Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to California’s State Prison System
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to California’s State Prison System
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to California’s State Prison System. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to California’s State Prison System

California’s state prison system, one of the largest in the United States, houses a vast population of incarcerated individuals. Understanding the geographical distribution of these institutions and the factors influencing their location is crucial for analyzing the system’s effectiveness, exploring its impact on communities, and formulating strategies for reform.
A Geographic Overview of California’s Prison System
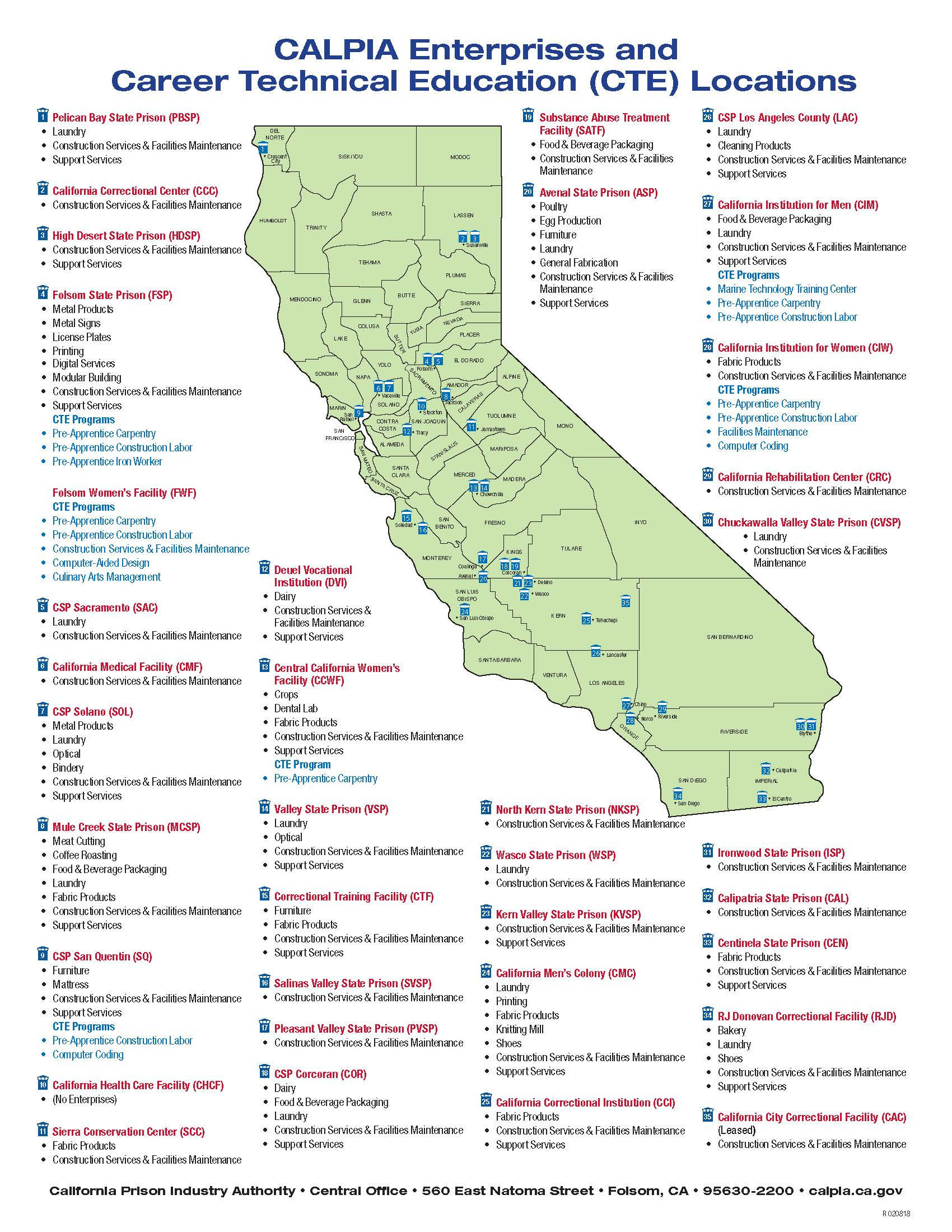
California’s state prisons are strategically dispersed across the state, reflecting a complex interplay of historical, political, and logistical considerations. The system comprises 35 institutions, categorized into three levels of security:
- Maximum Security: Designed for the most dangerous and violent offenders, these prisons feature high security measures and restricted movement for inmates. Examples include Pelican Bay State Prison (Del Norte County) and San Quentin State Prison (Marin County).
- Medium Security: Housing inmates who pose a moderate security risk, these prisons offer a more relaxed environment with greater opportunities for work and education. Examples include California State Prison, Corcoran (Kings County) and California State Prison, Sacramento (Sacramento County).
- Minimum Security: Inmates in these institutions are considered low-risk and often participate in work programs and have more freedom of movement. Examples include California Correctional Institution, Tehachapi (Kern County) and the California Substance Abuse Treatment Facility and State Prison, Corcoran (Kings County).
Factors Shaping the Location of California’s Prisons
The placement of California’s prisons is influenced by a combination of factors:
- Historical Context: Many of the earliest prisons were established in remote areas, often far from major population centers. This approach aimed to isolate inmates and deter escape attempts.
- Political Considerations: The location of prisons has often been influenced by political factors, such as the desire to appease local communities or secure economic benefits.
- Economic Considerations: The availability of land and labor, along with proximity to transportation networks, have also played a role in prison placement.
- Security Concerns: The need to secure a prison’s perimeter and minimize the risk of escape has been a primary concern in selecting locations.
- Accessibility to Resources: Proximity to healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and other essential services is crucial for the operation of a prison.
The Impact of Prison Location on Communities
The location of prisons has a significant impact on surrounding communities, both positive and negative. Some communities may benefit from the economic activity generated by prison construction and operation, while others may experience negative consequences such as increased crime rates, environmental pollution, and a decline in property values.
The Importance of Mapping California’s State Prisons
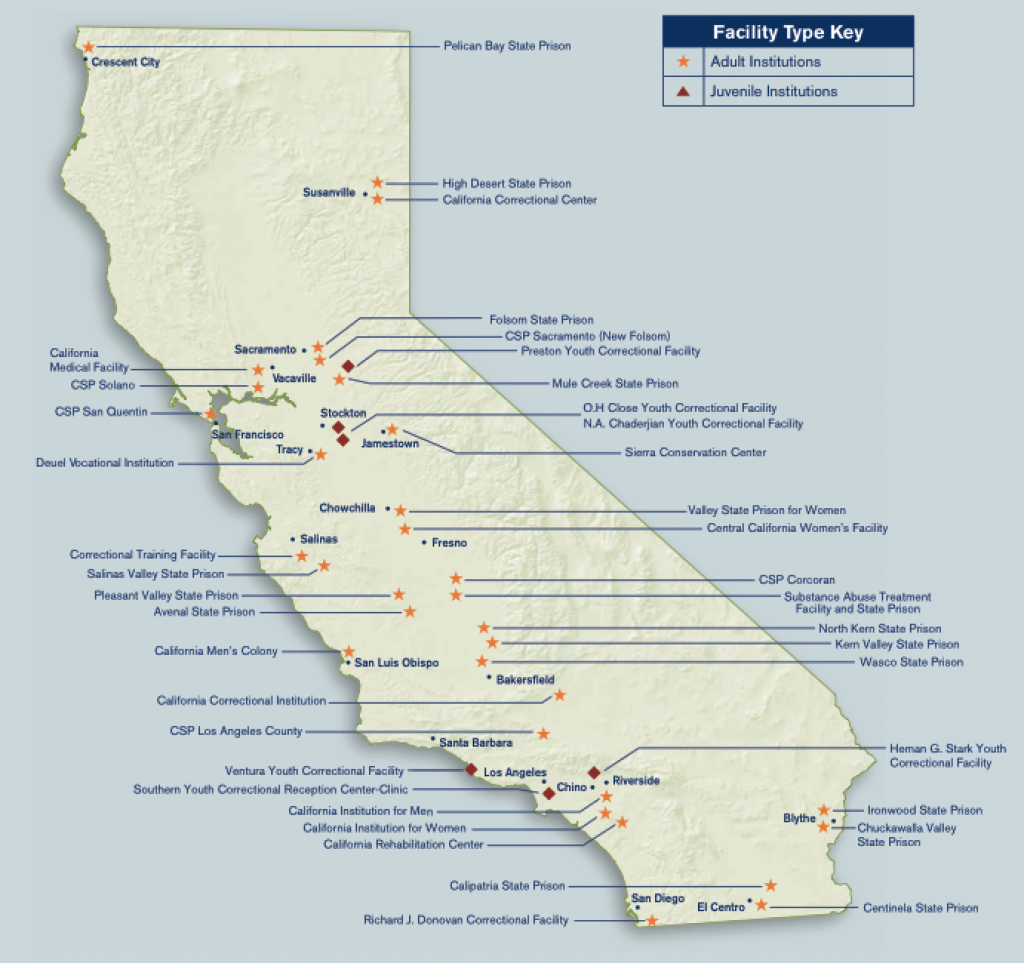
Mapping California’s state prisons provides a valuable tool for understanding the system’s geographic distribution and its impact on communities. This visualization allows for:
- Analyzing the concentration of prisons in specific regions: This information can reveal potential disparities in the distribution of correctional resources and highlight areas where community outreach and support may be particularly needed.
- Assessing the proximity of prisons to schools, hospitals, and other essential services: This helps evaluate the accessibility of these services for incarcerated individuals and the potential impact on surrounding communities.
- Identifying potential environmental risks associated with prison construction and operation: This can inform strategies for mitigating environmental hazards and promoting sustainable practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Mapping California’s State Prisons
1. Why is it important to map California’s state prisons?
Mapping California’s state prisons allows for a visual representation of the system’s geographic distribution, facilitating analysis of its impact on communities, resource allocation, and potential environmental risks.
2. What information is typically included on a map of California’s state prisons?
Maps typically include the location of each prison, its security level, its capacity, and sometimes additional information such as the number of inmates, staff, and programs offered.
3. How can mapping California’s state prisons be used to promote reform?
Mapping can help identify areas where prison populations are disproportionately concentrated, revealing potential disparities in access to resources and highlighting the need for equitable distribution of correctional services.
4. What are some of the challenges associated with mapping California’s state prisons?
Challenges include obtaining accurate and up-to-date data on prison locations and characteristics, as well as ensuring the map’s accessibility and user-friendliness.
5. How can I access maps of California’s state prisons?
Various online resources, including government websites and independent organizations, offer maps of California’s state prisons.
Tips for Using Maps of California’s State Prisons
- Consider the purpose of the map: Determine what information is most relevant to your specific needs and research objectives.
- Pay attention to the scale and legend: Ensure you understand the map’s scale and the symbols used to represent different types of information.
- Analyze the spatial patterns: Observe the concentration of prisons in specific regions and identify any potential disparities in distribution.
- Combine maps with other data sources: Integrate mapping data with demographic, economic, and environmental information for a more comprehensive understanding.
- Share your findings: Disseminate your analysis and insights to raise awareness about the prison system’s impact on communities and advocate for reform.
Conclusion
Mapping California’s state prisons provides a powerful tool for understanding the system’s geographic distribution, its impact on communities, and its potential for reform. By visualizing the location of these institutions and analyzing their spatial patterns, we gain valuable insights into the complexities of the correctional landscape and the need for equitable access to resources and services. This information can be used to advocate for policy changes, promote community engagement, and ultimately contribute to a more just and humane correctional system.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to California’s State Prison System. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!