Libya: A Nation at the Crossroads of History and Geography
Related Articles: Libya: A Nation at the Crossroads of History and Geography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Libya: A Nation at the Crossroads of History and Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Libya: A Nation at the Crossroads of History and Geography

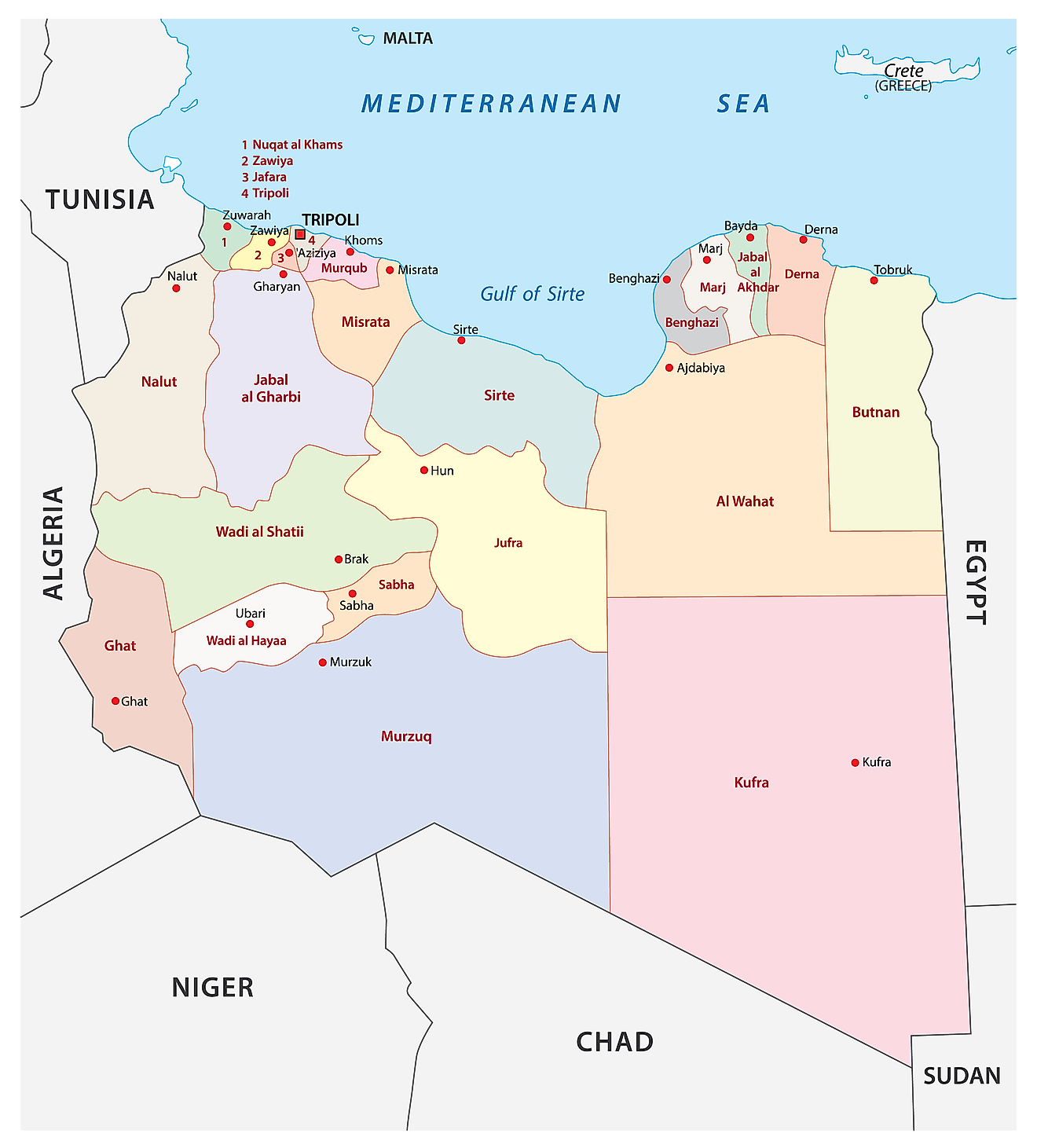
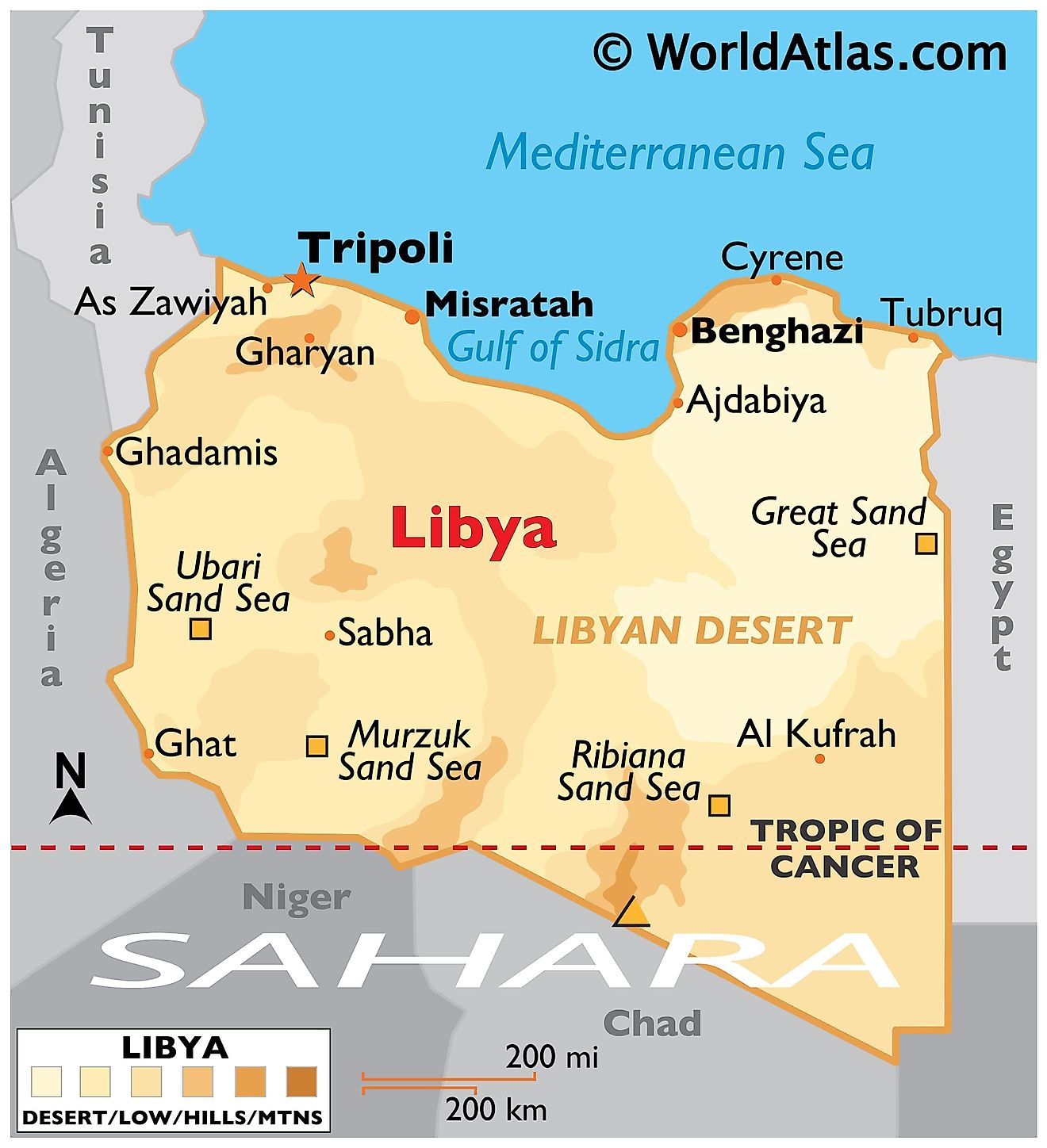
Libya, a North African nation bordering the Mediterranean Sea, holds a unique position on the world map. Its strategic location, rich history, and diverse landscape have shaped its identity and influence on the global stage. This article delves into the complexities of Libya’s geographical context, exploring its historical significance, economic potential, and contemporary challenges.
A Land of Contrasts: Geography and Resources
Libya’s geography is defined by its vast, arid landscape, encompassing the Sahara Desert, the fertile coastal plains, and the rugged Jabal al Akhdar mountains. This diversity creates distinct ecological zones, each with its own unique characteristics and resources. The vast desert, covering approximately 90% of the country, holds immense potential for oil and gas exploration, making Libya one of the world’s leading oil producers. The fertile coastal plains, on the other hand, are ideal for agriculture, supporting the cultivation of dates, olives, and other crops.
A Crossroads of Civilizations: Historical Significance
Libya’s historical tapestry is as rich and diverse as its landscape. It has been a crossroads for civilizations for millennia, witnessing the rise and fall of powerful empires, from the ancient Greeks and Romans to the Ottoman Turks. Ancient ruins like Leptis Magna and Cyrene, testament to the grandeur of Roman rule, stand as enduring symbols of Libya’s past. The country played a pivotal role in the trans-Saharan trade routes, connecting North Africa with sub-Saharan Africa and the Middle East, fostering cultural exchange and economic prosperity.
A Nation in Transition: Contemporary Challenges and Opportunities
Libya’s modern history has been marked by political instability and conflict. The overthrow of Muammar Gaddafi in 2011, while ushering in a period of democratic aspirations, also led to a power vacuum and a protracted civil war. The country remains deeply divided, with competing factions vying for control. This instability has hampered economic development and posed significant challenges to the Libyan people.
Despite these challenges, Libya holds immense potential. Its vast oil and gas reserves remain a crucial resource, capable of driving economic growth and improving living standards. The country also possesses significant agricultural potential, particularly in the fertile coastal areas. Investing in infrastructure, promoting education, and fostering reconciliation are essential for harnessing Libya’s potential and building a more prosperous future.
FAQs
Q: What is Libya’s strategic location?
A: Libya occupies a strategic location in North Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea and connecting the continent to Europe. Its location along ancient trade routes has made it a significant player in regional and global affairs.
Q: What are the main economic sectors in Libya?
A: Libya’s economy is heavily reliant on oil and gas production, which accounts for a significant portion of its GDP. Other sectors include agriculture, fishing, and tourism, with potential for growth in renewable energy and manufacturing.
Q: What are the major challenges facing Libya?
A: Libya faces significant challenges, including political instability, armed conflict, economic stagnation, and social divisions. The country also grapples with issues such as corruption, unemployment, and a lack of basic infrastructure.
Q: What are the prospects for Libya’s future?
A: Libya’s future depends on its ability to overcome political divisions, achieve peace and stability, and foster economic development. The country has the potential to become a prosperous and influential nation, but this will require significant investment, political will, and international cooperation.
Tips
1. Stay Informed: Keep abreast of developments in Libya through reputable news sources, think tanks, and international organizations. Understanding the complexities of the situation is crucial for forming informed opinions.
2. Support Peacebuilding Efforts: Advocate for peaceful solutions to the conflict in Libya. Support initiatives aimed at fostering dialogue, reconciliation, and national unity.
3. Promote Sustainable Development: Encourage investments in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and other sectors that can create jobs and reduce dependence on oil revenues.
4. Engage in Diplomacy: Encourage dialogue and cooperation between Libyan factions and the international community to address the challenges facing the country.
Conclusion
Libya stands at a crossroads, facing both challenges and opportunities. Its strategic location, rich history, and untapped resources present a compelling case for a brighter future. By addressing the complex challenges it faces, Libya can harness its potential, build a more stable and prosperous society, and reclaim its rightful place on the world map.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Libya: A Nation at the Crossroads of History and Geography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!