Navigating North America: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating North America: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating North America: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating North America: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
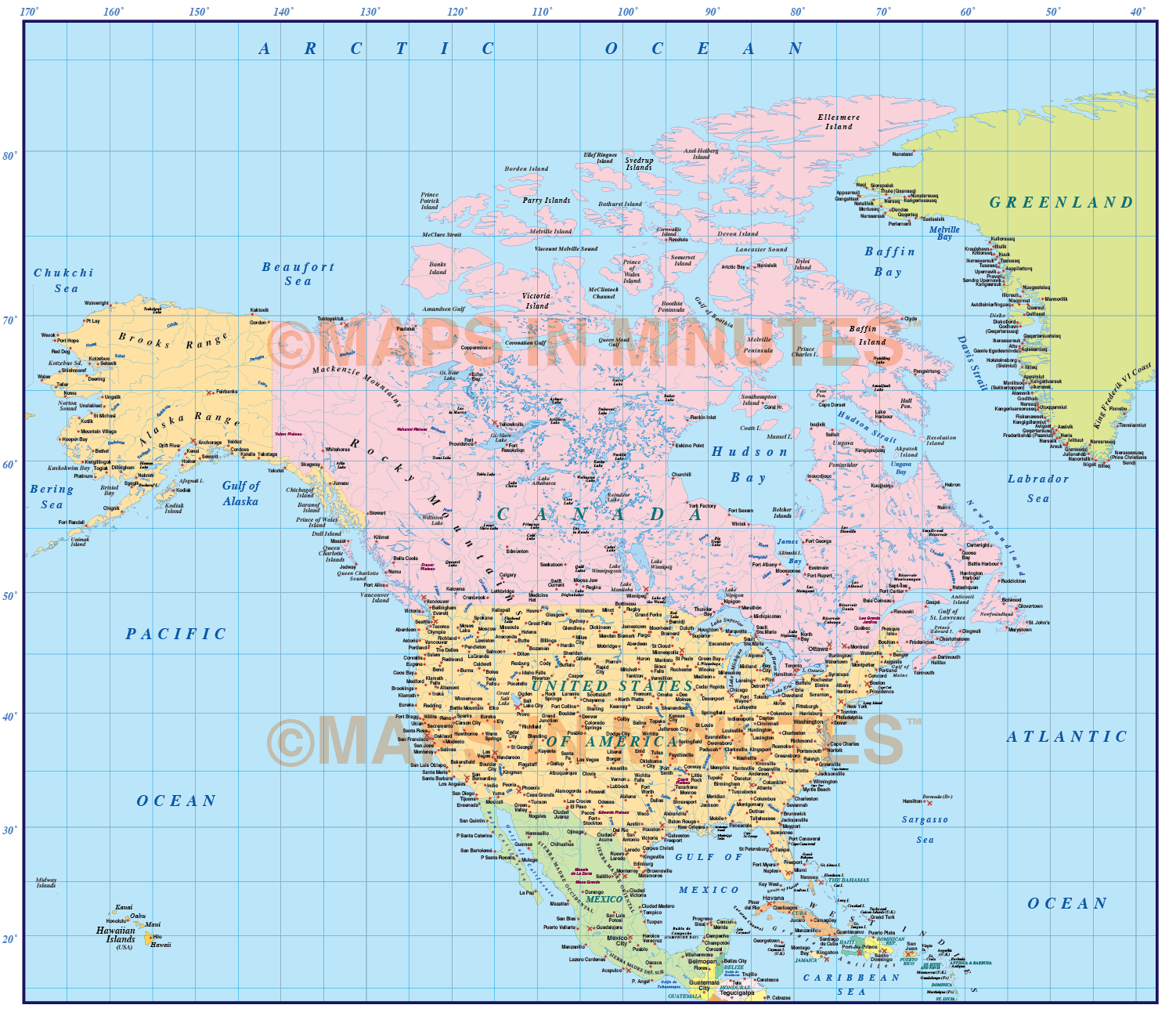
North America, a vast and diverse continent, is home to a myriad of landscapes, cultures, and natural wonders. To effectively explore and understand its geography, a fundamental understanding of latitude and longitude is essential. These two coordinates, working together, form the basis of a global grid system that allows us to pinpoint any location on Earth with remarkable accuracy.
Latitude: Lines of Parallel
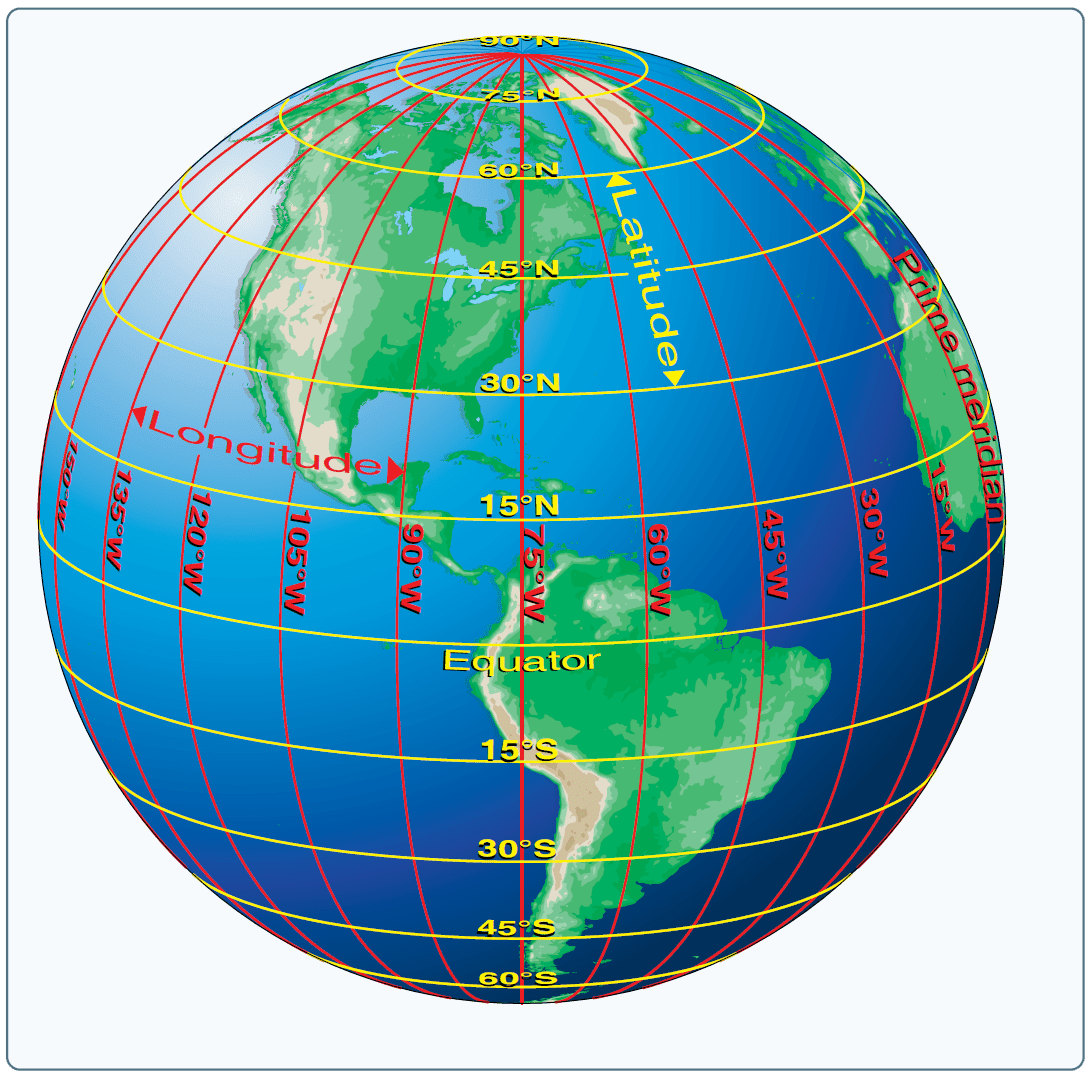
Imagine slicing through the Earth horizontally, like a loaf of bread. These imaginary lines, running parallel to the equator, are known as lines of latitude. The equator itself is the most important line of latitude, marking 0 degrees and dividing the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
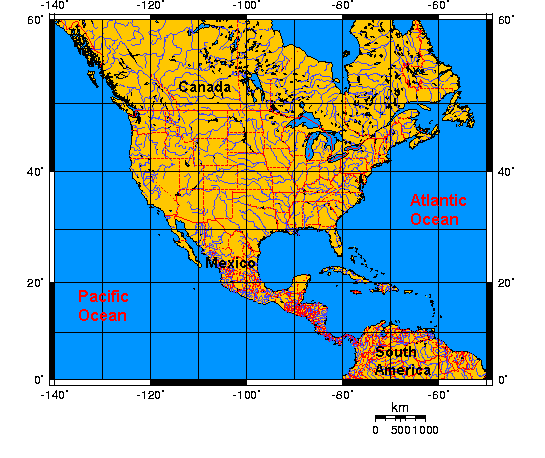
As we move away from the equator, the lines of latitude become smaller, each line representing one degree of distance. Every degree of latitude is approximately 69 miles (111 kilometers) apart. North America, situated primarily in the Northern Hemisphere, spans from approximately 83 degrees North at the Arctic Circle to 7 degrees North in the Caribbean.
Longitude: Lines of Meridian
Now, imagine slicing through the Earth vertically, like a wedge of pie. These imaginary lines, running from the North Pole to the South Pole, are known as lines of longitude, also known as meridians. The Prime Meridian, passing through Greenwich, England, is the zero-degree line of longitude.
Unlike lines of latitude, which maintain a consistent distance, lines of longitude converge at the poles. Therefore, the distance between two lines of longitude varies depending on their proximity to the poles. North America spans a considerable range of longitude, from approximately 168 degrees West in Alaska to 53 degrees West in Newfoundland.
The Power of Coordinates
Together, latitude and longitude create a precise grid system that allows us to locate any point on Earth. Each location can be uniquely identified by its specific latitude and longitude coordinates. For instance, the iconic Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco, California, can be pinpointed at 37.8197° N, 122.4783° W.
This system is crucial for various purposes, including:
- Navigation: Latitude and longitude are fundamental for navigation, enabling ships, aircraft, and even hikers to pinpoint their location and plan their routes.
- Mapping: Maps rely heavily on latitude and longitude to accurately represent geographical features and distances.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS uses latitude and longitude as the foundation for managing, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data, enabling applications in fields like urban planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster management.
- Communication: GPS technology, a cornerstone of modern communication and navigation, relies on precise latitude and longitude coordinates to determine location and provide directions.
Benefits of Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Beyond their practical applications, understanding latitude and longitude provides valuable insights into the Earth’s geography and its impact on different regions:
- Climate and Weather: Latitude plays a significant role in determining a region’s climate. Areas closer to the equator experience more direct sunlight and warmer temperatures, while those at higher latitudes experience colder climates.
- Daylight Hours: The angle of the sun’s rays, influenced by latitude, dictates the duration of daylight hours. Higher latitudes experience significant variations in daylight hours throughout the year, with long days in summer and short days in winter.
- Cultural and Historical Influences: Latitude and longitude can influence cultural and historical patterns. The proximity to the equator, for instance, can impact agricultural practices and cultural traditions.
FAQs about Latitude and Longitude in North America
1. What are the highest and lowest points in North America based on latitude and longitude?
The highest point in North America is Mount Denali (formerly Mount McKinley) in Alaska, at 63.0690° N, 151.0052° W. The lowest point is Death Valley in California, at 36.2400° N, 116.8100° W.
2. How does latitude affect the time zones in North America?
As the Earth rotates, different longitudes experience the sun’s rays at different times. To account for this, North America is divided into multiple time zones. Generally, each time zone covers approximately 15 degrees of longitude.
3. How does latitude impact the vegetation zones in North America?
Latitude significantly influences the types of vegetation found in different regions. For example, the warm, humid climate of the southern United States supports lush forests, while the cold, dry climate of northern Canada supports tundra vegetation.
4. How can I use latitude and longitude to explore different regions of North America?
Using online mapping tools or GPS devices, you can enter specific latitude and longitude coordinates to locate and explore different areas of North America. This can be a valuable tool for planning trips, exploring new destinations, or learning more about specific locations.
Tips for Using Latitude and Longitude
- Use online mapping tools: Tools like Google Maps or OpenStreetMap allow you to enter latitude and longitude coordinates to find specific locations.
- Utilize GPS devices: GPS devices use latitude and longitude to determine your current location and provide directions.
- Learn the basics of the coordinate system: Understanding how latitude and longitude work can enhance your understanding of maps and geographical data.
- Practice using latitude and longitude in real-world applications: Try using latitude and longitude to find specific locations in your city or region.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude form the foundation of our understanding of Earth’s geography. By understanding these coordinates and their relationship to North America, we gain valuable insights into the continent’s diverse landscapes, climates, and cultural patterns. Whether for navigation, mapping, or simply appreciating the vastness of our planet, latitude and longitude provide a powerful tool for exploration and understanding.

![]()



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating North America: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!