Mapping the Global Conflict: World War II and its Visual Representation
Related Articles: Mapping the Global Conflict: World War II and its Visual Representation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Global Conflict: World War II and its Visual Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Global Conflict: World War II and its Visual Representation

World War II, the most devastating conflict in human history, was fought across vast geographical expanses, involving nations from every continent. Understanding the intricate web of alliances, battlefronts, and territorial changes that defined this war requires a visual tool – a map. These maps, meticulously crafted and constantly updated, served as essential instruments for strategists, military leaders, and the general public alike. They provided a tangible representation of the conflict’s scale, its global reach, and its profound impact on the world order.
The Importance of World War II Maps:
World War II maps played a critical role in shaping the course of the war, facilitating strategic decision-making, and informing the public about the conflict’s progress. Their significance can be understood through several key aspects:
1. Strategic Planning and Decision-Making:
Military commanders relied heavily on maps to plan and execute military operations. Detailed maps showcasing terrain features, infrastructure, and enemy troop positions allowed for the development of effective strategies, troop movements, and logistical planning. The ability to visualize the battleground, understand the terrain, and anticipate enemy movements was crucial for achieving military success.
2. Communication and Information Dissemination:
Maps served as a powerful tool for communication, enabling the swift dissemination of information within and between military units. They facilitated coordination among different branches of the armed forces, allowing for the efficient allocation of resources and the synchronization of offensive and defensive operations.
3. Public Understanding and Awareness:
The general public also relied on maps to understand the war’s progression. Newspapers, radio broadcasts, and other media outlets frequently used maps to illustrate the changing battlefronts, the movement of troops, and the shifting geopolitical landscape. These visual representations helped to keep the public informed and engaged with the war effort.
4. Historical Documentation and Analysis:
World War II maps are invaluable historical documents, providing a snapshot of the war’s geographic scope and the evolution of battle lines. They offer insights into the strategic thinking of military leaders, the logistical challenges faced by both sides, and the impact of the war on different regions of the world.
Types of World War II Maps:
World War II maps encompass a wide range of types, each serving a specific purpose:
1. Operational Maps:
These maps were primarily used by military commanders and staff. They focused on specific regions, battlefields, or theaters of war, providing detailed information about terrain, enemy positions, troop movements, and logistical routes.
2. Tactical Maps:
These maps were designed for use at the unit level, focusing on smaller-scale operations and maneuvers. They included information about specific terrain features, enemy positions, and potential attack or defense strategies.
3. Strategic Maps:
These maps provided a broader view of the war, showcasing the global theater of operations, alliances, and the movement of major forces. They allowed for the visualization of the overall strategic situation and the planning of long-term campaigns.
4. Propaganda Maps:
These maps were used by governments and propaganda agencies to present a particular narrative about the war. They often exaggerated enemy strength or highlighted the successes of their own forces, aiming to influence public opinion and bolster morale.
5. Historical Maps:
These maps are designed to provide a comprehensive overview of the war, showcasing the geographic scope of the conflict, the major battlefronts, and the territorial changes that occurred. They are often used for educational purposes, providing a visual framework for understanding the war’s history.
Benefits of Studying World War II Maps:
Beyond their immediate practical applications, World War II maps offer several benefits for students of history, military strategy, and international relations:
1. Enhanced Historical Understanding:
Maps provide a powerful visual tool for understanding the geographic context of the war, the strategic choices made by leaders, and the impact of the conflict on different regions and populations.
2. Increased Spatial Awareness:
Maps help to develop spatial awareness and the ability to visualize large-scale events and complex relationships. This skill is valuable for understanding not only historical conflicts but also contemporary geopolitical issues.
3. Improved Analytical Skills:
By analyzing the information presented on maps, individuals can develop critical thinking and analytical skills. They can learn to identify patterns, draw inferences, and formulate conclusions based on visual data.
4. Fostering Empathy and Understanding:
Maps can help to humanize the war by providing a visual representation of the vast distances traveled by soldiers, the locations of battlefields, and the populations affected by the conflict. This can foster empathy and understanding for the human cost of war.
FAQs about World War II Maps:
1. What are the most important World War II maps?
This depends on the specific focus of interest. For military historians, operational and tactical maps of key battles are crucial. For broader historical understanding, strategic maps showcasing the global scope of the war are essential.
2. Where can I find World War II maps?
World War II maps are available in various sources, including historical archives, libraries, museums, online databases, and specialized publications.
3. How can I use World War II maps to learn more about the war?
By carefully analyzing the information presented on maps, identifying key locations, understanding troop movements, and tracing the evolution of battle lines, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the war’s strategic complexities.
4. What are the limitations of World War II maps?
Maps are only a representation of reality and can be influenced by the perspectives and biases of their creators. It’s important to consider the context, purpose, and potential limitations of any map before drawing conclusions.
Tips for Studying World War II Maps:
1. Consider the Context:
Always examine the map’s date of creation, its intended audience, and the purpose for which it was created. This information can help to understand the map’s potential biases and limitations.
2. Analyze the Details:
Pay attention to the map’s symbols, legends, and scale. Identify key locations, battlefronts, and strategic points of interest.
3. Compare and Contrast:
Compare different maps of the same region or time period to identify discrepancies and gain a more comprehensive understanding of the conflict.
4. Use Maps in Conjunction with Other Sources:
Combine maps with textual sources, photographs, and other historical documents to gain a richer and more nuanced understanding of the war.
Conclusion:
World War II maps serve as powerful visual tools for understanding the complexities of the war. They provide a tangible representation of the conflict’s geographic scope, the strategic decisions made by leaders, and the human cost of war. By studying these maps, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the historical significance of World War II, its impact on the world order, and the lessons we can learn from this pivotal moment in human history.
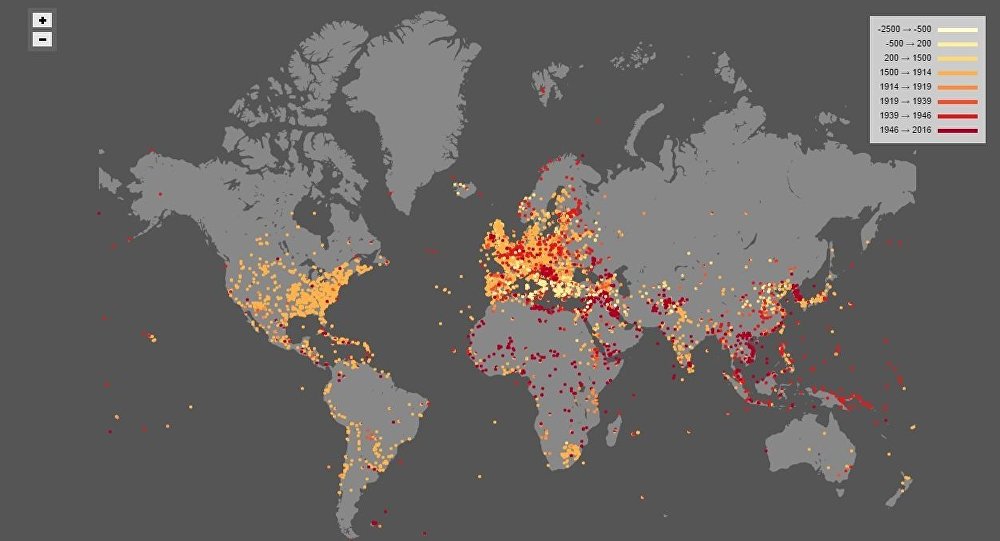
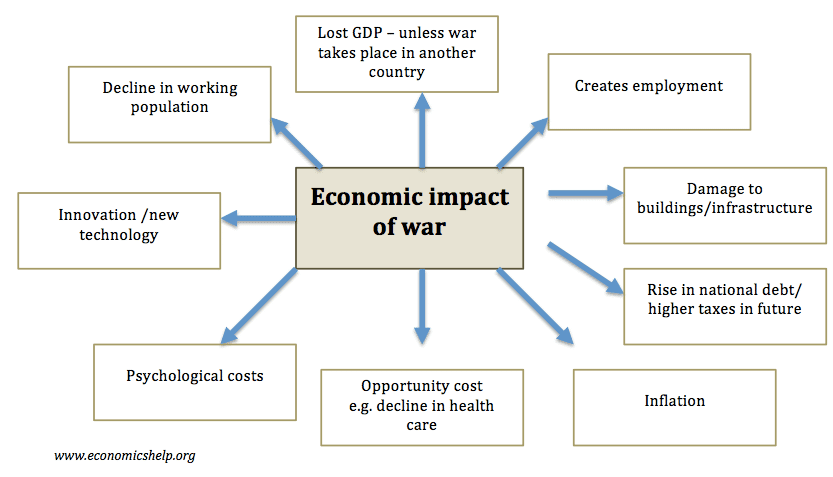
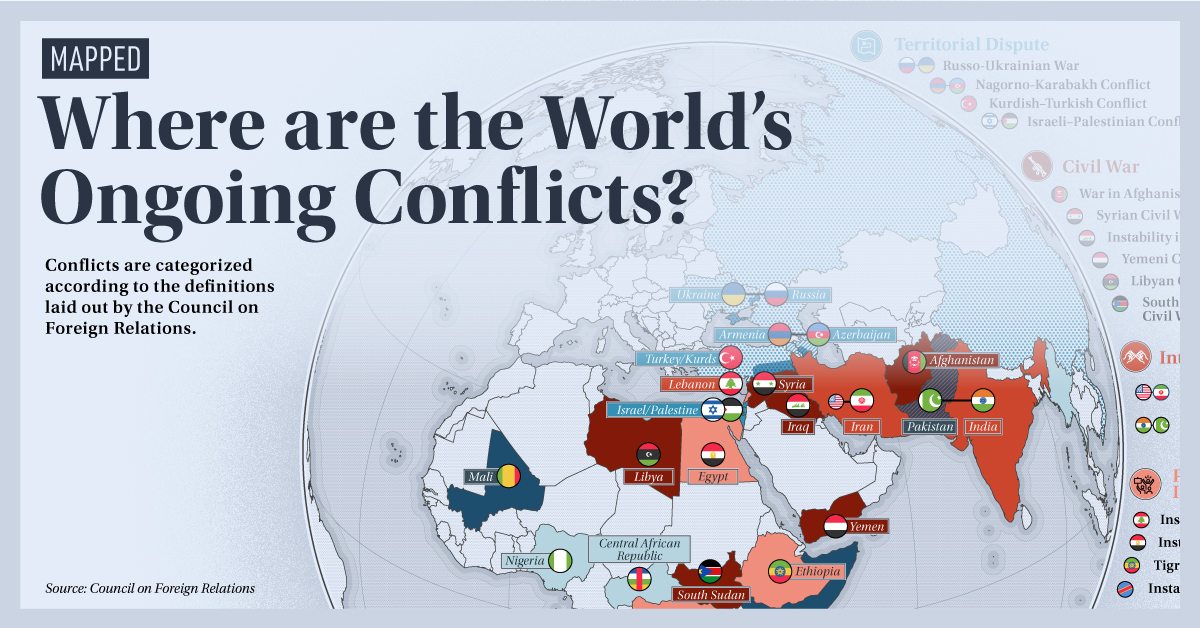
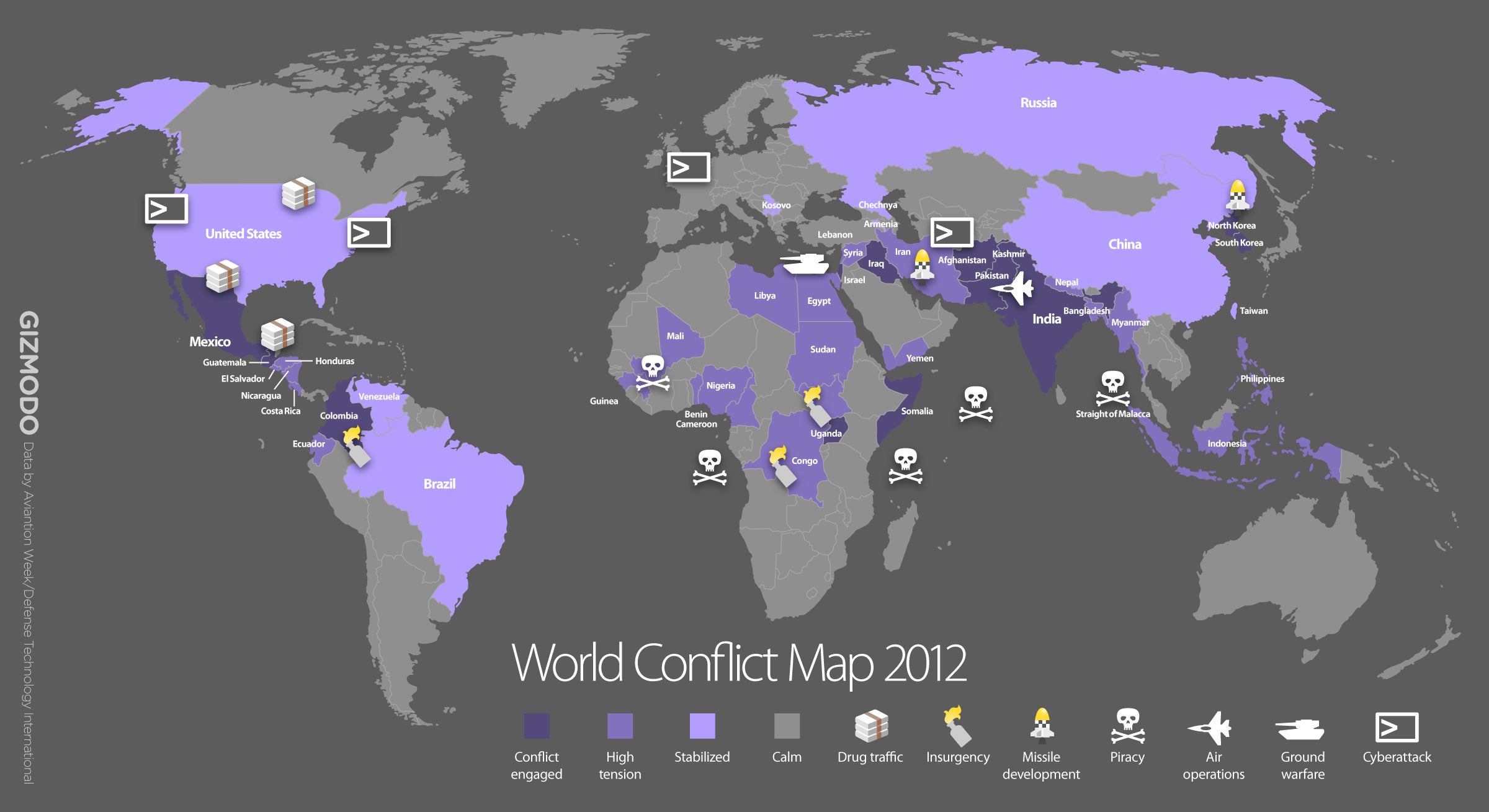


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Global Conflict: World War II and its Visual Representation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!