Decoding the NYISO Zone Map: A Deep Dive into New York’s Electrical energy Grid
Associated Articles: Decoding the NYISO Zone Map: A Deep Dive into New York’s Electrical energy Grid
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the NYISO Zone Map: A Deep Dive into New York’s Electrical energy Grid. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the NYISO Zone Map: A Deep Dive into New York’s Electrical energy Grid
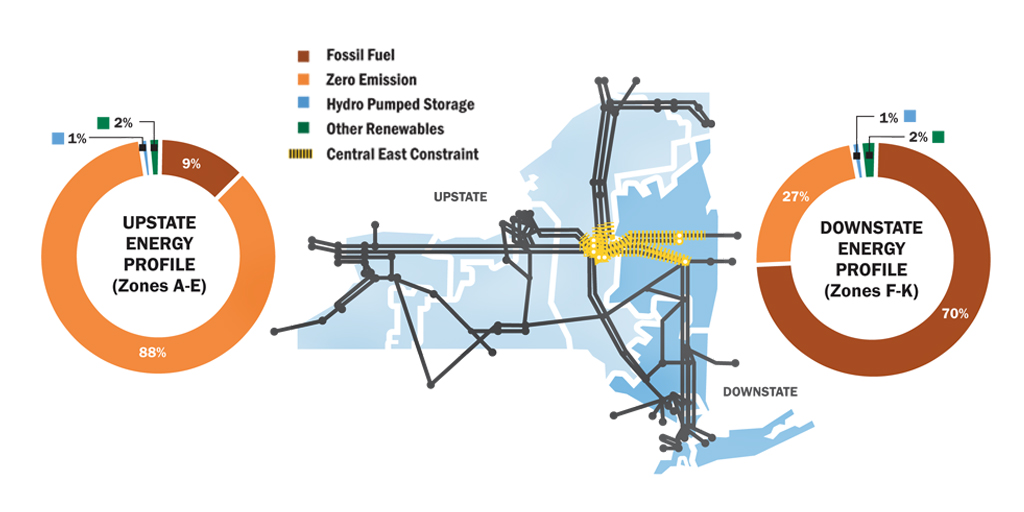
The New York Unbiased System Operator (NYISO) is chargeable for the dependable operation of New York State’s bulk electrical energy system. Understanding its operational zones is essential for comprehending how electrical energy flows, costs are decided, and the general well being of the state’s energy grid. This text gives a complete overview of the NYISO zone map, exploring its construction, its affect on power markets, and the evolving challenges it faces.
The Anatomy of the NYISO Zone Map:
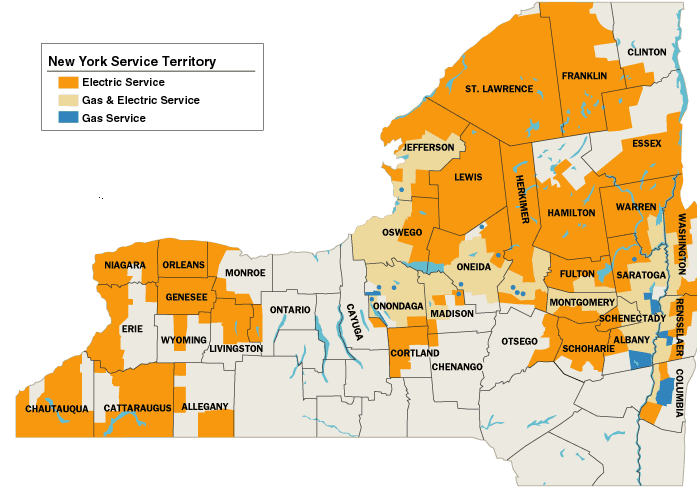
The NYISO zone map divides New York State into distinct geographical areas, every with its personal distinctive traits concerning electrical energy technology, transmission infrastructure, and demand. These zones will not be arbitrary divisions; they replicate the intricate community of energy traces, substations, and technology services that make up the state’s electrical energy grid. The first objective of this zonal construction is to facilitate environment friendly market operations and guarantee dependable electrical energy supply. The zones will not be static; they’ve developed over time to replicate modifications within the technology combine, transmission capability, and demand patterns.
The NYISO at the moment makes use of a locational marginal pricing (LMP) system, which means that the value of electrical energy varies by zone. This value displays the marginal value of supplying electrical energy to that particular zone, contemplating components like technology prices, transmission congestion, and demand. Understanding the nuances of every zone is due to this fact essential for members within the NYISO power market, together with mills, distributors, and enormous shoppers.
The key zones throughout the NYISO system are:
- Capital: This zone encompasses the Albany space and surrounding areas. It is characterised by a mixture of technology sources, together with nuclear, hydro, and fossil fuels.
- Central: It is a massive zone overlaying a good portion of central New York, together with Syracuse and Utica. Its technology combine is much like the Capital zone.
- Champlain: Positioned within the northern a part of the state, this zone depends closely on imports from neighboring areas, notably Canada and Vermont.
- Jap: This zone contains New York Metropolis and its surrounding areas, representing the very best demand area within the state. It is closely reliant on imports and has a various mixture of technology, together with gas-fired crops and a few renewables.
- Genesee: Positioned in western New York, this zone has a notable focus of renewable power sources, notably wind energy.
- Hudson: This zone spans alongside the Hudson River Valley, with a mixture of technology assets and rising reliance on renewable power.
- Lengthy Island: This zone encompasses Lengthy Island, characterised by excessive demand and a reliance on imports from the mainland by means of underwater transmission traces.
- MISO: Whereas not technically a NYISO zone, the Midcontinent Unbiased System Operator (MISO) is a big interconnection level, facilitating the trade of electrical energy between the NYISO and different elements of the nation. This interconnection is essential for sustaining grid stability and addressing regional imbalances.
- Niagara: Positioned in western New York, this zone boasts a big quantity of hydroelectric technology from Niagara Falls.
- North: This zone covers a big swathe of northern New York, with a mixture of hydro and fossil gasoline technology.
- West: This zone encompasses a good portion of western New York, with a technology combine much like different upstate zones.
The Affect of the Zonal Construction on Power Markets:
The NYISO’s zonal construction immediately impacts electrical energy pricing and market dynamics. The LMP system ensures that costs replicate the real-time situations inside every zone. Congestion in transmission traces can result in vital value variations between zones. For instance, in periods of excessive demand within the Jap zone, costs may be considerably larger than in much less congested zones just like the North or West. This value differential incentivizes mills to produce electrical energy to the highest-priced zones, guaranteeing environment friendly allocation of assets.
The zonal construction additionally influences funding selections in technology and transmission infrastructure. Builders of renewable power initiatives, for example, think about the placement and zonal pricing when figuring out the viability of their initiatives. Equally, transmission upgrades are prioritized based mostly on their potential to alleviate congestion and cut back value volatility between zones.
Moreover, the zonal construction performs a vital position in managing grid stability and reliability. By monitoring the real-time situations in every zone, the NYISO can proactively handle energy flows, forestall outages, and make sure the total safety of the electrical energy system. This entails subtle instruments and algorithms that optimize energy technology and transmission to fulfill demand whereas sustaining grid stability.
Challenges and Future Developments:
The NYISO zone map, whereas efficient, faces a number of challenges within the evolving power panorama. The rising penetration of renewable power sources, akin to photo voltaic and wind, poses vital challenges for grid administration. These intermittent sources introduce uncertainty into the system, requiring extra subtle forecasting and management mechanisms. Moreover, the combination of distributed power assets (DERs), akin to rooftop photo voltaic panels and battery storage techniques, provides additional complexity to grid administration.
The NYISO is actively addressing these challenges by means of numerous initiatives, together with:
- Superior forecasting strategies: Improved forecasting fashions are essential for precisely predicting renewable power output and demand, permitting for higher grid administration.
- Good grid applied sciences: Implementing good grid applied sciences, akin to superior sensors and communication networks, permits for real-time monitoring and management of the grid, enhancing its resilience and effectivity.
- Grid modernization: Upgrading transmission infrastructure is crucial to accommodate the rising penetration of renewable power and meet rising demand.
- Market design enhancements: Refining the market guidelines and mechanisms is essential for guaranteeing environment friendly and truthful electrical energy pricing within the face of adjusting market situations.
The NYISO can be exploring the potential of latest applied sciences, akin to power storage and demand-side administration packages, to additional improve grid stability and reliability. These applied sciences may help clean out the intermittency of renewable power sources and cut back peak demand, minimizing value volatility and enhancing total system effectivity.
Conclusion:
The NYISO zone map is a important part of New York State’s electrical energy grid, shaping power markets, influencing funding selections, and impacting the reliability of energy supply. Understanding its construction and the dynamics of every zone is crucial for anybody concerned within the state’s power sector. Because the power panorama continues to evolve, the NYISO faces vital challenges in managing the grid successfully and effectively. Nevertheless, by means of ongoing innovation and adaptation, the NYISO is striving to make sure a safe, dependable, and inexpensive electrical energy provide for all New Yorkers. The way forward for the NYISO zone map will doubtless contain additional refinements and variations to accommodate the continued transformation of the state’s power system, reflecting the rising integration of renewables and the rising sophistication of grid administration applied sciences. The continual evolution of the map itself displays the dynamic nature of the power business and the dedication to offering a sustainable and resilient energy grid for the long run.


![[July.2024]A Deep Dive into McDonald's: decoding the earnings of the](https://uscourseimg.moomoo.com/1721975978740.jpeg?imageMogr2/quality/100/ignore-error/1)

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into Decoding the NYISO Zone Map: A Deep Dive into New York’s Electrical energy Grid. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!