The Alpine Tapestry: A Global Exploration of Mountain Ranges
Related Articles: The Alpine Tapestry: A Global Exploration of Mountain Ranges
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Alpine Tapestry: A Global Exploration of Mountain Ranges. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Alpine Tapestry: A Global Exploration of Mountain Ranges
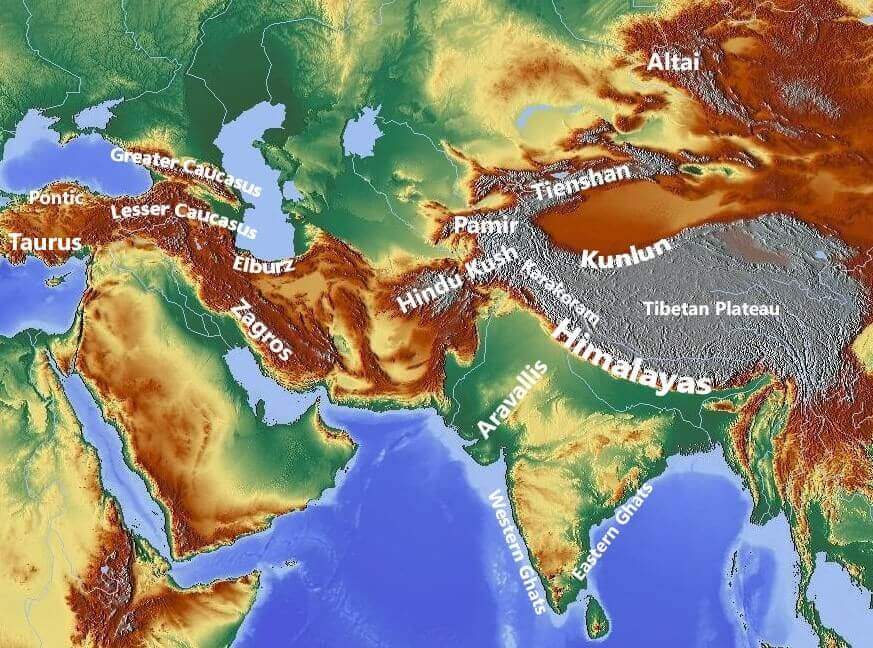
The term "Alps" often evokes images of snow-capped peaks, charming villages, and picturesque meadows in the heart of Europe. However, the alpine landscape, characterized by its distinctive features of high elevation, rugged terrain, and diverse ecosystems, extends far beyond the European Alps. This article delves into the global distribution of alpine environments, exploring their unique characteristics, ecological significance, and the diverse human communities that call them home.
A Global Network of Mountain Ranges:
While the European Alps are undoubtedly iconic, they are just one thread in the global tapestry of alpine regions. These mountainous areas are found on every continent, each with its own unique geological history, biodiversity, and cultural imprint.
-
The Himalayas: The world’s highest mountain range, encompassing the iconic Mount Everest, stretches across Nepal, India, China, Bhutan, and Pakistan. Its towering peaks and glaciers are a source of major river systems, impacting the lives of millions.
-
The Andes: Running along the western edge of South America, the Andes are the longest mountain range on Earth. They host a diverse range of ecosystems, from the arid Atacama Desert to the lush Amazon rainforest.
-
The Rocky Mountains: These majestic peaks traverse the western United States and Canada, offering breathtaking scenery and a wealth of natural resources.
-
The Alps: The European Alps, encompassing parts of France, Italy, Switzerland, Austria, Germany, Slovenia, and Liechtenstein, are renowned for their stunning scenery, charming villages, and thriving tourism industry.
-
The Caucasus Mountains: Situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, these mountains are home to a diverse range of cultures and languages, including the Caucasus region’s unique biodiversity.
-
The Atlas Mountains: Stretching across Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia, these mountains are a vital source of water and a haven for unique flora and fauna.
-
The Drakensberg Mountains: Located in South Africa, these dramatic peaks offer stunning views and are known for their rich cultural heritage.
-
The Ural Mountains: These mountains form a natural boundary between Europe and Asia, and are renowned for their mineral resources and diverse ecosystems.
-
The Appalachian Mountains: These ancient mountains stretch along the eastern edge of North America, offering stunning landscapes and a wealth of history.
-
The New Zealand Alps: These dramatic peaks, including Mount Cook, offer breathtaking scenery and are a haven for adventure tourism.
Shared Characteristics and Ecological Significance:
Despite their geographical diversity, alpine regions share several key characteristics:
-
High Altitude: The defining feature of alpine environments is their elevation, typically exceeding 1,500 meters above sea level. This leads to lower atmospheric pressure, colder temperatures, and reduced oxygen levels.
-
Rugged Terrain: Alpine landscapes are characterized by steep slopes, jagged peaks, and deep valleys, shaped by tectonic forces and glacial activity.
-
Diverse Ecosystems: Altitude and topography create a mosaic of microclimates, supporting a wide variety of plant and animal life. From alpine meadows to rocky summits, these environments are home to unique adaptations and specialized species.
-
Glaciers and Snowfields: Many alpine regions are characterized by glaciers and snowfields, which play a vital role in regulating water resources and shaping the landscape.
-
Vulnerability to Climate Change: Alpine ecosystems are particularly sensitive to climate change, with rising temperatures impacting glaciers, permafrost, and biodiversity.
Human Communities and Cultural Significance:
Alpine regions have long been inhabited by diverse human communities, each with its own unique cultural heritage and relationship with the environment.
-
Traditional Farming Practices: Alpine communities have developed sustainable farming practices, adapting to the challenging conditions and utilizing the resources available.
-
Tourism and Recreation: The stunning scenery and outdoor opportunities have made alpine regions popular destinations for tourism and recreation, contributing to the local economy.
-
Conservation and Sustainability: Recognizing the ecological significance and vulnerability of alpine environments, conservation efforts are underway to protect biodiversity and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
FAQs About Alpine Regions:
Q: What are the main challenges facing alpine regions?
A: Alpine regions face a range of challenges, including climate change, habitat loss, pollution, and unsustainable tourism practices. Climate change is a significant threat, impacting glaciers, permafrost, and biodiversity. Habitat loss due to development and land use changes is also a concern, particularly for endangered species. Pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and tourism can degrade water quality and impact ecosystems.
Q: What are the benefits of alpine regions?
A: Alpine regions offer a multitude of benefits, including:
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Alpine ecosystems are rich in biodiversity, supporting unique species adapted to challenging conditions.
- Water Resources: Alpine glaciers and snowfields are a vital source of water for downstream communities, providing drinking water, irrigation, and hydropower.
- Tourism and Recreation: The stunning scenery and outdoor opportunities attract tourists and recreational enthusiasts, contributing to local economies.
- Cultural Heritage: Alpine regions are home to diverse human communities with unique cultural traditions and historical significance.
Q: What can be done to protect alpine regions?
A: Protecting alpine regions requires a multifaceted approach:
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial to mitigate the impacts of climate change on alpine ecosystems.
- Sustainable Tourism: Promoting responsible tourism practices that minimize environmental impact and support local communities is essential.
- Conservation and Management: Establishing protected areas and implementing sustainable land management practices are vital to protect biodiversity and habitat.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in decision-making processes and promoting traditional knowledge are crucial for effective conservation efforts.
Tips for Exploring Alpine Regions:
- Respect the Environment: Be mindful of your impact on the fragile alpine ecosystem. Stay on designated trails, dispose of waste responsibly, and avoid disturbing wildlife.
- Plan Ahead: Alpine environments can be challenging, so plan your trip carefully, pack appropriate gear, and be aware of weather conditions.
- Learn About Local Culture: Engage with the local communities and learn about their traditions and customs.
- Support Sustainable Tourism: Choose businesses that promote responsible practices and contribute to local economies.
Conclusion:
The global network of alpine regions represents a vibrant tapestry of landscapes, ecosystems, and human communities. These mountains are not only visually stunning but also ecologically significant, playing a vital role in regulating water resources, supporting biodiversity, and providing livelihoods for millions. Recognizing the challenges and benefits of these environments is crucial for ensuring their long-term conservation and the well-being of the people who call them home. By promoting sustainable practices, supporting local communities, and mitigating the impacts of climate change, we can help preserve the beauty and ecological integrity of these unique and valuable landscapes.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Alpine Tapestry: A Global Exploration of Mountain Ranges. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!