Understanding the Shia-Sunni Divide: A Geographical Perspective
Related Articles: Understanding the Shia-Sunni Divide: A Geographical Perspective
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Shia-Sunni Divide: A Geographical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Shia-Sunni Divide: A Geographical Perspective
The division between Shia and Sunni Muslims is one of the most significant and enduring fissures within Islam. This historical schism, rooted in the succession of Prophet Muhammad after his death in 632 CE, has shaped the religious, political, and social landscape of the Muslim world for centuries. While the theological differences between Shia and Sunni Muslims are complex and nuanced, a geographical understanding of their distribution offers a valuable framework for comprehending the dynamics of this division.
A Visual Representation of the Divide:
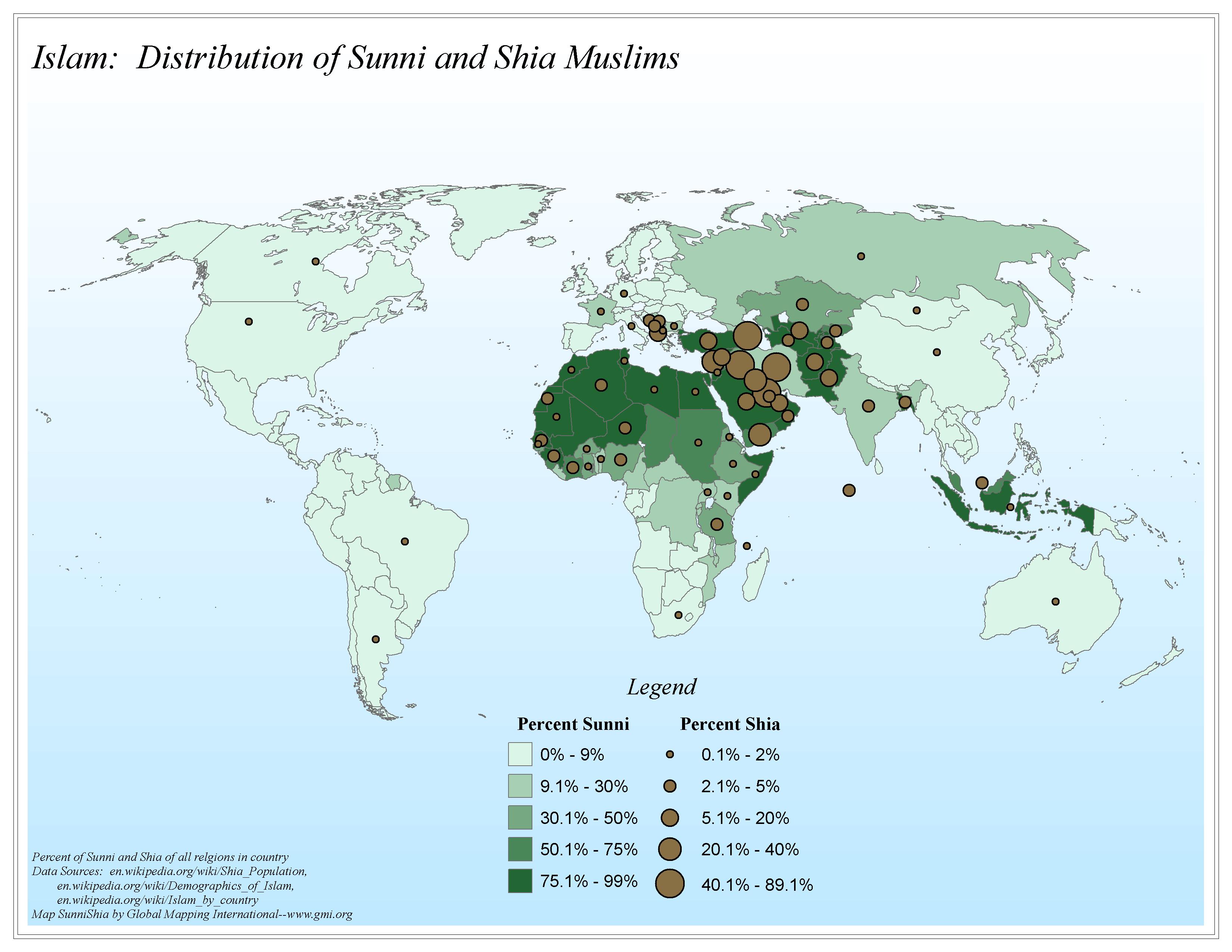
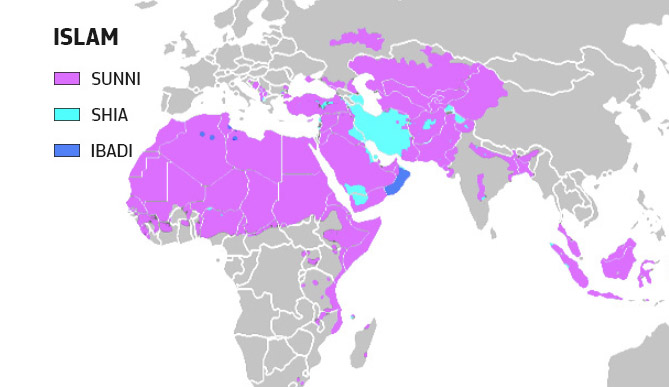
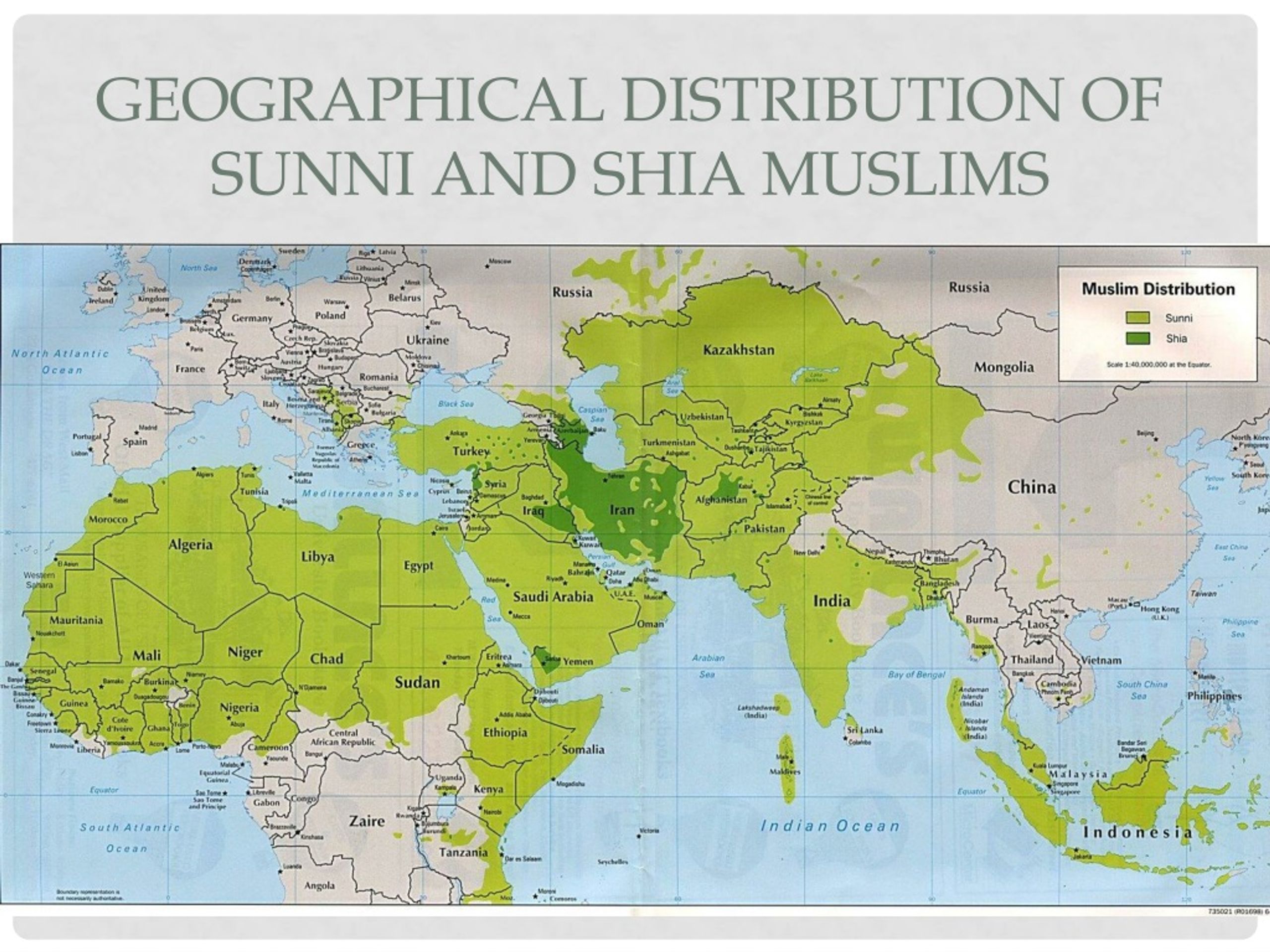
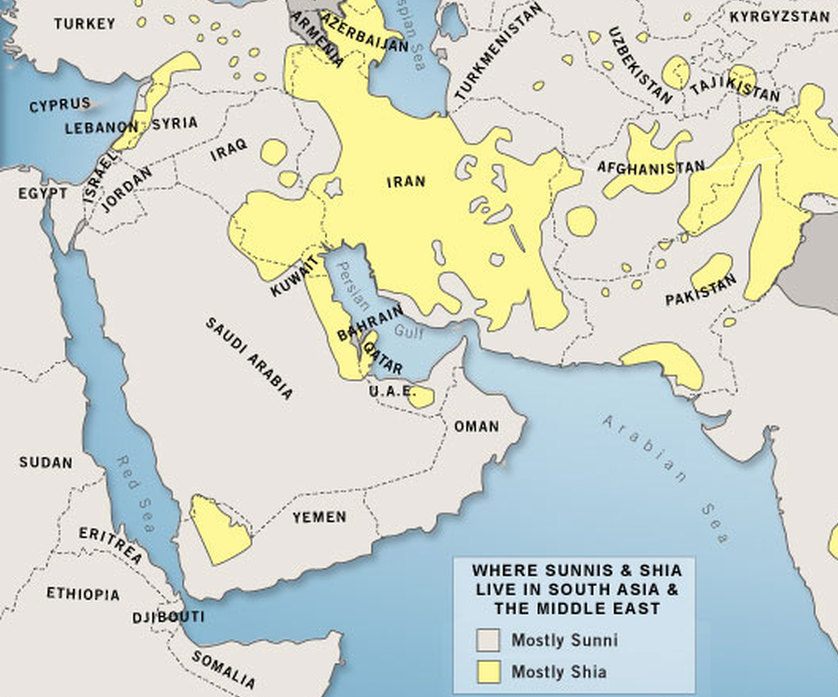
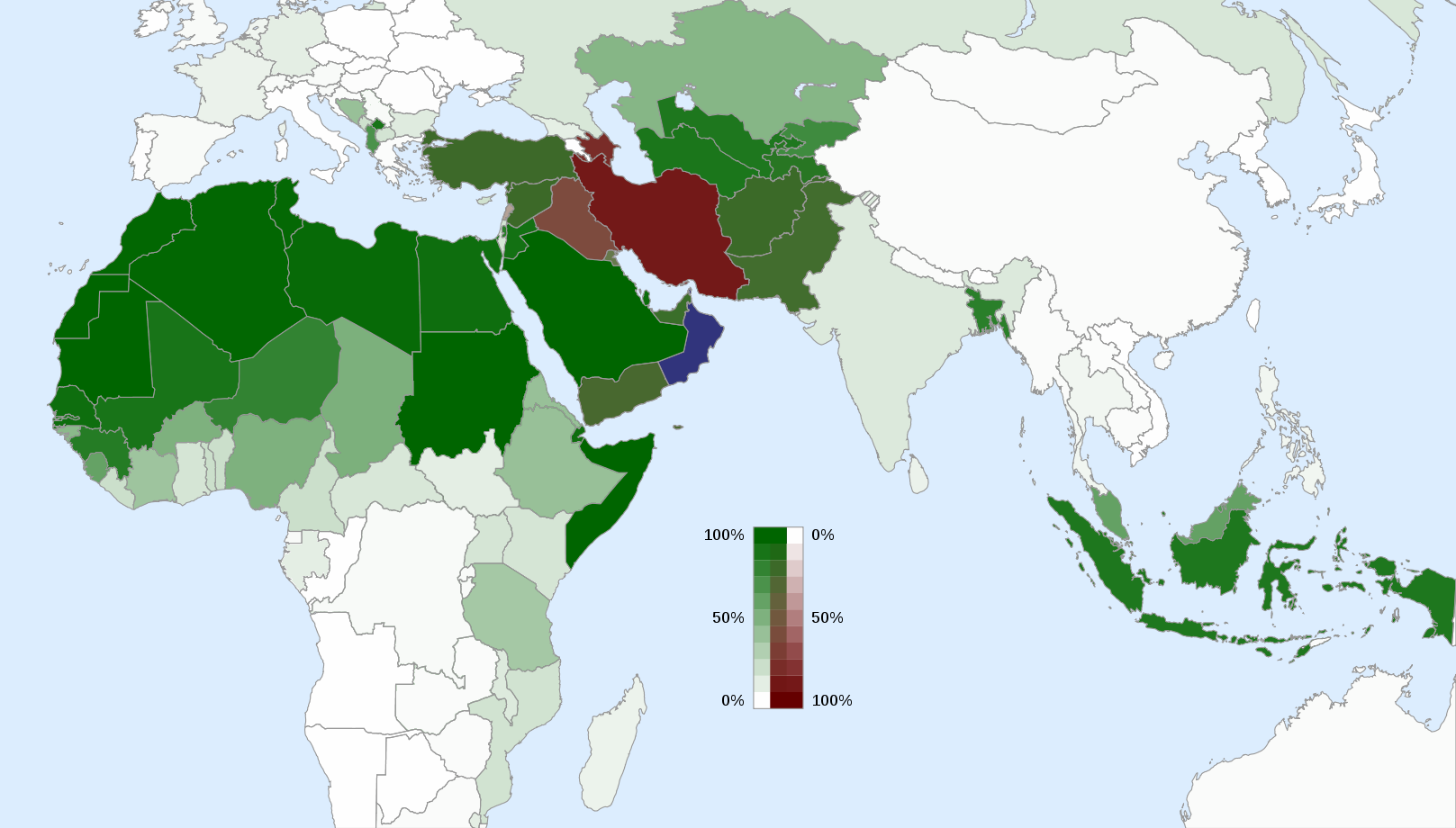
A Shia-Sunni map, depicting the geographic distribution of these two major branches of Islam, provides a powerful visual representation of this historical and contemporary reality. Such maps typically highlight the predominant religious affiliation in various regions, often using distinct colors to distinguish Shia and Sunni populations.
Understanding the Map:
The Shia-Sunni map reveals a complex and dynamic landscape. While certain regions exhibit a clear majority of either Shia or Sunni Muslims, others display a more intricate mosaic of diverse denominations and even instances of co-existence.
Key Geographical Patterns:
-
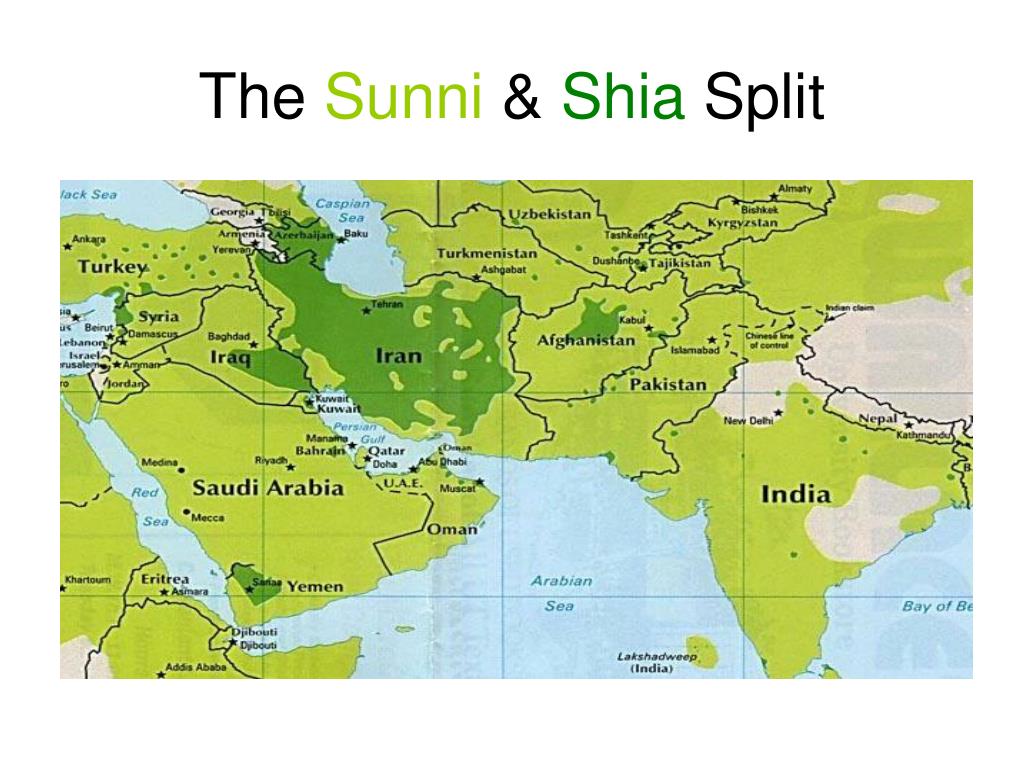
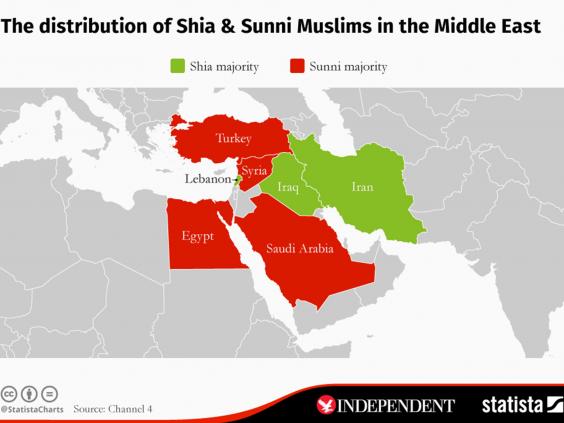
Iran: The Islamic Republic of Iran is predominantly Shia, with the Twelver Shia branch holding the most significant following. This dominance is reflected in Iran’s political and cultural landscape.
-
Iraq: Iraq, neighboring Iran, also features a substantial Shia population, particularly in the southern and central regions. This has contributed to a complex sectarian dynamic in the country.
-
Lebanon: Lebanon, with its diverse religious communities, exhibits a significant Shia presence, particularly in the southern regions. The country’s political system reflects this demographic reality.
-
Saudi Arabia: The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, with its Wahhabi interpretation of Sunni Islam, holds a dominant Sunni population. This has shaped the country’s religious policies and its influence within the broader Muslim world.
-
Yemen: Yemen, with its intricate religious landscape, exhibits a mixture of Shia and Sunni populations. The country has been embroiled in a protracted conflict with sectarian dimensions.
-
Afghanistan: Afghanistan, with its Pashtun majority, is predominantly Sunni. However, a significant Shia population, primarily Hazara, also exists, contributing to the country’s complex sectarian dynamics.
-
Pakistan: Pakistan, with its diverse ethnic and religious makeup, has a majority Sunni population. However, a significant Shia community exists, primarily in the eastern regions.
-
India: India, with its large Muslim population, exhibits a diverse religious landscape, including both Shia and Sunni communities.
Beyond the Map:
While the Shia-Sunni map offers a valuable snapshot of the geographic distribution of these two branches of Islam, it’s crucial to acknowledge its limitations. This map cannot capture the full complexity of the Shia-Sunni relationship, including the internal diversity within each branch, the presence of other Islamic denominations, and the historical and political factors that influence the dynamics of this divide.
The Significance of the Shia-Sunni Map:
Understanding the geographical distribution of Shia and Sunni Muslims provides valuable insights into:
-
Historical and cultural influences: The map helps trace the historical development of these two branches of Islam and understand how geographical factors have shaped their respective identities.
-
Political and social dynamics: The map reveals the potential for conflict and cooperation based on religious affiliation. It highlights the importance of understanding the sectarian complexities in various regions.
-
Global religious landscape: The map provides a visual representation of the global distribution of Islam and its diverse branches, contributing to a broader understanding of the world’s religious map.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The Shia-Sunni divide presents both challenges and opportunities. While sectarian tensions can lead to conflict and instability, understanding and fostering dialogue can pave the way for peaceful coexistence and cooperation.
FAQs
Q: What are the key differences between Shia and Sunni Muslims?
A: The primary difference lies in the succession of Prophet Muhammad after his death. Shia Muslims believe that Ali ibn Abi Talib, Muhammad’s cousin and son-in-law, was the rightful successor, while Sunni Muslims believe that Abu Bakr, Muhammad’s close companion, was the rightful successor. This difference in belief has led to distinct interpretations of Islamic law, religious practices, and political leadership.
Q: How do the Shia-Sunni tensions affect the broader world?
A: The Shia-Sunni divide has influenced global politics, regional conflicts, and international relations. It has been a significant factor in conflicts in Iraq, Syria, Yemen, and Afghanistan.
Q: Can the Shia-Sunni divide be overcome?
A: Overcoming the Shia-Sunni divide is a complex and challenging task. However, fostering dialogue, promoting understanding, and addressing the root causes of tensions can contribute to a more peaceful and harmonious future.
Tips for Understanding the Shia-Sunni Divide:
-
Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out resources from both Shia and Sunni scholars to gain a comprehensive understanding of their respective viewpoints.
-
Focus on shared values: Recognize the common ground between Shia and Sunni Muslims, emphasizing their shared faith and commitment to Islamic principles.
-
Promote interfaith dialogue: Encourage conversations and interactions between Shia and Sunni communities to foster understanding and build bridges.
Conclusion:
The Shia-Sunni map serves as a valuable tool for understanding the geographic distribution of these two major branches of Islam. It highlights the historical and contemporary realities of this complex division, emphasizing the need for nuanced understanding and respectful dialogue. While the challenges posed by the Shia-Sunni divide are significant, promoting interfaith understanding and cooperation is crucial for fostering a more peaceful and harmonious future for the Muslim world and beyond.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Shia-Sunni Divide: A Geographical Perspective. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
