Navigating the Tapestry of Sovereignty: Understanding Oklahoma’s Indian Reservations
Related Articles: Navigating the Tapestry of Sovereignty: Understanding Oklahoma’s Indian Reservations
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tapestry of Sovereignty: Understanding Oklahoma’s Indian Reservations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tapestry of Sovereignty: Understanding Oklahoma’s Indian Reservations

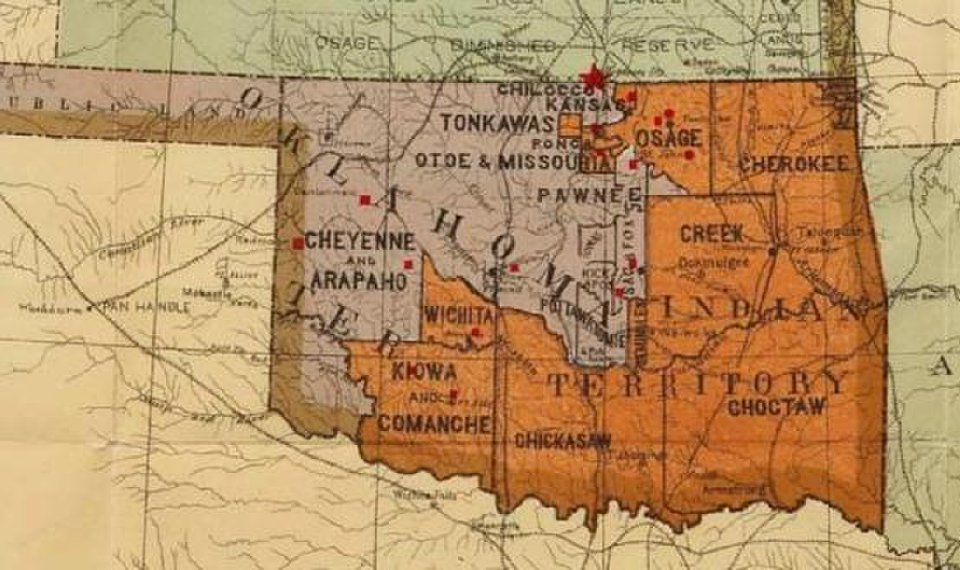
Oklahoma’s landscape is marked by a complex and intricate tapestry of sovereign lands, a legacy of the forced removal of Native American tribes during the 19th century and the subsequent establishment of reservations. This unique history has resulted in a state where tribal lands and cultures are deeply interwoven with the broader Oklahoma fabric, creating a dynamic and often misunderstood dynamic.
Understanding Oklahoma’s Indian reservations requires navigating a complex web of history, law, and cultural nuances. This article aims to shed light on the geographical and legal framework of these reservations, highlighting their significance in the present-day context.
The Historical Context of Oklahoma’s Reservations:
The forced relocation of Native American tribes from their ancestral homelands in the eastern United States to Oklahoma, known as the "Trail of Tears," laid the foundation for the establishment of reservations. This period saw the displacement of numerous tribes, including the Cherokee, Choctaw, Chickasaw, Creek, and Seminole, who were assigned specific territories within the newly formed Indian Territory.
The Indian Territory was initially governed by tribal governments, with the federal government playing a limited role. However, with the influx of non-Native settlers, the federal government gradually asserted more control, eventually leading to the statehood of Oklahoma in 1907.
While the Indian Territory was dissolved, many tribes retained their land holdings, which were officially designated as reservations. These reservations were subject to federal jurisdiction, with the tribes granted limited self-governance.
The Legal Framework of Oklahoma’s Reservations:
The legal framework governing Oklahoma’s reservations is complex, a result of centuries of evolving legislation and court rulings. The primary legal basis for tribal sovereignty stems from the 1832 Supreme Court case, Worcester v. Georgia, which affirmed the right of tribes to self-governance within their territories. This principle has been upheld in subsequent court decisions, including the 1978 case, Oliphant v. Suquamish Indian Tribe, which reaffirmed the right of tribes to exercise criminal jurisdiction over their members within reservation boundaries.
However, the legal framework governing reservations is not without its challenges. The "Indian Country" status of reservations has been subject to ongoing litigation, with the boundaries of tribal jurisdiction often contested. The 1978 Public Law 95-600, also known as the Oklahoma Indian Gaming Regulatory Act, established a framework for tribal gaming operations, but it also opened a new avenue for legal challenges.
The Significance of Oklahoma’s Reservations:
Oklahoma’s Indian reservations hold significant cultural, economic, and political importance. They represent a vital link to Native American heritage and traditions, providing a platform for cultural preservation and revitalization.
Cultural Significance:
Reservations serve as cultural centers, preserving tribal languages, traditions, and spiritual practices. They are home to numerous cultural institutions, museums, and community centers that promote cultural awareness and education.
Economic Significance:
Reservations play a crucial role in the state’s economy, contributing significantly to various sectors, including tourism, gaming, and agriculture. Tribal businesses, ranging from casinos to healthcare facilities, provide employment opportunities and generate revenue within reservation communities.
Political Significance:
Reservations represent a unique form of self-governance within the state, allowing tribes to exercise their sovereignty and manage their affairs independently. Tribal governments play a vital role in providing services to their members, including education, healthcare, and law enforcement.
The Importance of Understanding Oklahoma’s Reservations:
Understanding Oklahoma’s Indian reservations is crucial for fostering a respectful and collaborative relationship between Native American communities and the broader society. It requires acknowledging the historical context, legal framework, and the unique challenges faced by these communities.
FAQs Regarding Oklahoma’s Indian Reservations:
1. How many Indian reservations are there in Oklahoma?
There are 39 federally recognized tribes in Oklahoma, with each tribe having its own reservation or trust lands. The exact number of reservations can vary depending on how they are defined, as some tribes have multiple reservations or trust lands within the state.
2. What are the largest Indian reservations in Oklahoma?
The largest Indian reservation in Oklahoma is the Cherokee Nation Reservation, which covers a significant portion of northeastern Oklahoma. Other large reservations include the Choctaw Nation Reservation and the Chickasaw Nation Reservation.
3. What are the main economic activities on Oklahoma’s reservations?
Economic activities on reservations vary widely, but common activities include:
- Gaming: Casinos are a major source of revenue for many tribes, providing employment and economic development opportunities.
- Tourism: Many reservations have developed tourism attractions, such as museums, cultural centers, and historic sites.
- Agriculture: Agriculture remains an important economic activity on some reservations, with tribes involved in farming, ranching, and forestry.
- Energy: Some reservations have resources like oil and gas, which contribute to their economies.
4. What are the challenges faced by Oklahoma’s reservations?
Oklahoma’s reservations face a number of challenges, including:
- Poverty: Despite economic development efforts, poverty rates remain high on many reservations.
- Lack of access to resources: Reservations often lack access to adequate housing, healthcare, and education resources.
- Environmental issues: Some reservations face environmental challenges, such as pollution and water contamination.
- Legal challenges: The legal framework governing reservations is complex and subject to ongoing litigation.
5. What can be done to improve the lives of people living on Oklahoma’s reservations?
There are various ways to address the challenges faced by Oklahoma’s reservations, including:
- Increased federal funding: Providing more resources to tribes for education, healthcare, housing, and infrastructure development.
- Economic development initiatives: Supporting tribal businesses and promoting economic opportunities on reservations.
- Addressing environmental concerns: Investing in environmental protection and restoration projects on reservations.
- Strengthening tribal sovereignty: Protecting the legal rights of tribes and promoting self-governance.
Tips for Engaging with Oklahoma’s Reservations:
- Respect tribal sovereignty: Acknowledge the right of tribes to govern their own affairs.
- Learn about tribal history and culture: Educate yourself about the unique cultures and traditions of Oklahoma’s tribes.
- Support tribal businesses and organizations: Patronize tribal businesses and donate to organizations that support Native American communities.
- Engage in respectful dialogue: Listen to and learn from the perspectives of Native American people.
Conclusion:
Oklahoma’s Indian reservations are a testament to the resilience and cultural heritage of Native American tribes. They represent a complex and often overlooked aspect of the state’s history and identity. By understanding the historical context, legal framework, and the significance of these reservations, we can foster a more inclusive and equitable society that respects the rights and contributions of Native American communities.
The future of Oklahoma’s Indian reservations depends on continued dialogue, collaboration, and a commitment to preserving tribal sovereignty and promoting economic and social justice. Only through a shared understanding and respect for these communities can we truly appreciate the rich tapestry of Oklahoma’s history and its diverse cultural heritage.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tapestry of Sovereignty: Understanding Oklahoma’s Indian Reservations. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!