding bodies of water, have played a significant role in shaping the continent’s geography, history, and cultural identity. Understanding the European peninsulas map provides a unique perspective on the continent’s evolution and its complex tapestry of interactions.
A Geography of Diversity: The Peninsulas of Europe
The European peninsulas are not merely geographical features; they are distinct regions, each with its unique set of characteristics. Their varied landscapes, climates, and historical trajectories have led to the development of diverse cultures and societies.
-
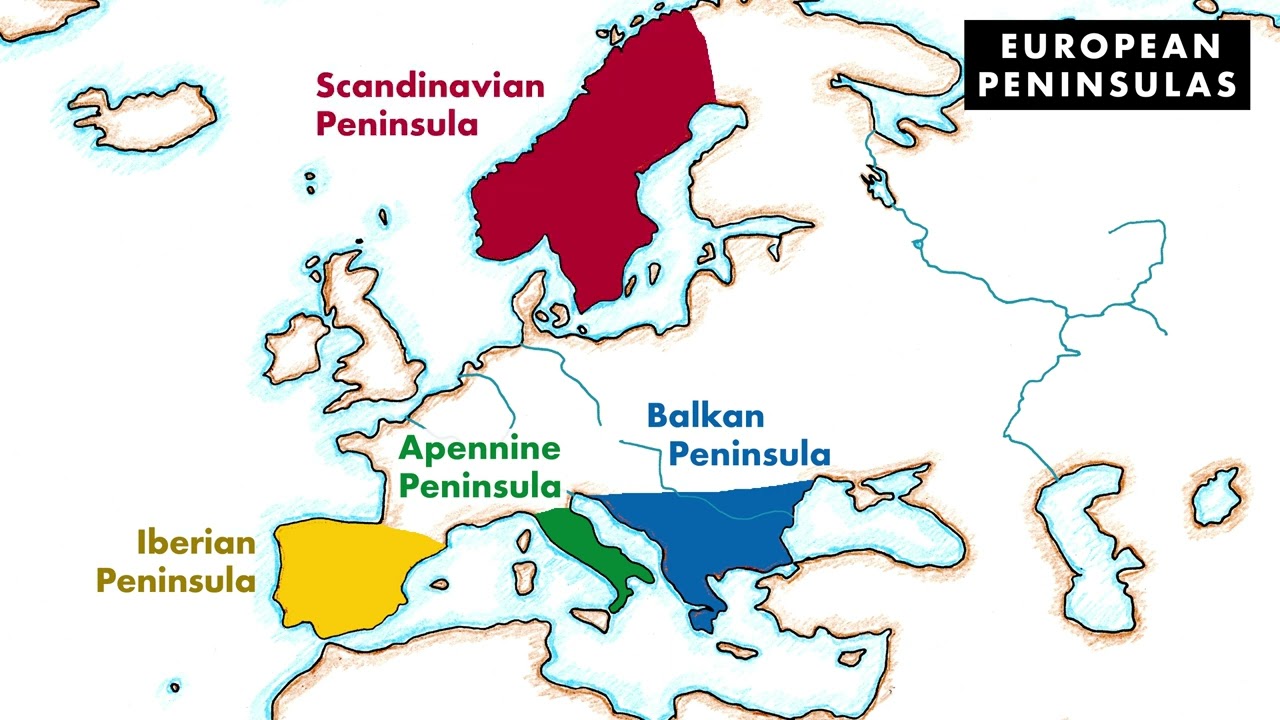
The Iberian Peninsula: Home to Spain and Portugal, the Iberian Peninsula is characterized by its rugged mountain ranges, vast plains, and long coastline. Its strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Africa has made it a melting pot of cultures, influencing the development of both the Iberian Peninsula and the rest of Europe. The peninsula’s rich history, encompassing Roman, Moorish, and Christian influences, continues to resonate in its architecture, language, and traditions.
-
The Italian Peninsula: Known for its iconic boot shape, the Italian Peninsula is a land of contrasts, encompassing the majestic Alps, fertile plains, and the azure waters of the Mediterranean. Its historical significance is undeniable, having been the birthplace of the Roman Empire and the Renaissance. This legacy is evident in its architectural marvels, artistic treasures, and the enduring influence of Roman law and culture.
-
The Balkan Peninsula: A region of significant geopolitical importance, the Balkan Peninsula is a crossroads of cultures and civilizations. Its diverse topography, ranging from mountains and valleys to coastal plains, has shaped the development of numerous ethnic groups and languages. The peninsula’s history has been marked by conflict and cooperation, leaving an indelible mark on its cultural landscape.
-
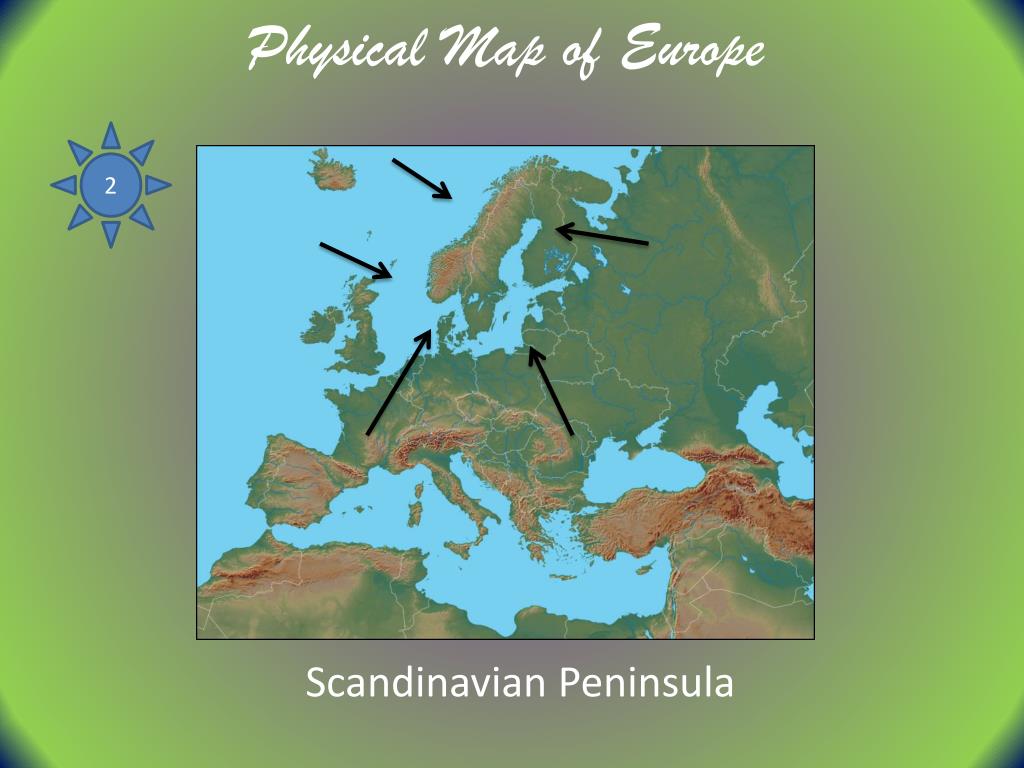
The Scandinavian Peninsula: Encompassing Norway and Sweden, the Scandinavian Peninsula is renowned for its dramatic fjords, vast forests, and rugged mountains. Its proximity to the Arctic Circle has shaped its climate and culture, leading to the development of unique traditions and adaptations. The peninsula’s strong sense of identity and its commitment to environmental sustainability are defining characteristics.
-
The Jutland Peninsula: Located in Denmark, the Jutland Peninsula is a land of rolling hills, sandy beaches, and fertile farmland. Its strategic location at the heart of Northern Europe has made it a crucial link between Scandinavia and the rest of the continent. Its rich history, encompassing Viking raids and Danish rule, has shaped its cultural identity.
The Importance of the European Peninsulas
The European peninsulas have played a pivotal role in shaping the continent’s history, culture, and economy. Their strategic locations have facilitated trade and cultural exchange, leading to the development of vibrant cities and bustling ports. Their diverse landscapes have fostered a rich tapestry of cultures, traditions, and languages.
-
Trade and Commerce: The peninsulas have historically served as gateways for trade and cultural exchange. The Iberian Peninsula, with its ports on the Atlantic and Mediterranean, played a vital role in the spice trade and the spread of Islamic culture. The Italian Peninsula, with its strategic location in the Mediterranean, became a hub for trade and commerce, connecting Europe to the East. The Scandinavian Peninsula, with its long coastline and access to the North Sea, has played a crucial role in maritime trade and fishing.
-
Cultural Exchange: The peninsulas have been melting pots of cultures, facilitating the exchange of ideas, art, and religion. The Iberian Peninsula, influenced by Roman, Moorish, and Christian cultures, has a unique cultural heritage. The Italian Peninsula, the birthplace of the Renaissance, witnessed a flowering of art, literature, and science that had a profound impact on Europe. The Balkan Peninsula, with its diverse ethnic groups and languages, has a rich cultural heritage, reflecting the confluence of Byzantine, Ottoman, and Slavic influences.
-
Economic Development: The peninsulas have contributed significantly to the economic development of Europe. The Iberian Peninsula, with its rich mineral resources and agricultural production, has played a vital role in the European economy. The Italian Peninsula, with its thriving tourism industry and manufacturing sector, is a major economic powerhouse. The Scandinavian Peninsula, with its emphasis on sustainability and innovation, is a leader in renewable energy and technology.
FAQs about the European Peninsulas
Q: What is the largest peninsula in Europe?
A: The Scandinavian Peninsula, encompassing Norway and Sweden, is the largest peninsula in Europe.
Q: What is the smallest peninsula in Europe?
A: Determining the smallest peninsula in Europe is subjective, as there are numerous small peninsulas scattered across the continent. However, the Istrian Peninsula, located in Croatia, is considered one of the smallest.
Q: What are the main geographical features of the European peninsulas?
A: The European peninsulas are characterized by a wide range of geographical features, including:
-
Mountains: The Iberian Peninsula features the Pyrenees, the Sierra Nevada, and the Cantabrian Mountains. The Italian Peninsula is home to the Alps, the Apennines, and the Dolomites. The Balkan Peninsula is marked by the Dinaric Alps, the Balkan Mountains, and the Rhodope Mountains. The Scandinavian Peninsula features the Scandinavian Mountains, the Kjølen Mountains, and the Dovrefjell Mountains.
-
Plains: The Iberian Peninsula has the Duero Plain, the Ebro Plain, and the Guadalquivir Plain. The Italian Peninsula features the Po Plain and the Campanian Plain. The Balkan Peninsula has the Thracian Plain, the Pannonian Plain, and the Vardar Valley. The Scandinavian Peninsula has the Swedish Plain and the Norwegian Plain.
-
Coastlines: The European peninsulas boast diverse coastlines, ranging from rocky cliffs and sandy beaches to fjords and inlets. The Iberian Peninsula has a long coastline on the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. The Italian Peninsula has a long coastline on the Mediterranean Sea. The Balkan Peninsula has a coastline on the Adriatic Sea, the Aegean Sea, and the Black Sea. The Scandinavian Peninsula has a long coastline on the North Sea, the Baltic Sea, and the Norwegian Sea.
Q: What are the main cultural influences on the European peninsulas?
A: The European peninsulas have been shaped by a complex interplay of cultural influences, including:
-
Roman Influence: The Roman Empire left an enduring legacy on the Iberian Peninsula, the Italian Peninsula, and the Balkan Peninsula, influencing their languages, laws, and architecture.
-
Moorish Influence: The Moorish conquest of the Iberian Peninsula had a profound impact on its culture, introducing Arabic language, Islamic art, and architectural styles.
-
Christian Influence: Christianity has played a significant role in shaping the cultural landscape of the European peninsulas, influencing their art, literature, and social norms.
-
Slavic Influence: Slavic languages and cultures have had a significant impact on the Balkan Peninsula, shaping its linguistic and cultural diversity.
-
Viking Influence: Viking raids and settlements have left their mark on the Scandinavian Peninsula, influencing its language, culture, and traditions.
Tips for Understanding the European Peninsulas Map
-
Visualize the Shapes: Pay attention to the distinctive shapes of the peninsulas, which can help you remember their locations.
-
Connect the Peninsulas to Surrounding Waters: Understand the geographical relationship between the peninsulas and the surrounding bodies of water, such as the Mediterranean Sea, the Atlantic Ocean, and the Baltic Sea.
-
Identify Key Geographic Features: Focus on the major mountain ranges, plains, and rivers that define the peninsulas.
-
Explore the Historical Connections: Research the historical events and influences that have shaped the cultural and linguistic diversity of each peninsula.
-
Consider the Cultural Landscape: Understand the cultural and linguistic differences between the peninsulas and the factors that have contributed to their unique identities.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of Landscapes and Cultures
The European peninsulas map is not just a geographical representation; it is a window into the continent’s rich history, diverse cultures, and complex interactions. Understanding the shapes, locations, and historical significance of these landmasses provides a unique perspective on the evolution of Europe and its enduring cultural tapestry. From the rugged mountains of the Iberian Peninsula to the fertile plains of the Italian Peninsula, each peninsula offers a unique glimpse into the continent’s diverse landscapes and vibrant cultures.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Europe’s Peninsulas: Understanding the Shapes of History. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!