Haiti: A Caribbean Island Nation – Its Geographic Location and Significance
Associated Articles: Haiti: A Caribbean Island Nation – Its Geographic Location and Significance
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Haiti: A Caribbean Island Nation – Its Geographic Location and Significance. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Haiti: A Caribbean Island Nation – Its Geographic Location and Significance

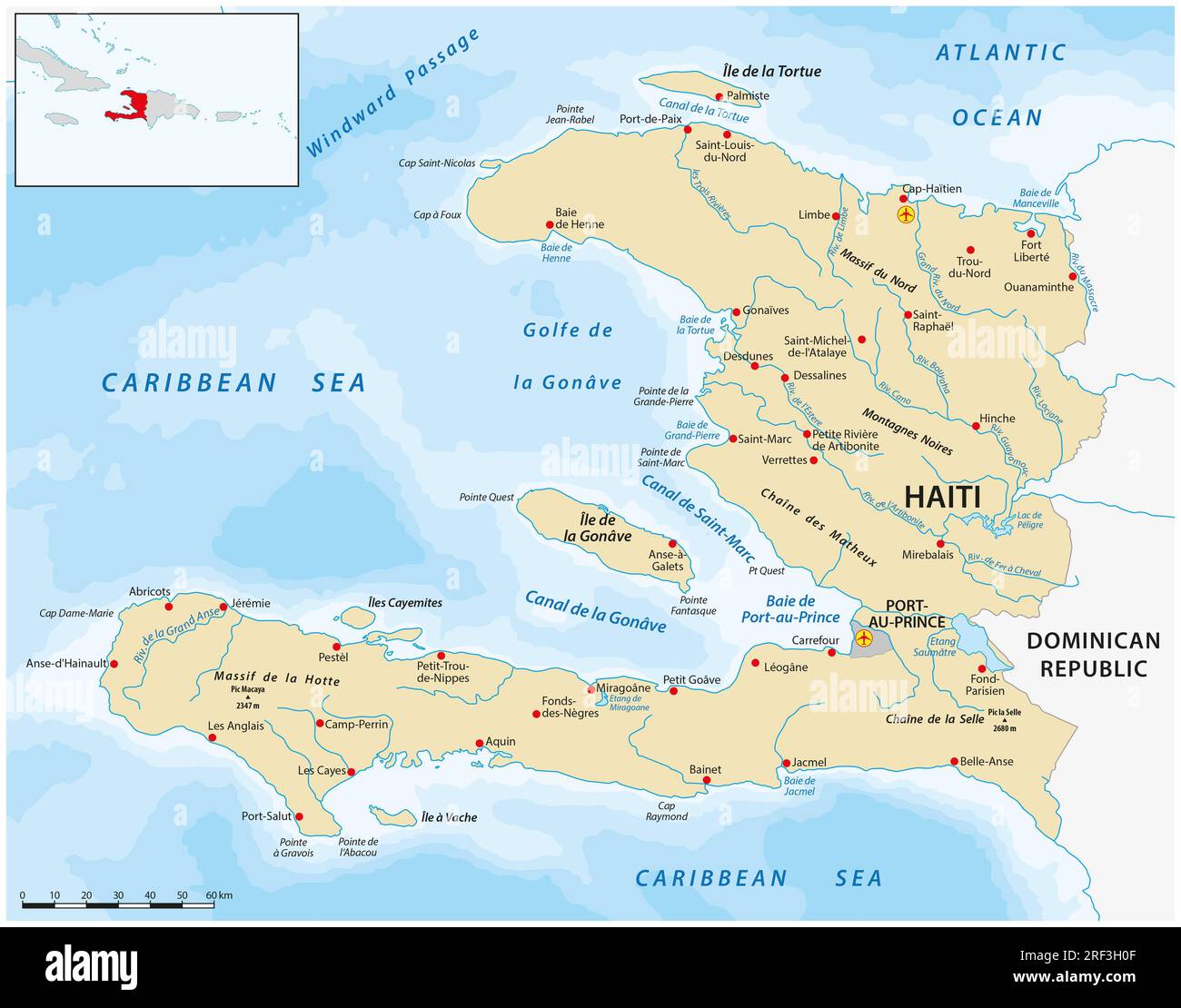
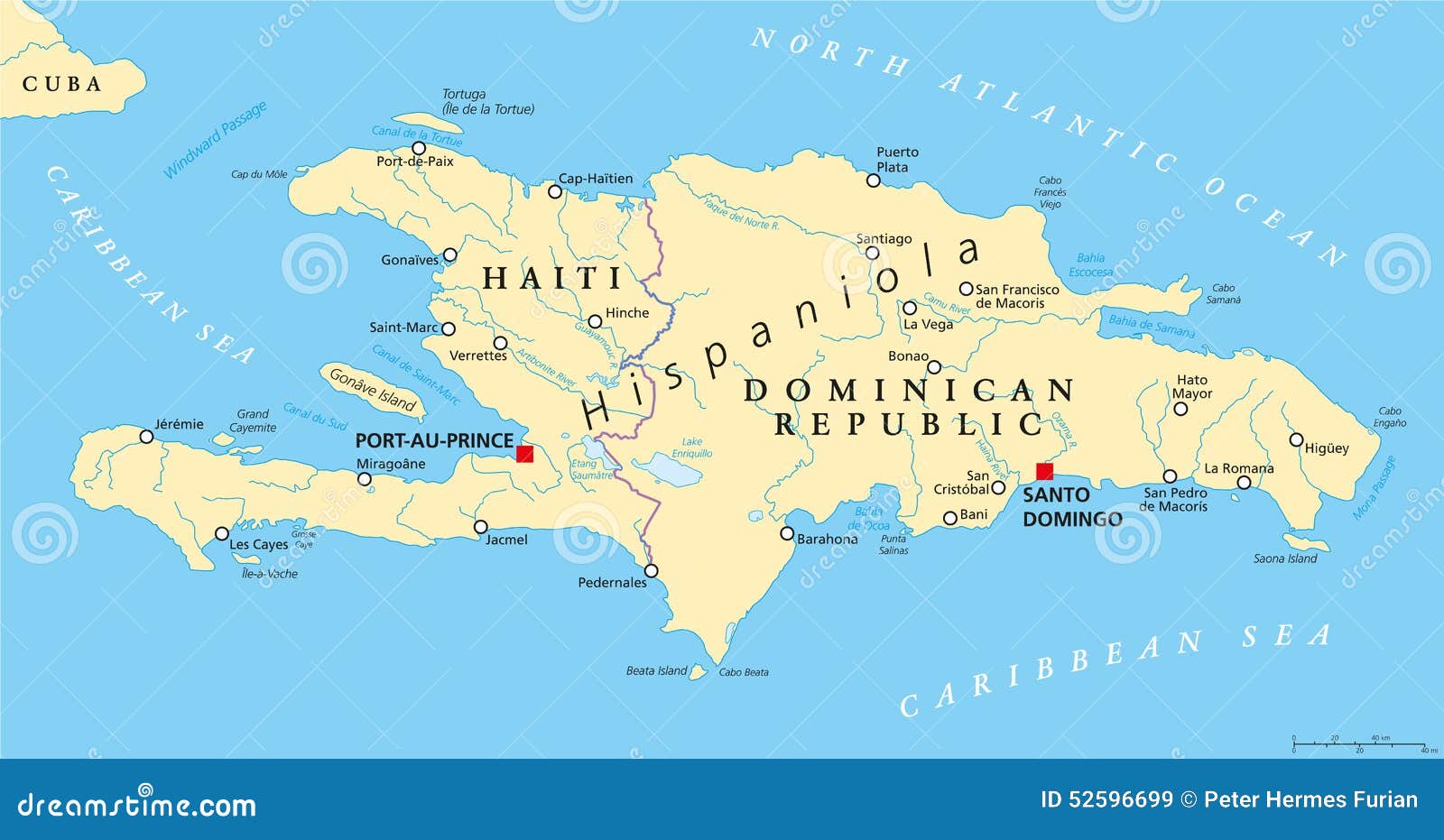
Haiti, formally the Republic of Haiti, occupies the western third of the island of Hispaniola, sharing its jap border with the Dominican Republic. Its strategic location within the Higher Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea considerably shapes its historical past, tradition, financial system, and vulnerability to pure disasters. Understanding Haiti’s exact location on the map is essential to comprehending these multifaceted features of the nation.
Geographical Coordinates and Boundaries:
Haiti’s geographical coordinates are roughly 19°N latitude and 72°W longitude. This locations it squarely inside the tropical zone of the Northern Hemisphere, a location that contributes to its heat, humid local weather and susceptibility to hurricanes. The nation’s boundaries are comparatively simple, although complicated in sure areas:
- North: The Atlantic Ocean defines Haiti’s northern boundary, exposing its shoreline to the complete drive of Atlantic climate methods.
- East: The border with the Dominican Republic runs alongside the mountainous backbone of Hispaniola, a traditionally contested and infrequently ill-defined boundary marked by quite a few rivers and peaks. This border has been a supply of rigidity all through the historical past of each nations.
- South: The Caribbean Sea types Haiti’s southern boundary, offering entry to vital transport lanes and influencing its maritime tradition.
- West: The Windward Passage, a comparatively slim waterway separating Hispaniola from Cuba, defines Haiti’s western boundary, offering a important maritime hyperlink to different Caribbean islands and past.
The exact delineation of the Haiti-Dominican Republic border has been a topic of ongoing negotiation and dispute. The mountainous terrain and lack of clearly outlined markers in sure areas have led to ambiguities and occasional conflicts over land possession and useful resource entry. Worldwide agreements and surveys have tried to resolve these points, however the legacy of historic disputes continues to affect the connection between the 2 nations.
Topographical Options and Their Affect:
Haiti’s topography is remarkably numerous, starting from coastal plains to rugged mountain ranges. The Massif de la Hotte, Massif de la Selle, and the northern mountain vary dominate the panorama, creating important challenges for infrastructure growth and agricultural practices. These mountains will not be solely visually placing but additionally play a important function in shaping the nation’s local weather, water assets, and biodiversity.
The coastal plains, whereas comparatively flat, are sometimes slim and topic to erosion and flooding. These plains are essential for agricultural manufacturing, supporting the cultivation of crops like sugarcane, espresso, and mangoes. Nonetheless, their vulnerability to pure disasters makes them difficult areas for sustainable growth.
The rivers that circulation from the mountains to the ocean are important sources of freshwater, however their unpredictable circulation patterns, usually intensified by heavy rainfall, can result in devastating floods through the hurricane season. The rivers additionally play a big function in shaping the panorama, creating fertile valleys and deltas which might be vital for agriculture.
Local weather and its Influence:
Haiti’s tropical location and mountainous terrain end in a various local weather. The coastal areas expertise a sizzling and humid local weather all year long, whereas the upper elevations take pleasure in cooler temperatures. The nation is very susceptible to hurricanes, which continuously strike through the Atlantic hurricane season (June to November). These storms may cause widespread devastation, destroying infrastructure, disrupting agriculture, and resulting in important lack of life. Droughts are additionally a recurring downside, significantly within the drier areas of the nation. The interaction of those climatic elements considerably impacts Haiti’s agricultural productiveness, financial stability, and total growth.
Strategic Significance and Geopolitical Context:
Haiti’s location on the crossroads of the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean has imbued it with important geopolitical significance all through historical past. Its proximity to main transport lanes and its strategic place relative to different Caribbean islands and North and South America have made it a goal for colonial powers and a key participant in regional dynamics.
The island’s historical past as a middle of colonial exploitation, first by Spain after which by France, considerably formed its financial and social buildings. Its subsequent independence and struggles for stability have positioned it on the heart of varied regional and worldwide political debates. Its vulnerability to pure disasters and its persistent financial challenges have additionally attracted important worldwide help and humanitarian intervention.
Cartographic Representations and Mapping Challenges:
Precisely mapping Haiti presents distinctive challenges. The rugged terrain, dense vegetation, and lack of detailed surveying in sure areas have made it tough to create exact and complete maps. Moreover, the historic disputes over the border with the Dominican Republic have additional difficult cartographic efforts.
Regardless of these challenges, advances in distant sensing expertise, akin to satellite tv for pc imagery and GPS, have considerably improved the accuracy and element of maps of Haiti. These applied sciences are more and more getting used for catastrophe response, infrastructure planning, and environmental monitoring. Nonetheless, the challenges of sustaining up-to-date and accessible maps stay important, significantly within the context of restricted assets and ongoing political and social instability.
Conclusion:
Haiti’s location on the map is greater than only a set of coordinates; it’s a important issue shaping its historical past, tradition, financial system, and vulnerability. Understanding its geographical place inside the Caribbean, its numerous topography, its susceptibility to pure disasters, and its strategic geopolitical significance is crucial to comprehending the complicated challenges and alternatives that face this nation. Correct mapping and ongoing geographic analysis are essential for supporting sustainable growth, catastrophe preparedness, and efficient governance in Haiti. The way forward for Haiti is inextricably linked to its location, and a deeper understanding of this location is essential for fostering progress and stability within the years to return.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered beneficial insights into Haiti: A Caribbean Island Nation – Its Geographic Location and Significance. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!