Mapping the Voters: An Exploration of Votes Maps and Their Significance
Associated Articles: Mapping the Voters: An Exploration of Votes Maps and Their Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by the intriguing subject associated to Mapping the Voters: An Exploration of Votes Maps and Their Significance. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mapping the Voters: An Exploration of Votes Maps and Their Significance

Votes maps, also referred to as electoral maps or cartograms, are highly effective visible representations of election outcomes. They translate advanced statistical information into simply digestible geographical visualizations, showcasing the distribution of votes throughout totally different areas. These maps usually are not merely aesthetically pleasing; they function essential instruments for understanding voting patterns, figuring out political traits, and analyzing the impression of geographical components on election outcomes. This text delves into the varied sorts of votes maps, their building, interpretation, and their broader implications for political science, journalism, and public understanding of elections.
Varieties of Votes Maps:
The best type of a votes map shows the profitable social gathering or candidate in every geographical unit, usually a county, state, or district. These maps usually use distinct colours to characterize totally different political affiliations, immediately revealing the general "winner" at a look. Nevertheless, this simplistic illustration masks essential nuances. A extra informative strategy entails incorporating the proportion of votes obtained by every candidate or social gathering inside every unit. This may be achieved by a number of strategies:
-
Choropleth Maps: These are the most typical sort of votes map. They use colour shading or patterns to characterize the proportion of votes for a specific candidate or social gathering inside every geographical unit. Darker shades usually point out larger vote percentages, permitting for a transparent visible comparability throughout areas. Nevertheless, the interpretation of choropleth maps requires warning, because the visible impression may be skewed by the scale of the geographical models. A small county with a excessive proportion of votes for one candidate would possibly seem visually dominant over a a lot bigger county with a barely decrease proportion.
-
Cartogram Maps: In contrast to choropleth maps which keep the geographical accuracy of the models, cartograms distort the scale of geographical models to mirror the variety of votes forged inside them. A county with numerous votes might be proportionally bigger on the cartogram, whereas a county with fewer votes might be smaller. This methodology permits for a extra correct illustration of the general distribution of votes, minimizing the potential for misinterpretation brought on by various unit sizes. Nevertheless, the distortion of geographical boundaries could make it tough to precisely find particular areas.
-
Dot Density Maps: These maps use dots to characterize particular person votes, with the focus of dots reflecting the voting density in a specific space. Whereas visually interesting and comparatively easy to interpret, dot density maps can change into cluttered and tough to learn, particularly in areas with excessive inhabitants density and quite a few votes. They’re simpler when visualizing smaller-scale elections or specializing in particular areas.
-
Animated Maps: These maps provide a dynamic visualization of election outcomes over time, displaying the altering distribution of votes as outcomes are tallied. This strategy is especially helpful for understanding the circulate of votes and figuring out areas the place assist shifts considerably in the course of the counting course of.
Building and Information Sources:
The development of votes maps requires entry to dependable and correct election information. This information is normally collected and revealed by election authorities at numerous ranges of presidency. The info usually consists of the full variety of votes forged, the variety of votes obtained by every candidate or social gathering, and the geographical location of every voting precinct or unit. Geographic Info Methods (GIS) software program is usually used to course of this information and create the maps. The selection of geographical models (counties, states, and so forth.) considerably impacts the map’s interpretation, and cautious consideration ought to be given to the extent of element required.
Interpretation and Limitations:
Deciphering votes maps requires cautious consideration of a number of components:
-
Geographical Context: Understanding the geographical traits of the area, together with inhabitants density, city vs. rural areas, and historic voting patterns, is essential for correct interpretation. A seemingly homogenous sample would possibly reveal underlying complexities when thought of within the context of those components.
-
Scale and Aggregation: The extent of geographical aggregation (e.g., county vs. precinct) considerably influences the map’s message. Aggregating information to a coarser stage can masks localized variations in voting patterns.
-
Information High quality: The accuracy of the map relies upon fully on the standard of the underlying election information. Errors or inconsistencies within the information can result in misinterpretations.
-
Visible Bias: The selection of colours, shading, and map projection can subtly affect the viewer’s notion of the info. Mapmakers ought to attempt for objectivity and transparency of their design selections.
-
Ecological Fallacy: A standard pitfall is assuming that the traits of a geographical unit mirror the traits of the people inside it. For example, a county voting predominantly for one candidate would not essentially imply that each particular person inside that county voted for that candidate.
Purposes and Significance:
Votes maps are extensively utilized in numerous contexts:
-
Political Evaluation: They supply useful insights into voting patterns, serving to political scientists perceive the affect of demographics, socioeconomic components, and political ideologies on election outcomes.
-
Journalism and Media: Votes maps are continuously utilized by information organizations to visually characterize election outcomes and talk advanced information to a wider viewers.
-
Marketing campaign Technique: Political campaigns use votes maps to establish key areas of assist and opposition, guiding useful resource allocation and focusing on efforts.
-
Public Engagement: Votes maps can enhance public consciousness and understanding of election outcomes, selling civic engagement and participation.
-
Historic Evaluation: Analyzing votes maps from previous elections can reveal long-term traits and shifts in voter preferences, offering useful historic context for understanding present political dynamics.
Conclusion:
Votes maps are indispensable instruments for visualizing and analyzing election outcomes. Their effectiveness lies of their capability to translate advanced statistical information into accessible visible representations. Nevertheless, their interpretation requires vital pondering and consciousness of potential biases and limitations. By rigorously contemplating the kind of map used, the info sources, and the geographical context, we will leverage votes maps to realize a deeper understanding of electoral processes and the forces that form political landscapes. The event of refined mapping methods and the rising availability of information promise much more insightful and nuanced functions of votes maps sooner or later, enriching our understanding of elections and their impression on society.

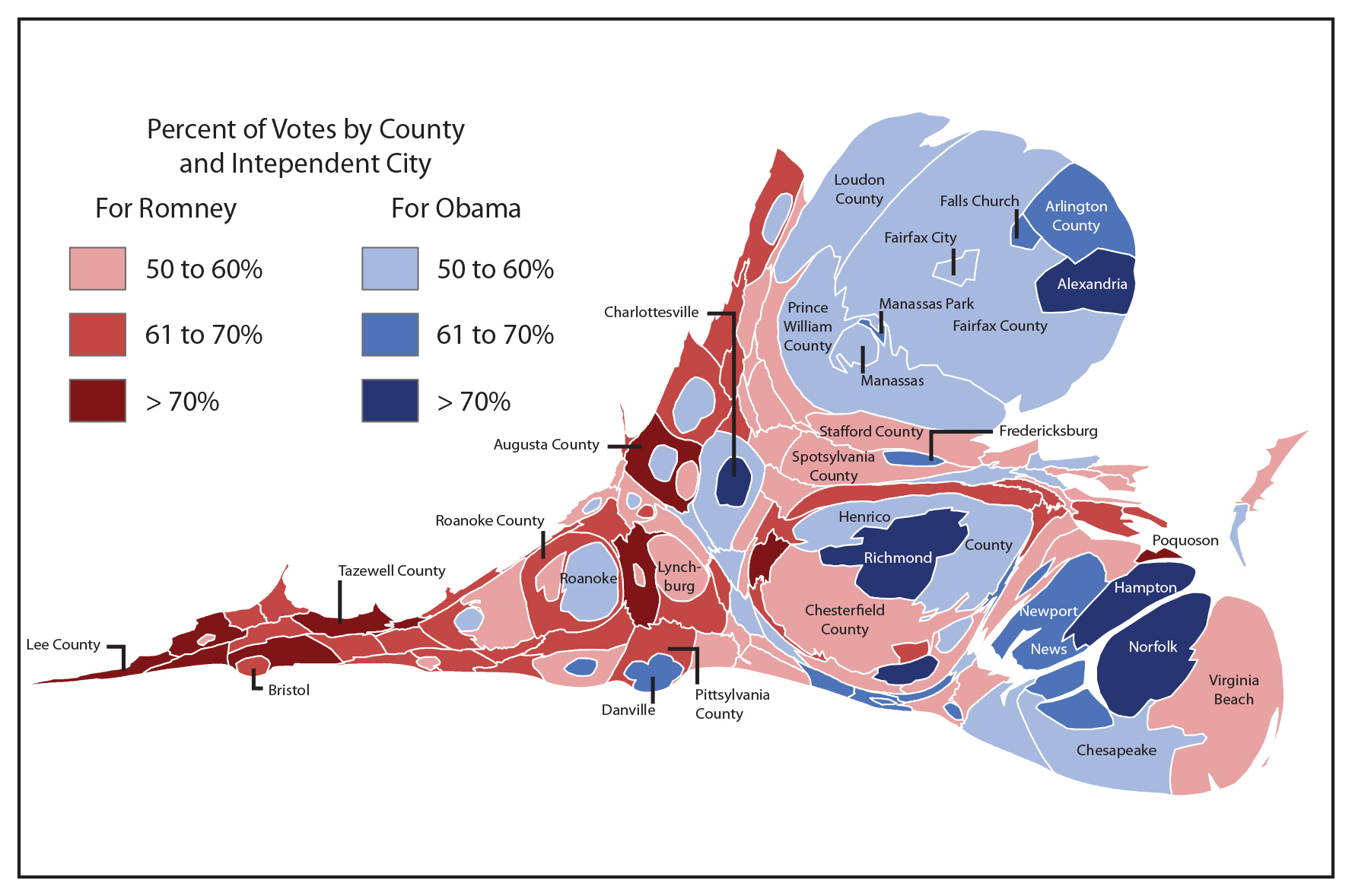

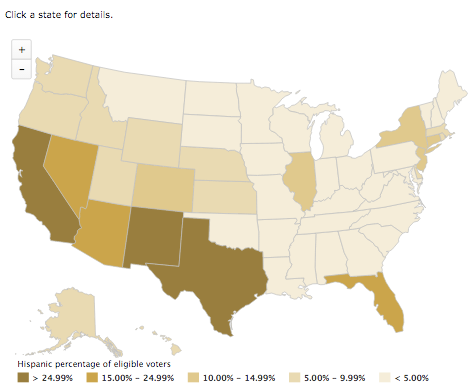


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Mapping the Voters: An Exploration of Votes Maps and Their Significance. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!
