Unveiling the World Via Thematic Maps: A Complete Information to Map Sorts
Associated Articles: Unveiling the World Via Thematic Maps: A Complete Information to Map Sorts
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Unveiling the World Via Thematic Maps: A Complete Information to Map Sorts. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Unveiling the World Via Thematic Maps: A Complete Information to Map Sorts

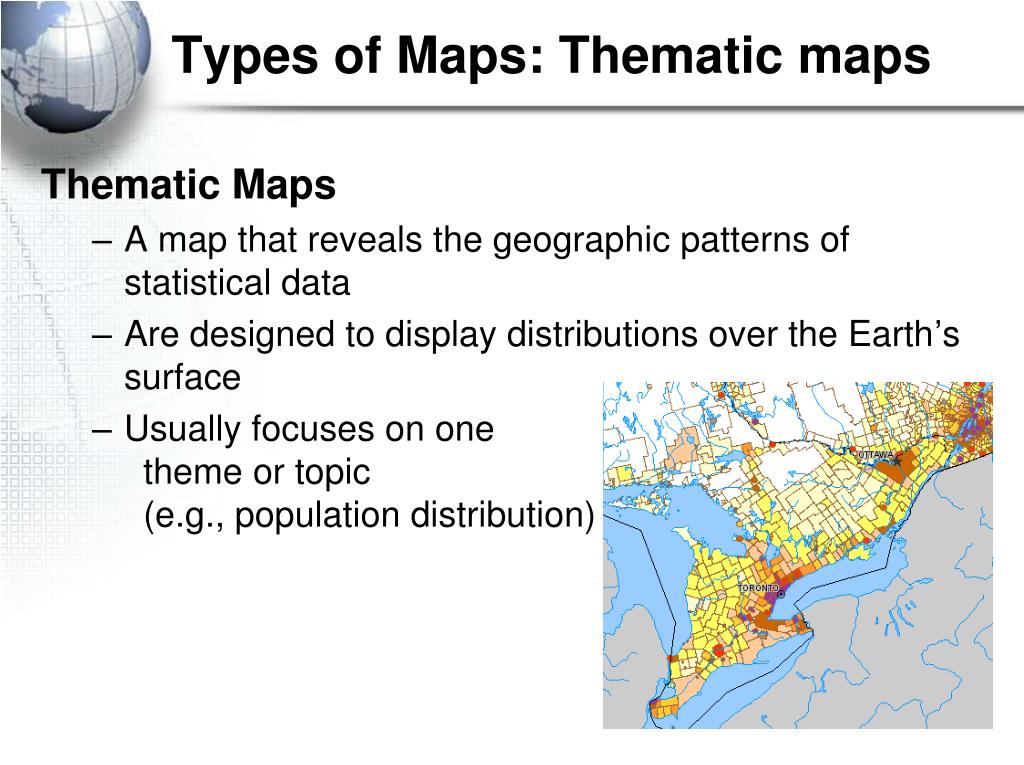
Thematic maps, in contrast to general-purpose maps that primarily present geographical options, concentrate on a particular attribute or theme throughout a geographical space. They’re highly effective instruments for visualizing information, revealing patterns, and speaking complicated data successfully. From the distribution of inhabitants density to the unfold of a illness, thematic maps supply a visible narrative that transcends the restrictions of uncooked information. This text explores the varied vary of thematic map sorts, their functions, strengths, and limitations.
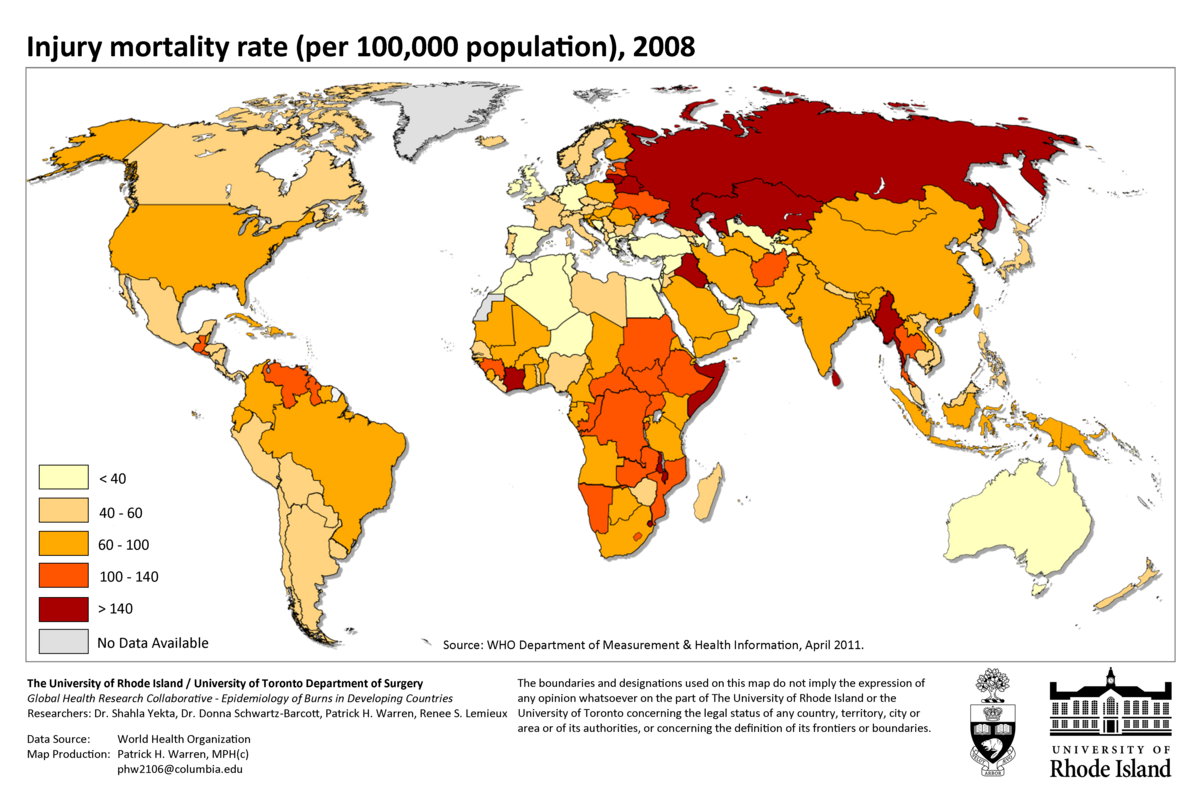
I. Choropleth Maps: Portray a Image with Coloration
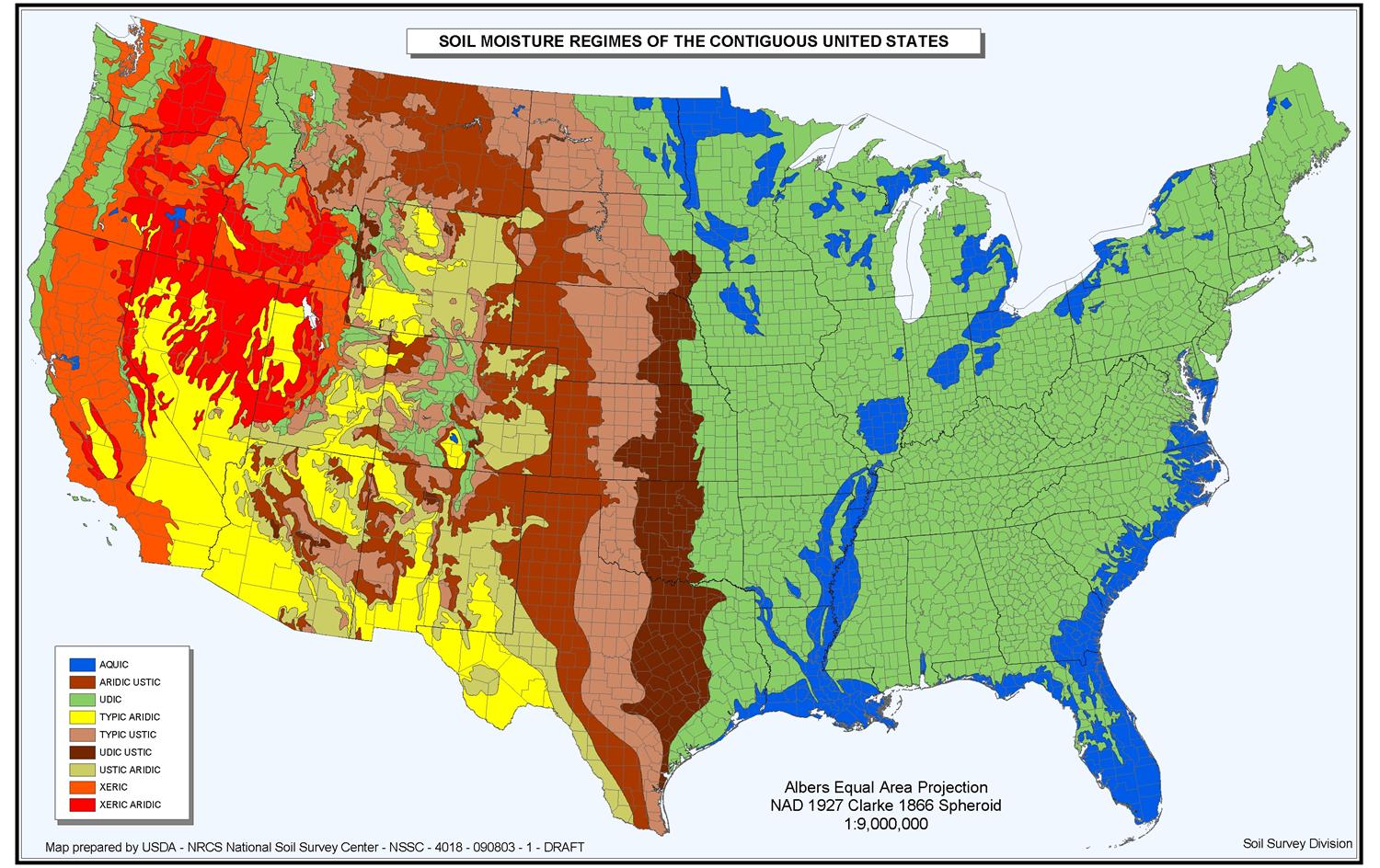
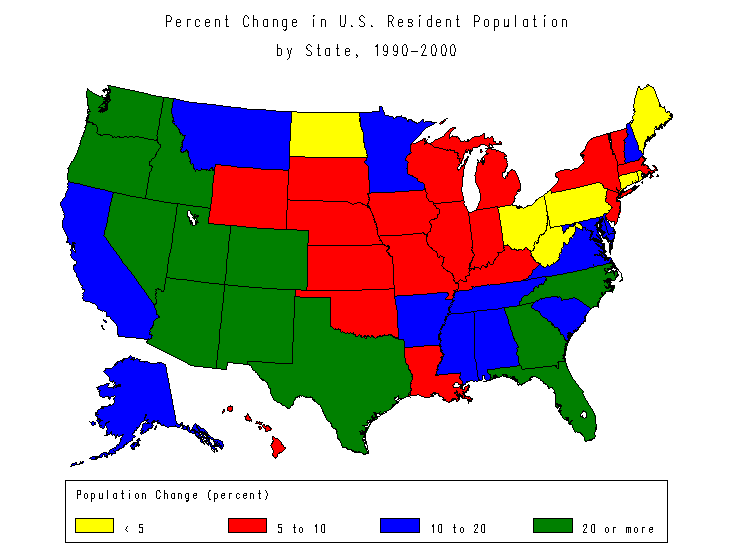
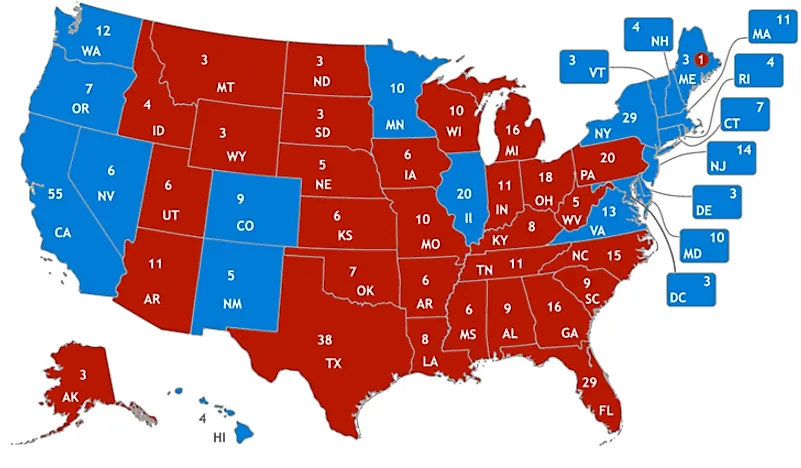
Choropleth maps are arguably the most typical kind of thematic map. They characterize information aggregated for administrative models (counties, states, international locations) utilizing shade shading or patterns. The darker the shade or the extra intense the sample, the upper the worth of the attribute being mapped. For example, a choropleth map may depict inhabitants density, the place darker shades characterize areas with increased inhabitants concentrations.
Strengths:
- Straightforward to grasp: The visible illustration of knowledge by means of shade is intuitive and readily grasped by a large viewers.
- Efficient for displaying spatial patterns: Choropleth maps successfully spotlight areas of excessive and low values, revealing regional variations.
- Versatile: They can be utilized to map all kinds of knowledge, together with demographic data, financial indicators, and environmental variables.
Limitations:
- Information aggregation bias: Information is aggregated to administrative models, masking intra-unit variations. A county may seem to have a uniform worth, even when the fact is extremely heterogeneous.
- Delicate to classification: The selection of shade scheme and classification technique (e.g., equal interval, quantile, pure breaks) considerably impacts the interpretation of the map. Poor classification can result in deceptive visualizations.
- Troublesome to characterize small areas: Small administrative models is likely to be too small to be successfully represented on the map, resulting in inaccuracies or lack of element.
II. Dot Maps: Counting the Dots
Dot maps use dots to characterize particular person occurrences of a phenomenon. Every dot represents a particular variety of occasions or entities, permitting for a exact depend of the phenomenon’s distribution. For instance, a dot map may present the placement of particular person homes, every dot representing one family.
Strengths:
- Exact illustration of particular person information factors: In contrast to choropleth maps, dot maps present the precise location of every information level.
- Straightforward to grasp: The visible illustration of knowledge by means of dots is simple and simply interpreted.
- Efficient for displaying density: The clustering of dots reveals areas of excessive focus.
Limitations:
- Information overload: For giant datasets, the map can turn out to be cluttered and troublesome to interpret.
- Scale dependency: The dimensions of the dot and the variety of occasions represented by every dot have to be rigorously chosen to keep away from overcrowding or under-representation.
- Troublesome to characterize steady information: Dot maps are primarily suited to discrete information moderately than steady variables.
III. Isopleth Maps: Strains of Equal Worth
Isopleth maps use traces (isopleths) to attach factors of equal worth. These traces characterize contours of a steady variable, similar to elevation, temperature, or rainfall. Areas enclosed by isopleths characterize zones of comparable values.
Strengths:
- Efficient for representing steady information: Isopleth maps are perfect for displaying gradual adjustments in a variable throughout area.
- Exact illustration of gradients: They spotlight the spatial distribution of steady information with precision.
- Helpful for interpolation: Isopleths can be utilized to estimate values at places the place information isn’t out there.
Limitations:
- Information interpolation assumptions: The accuracy of the map will depend on the accuracy of the info interpolation technique used.
- Advanced to create: Producing isopleth maps requires refined spatial evaluation strategies.
- May be visually cluttered: A lot of carefully spaced isopleths could make the map troublesome to learn.
IV. Proportional Image Maps: Measurement Issues
Proportional image maps use symbols (circles, squares, and so on.) of various sizes to characterize the magnitude of a variable at totally different places. The dimensions of the image is instantly proportional to the worth of the attribute. For instance, a proportional image map may present the inhabitants of cities, with bigger circles representing bigger cities.
Strengths:
- Direct visible illustration of magnitude: The dimensions of the image instantly displays the worth of the attribute, making it straightforward to check values throughout places.
- Efficient for displaying relative magnitudes: It permits for simple comparability of values between totally different places.
- Versatile: Can be utilized for a variety of knowledge, together with inhabitants, financial output, and environmental indicators.
Limitations:
- Image overlap: In areas with excessive concentrations of symbols, overlap can happen, making the map troublesome to learn.
- Troublesome to interpret exact values: It may be difficult to precisely estimate the exact worth represented by a logo based mostly on its measurement.
- Visible distortion at small scales: At smaller scales, smaller symbols can turn out to be troublesome to see.
V. Cartogram Maps: Distorting Actuality for Readability
Cartograms distort the geographic shapes of areas to emphasise the magnitude of a selected attribute. Areas with increased values are enlarged, whereas areas with decrease values are shrunk. This method permits for a extra visually placing illustration of knowledge, highlighting relative magnitudes.
Strengths:
- Efficient for emphasizing relative magnitudes: Cartograms successfully spotlight the relative significance of various areas based mostly on the chosen attribute.
- Visually placing: The distorted geography makes the map visually partaking and memorable.
- Helpful for evaluating values throughout areas: It permits for simple comparability of values between totally different areas.
Limitations:
- Distortion of geographic area: The distortion of geographic shapes will be complicated and deceptive if not clearly defined.
- Troublesome to make use of for detailed spatial evaluation: The distorted geography makes it troublesome to carry out detailed spatial evaluation.
- Restricted applicability: Cartograms are finest suited to information that has a transparent geographic element.
VI. Movement Maps: Exhibiting Motion
Movement maps illustrate the motion of individuals, items, or data between totally different places. They sometimes use traces of various thickness or shade to characterize the magnitude of the stream. For example, a stream map may present the migration patterns of individuals between totally different international locations.
Strengths:
- Efficient for displaying motion patterns: Movement maps clearly illustrate the course and magnitude of flows between places.
- Visually partaking: The usage of traces and arrows makes the map visually interesting and straightforward to grasp.
- Helpful for analyzing transportation networks: They can be utilized to research transportation networks, commerce routes, and communication flows.
Limitations:
- May be cluttered: A lot of flows could make the map troublesome to learn.
- Troublesome to characterize complicated flows: Representing flows with a number of origins and locations will be difficult.
- Restricted use for static information: Movement maps are primarily suited to information that represents motion or stream.
Conclusion:
Thematic maps are versatile instruments for visualizing and speaking geographic information. The selection of map kind will depend on the kind of information being mapped, the supposed viewers, and the message to be conveyed. Understanding the strengths and limitations of every map kind is essential for creating efficient and correct visualizations that precisely characterize the info and talk insights successfully. By rigorously choosing the suitable map kind and using finest practices in cartographic design, we will unlock the ability of thematic maps to disclose compelling tales hidden inside geographic information. Moreover, the continued growth of Geographic Info Methods (GIS) and associated applied sciences guarantees much more refined and insightful thematic map creation sooner or later.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Unveiling the World Via Thematic Maps: A Complete Information to Map Sorts. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!