Deciphering the Panorama: Understanding Contour Intervals and Their Significance
Associated Articles: Deciphering the Panorama: Understanding Contour Intervals and Their Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing subject associated to Deciphering the Panorama: Understanding Contour Intervals and Their Significance. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Deciphering the Panorama: Understanding Contour Intervals and Their Significance

Maps are highly effective instruments, shrinking huge landscapes into manageable representations. They permit us to visualise terrain, navigate unfamiliar territories, and perceive the three-dimensional world in a two-dimensional format. Central to the accuracy and usefulness of topographic maps, the important thing to deciphering the elevation adjustments, is the contour interval. This text delves deep into the idea of contour intervals, explaining their calculation, significance in varied purposes, and the potential challenges of their interpretation.
What’s a Contour Interval?
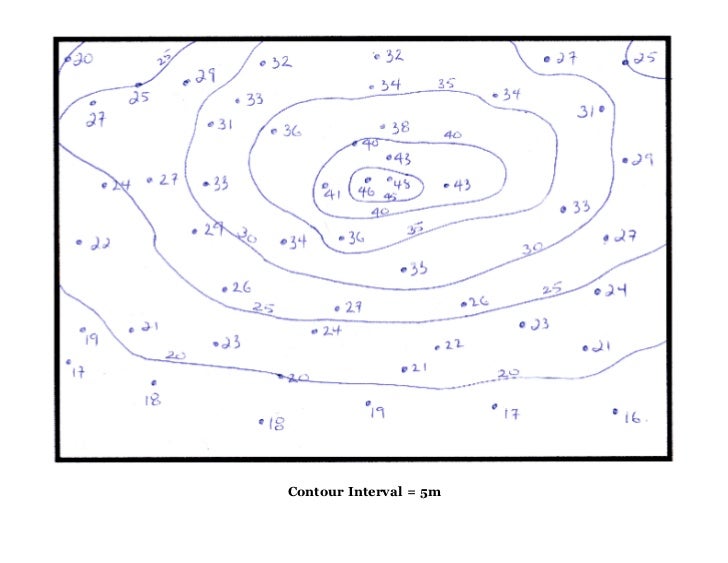
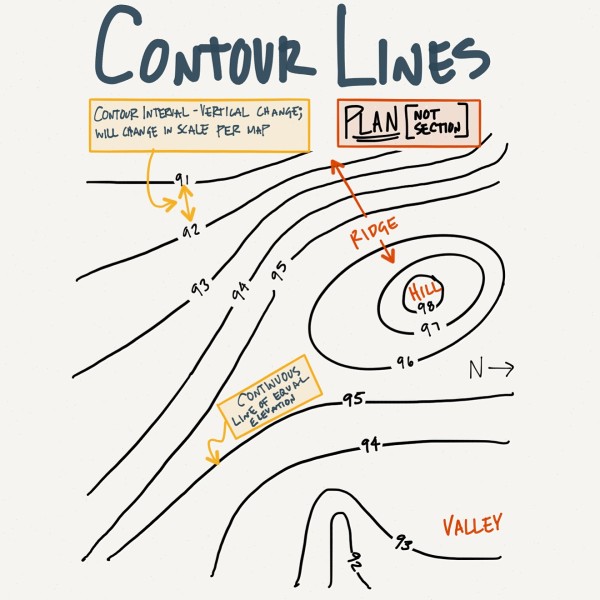
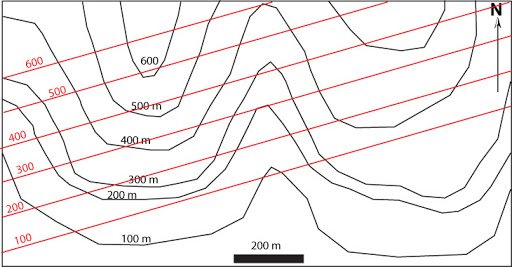
A contour interval is the vertical distance between adjoining contour strains on a topographic map. Contour strains themselves are imaginary strains connecting factors of equal elevation. Think about slicing a panorama with a collection of completely horizontal planes at common vertical intervals. The intersection of every airplane with the earth’s floor would hint a contour line. The distinction in elevation between any two adjoining planes—and subsequently, between the corresponding contour strains—is the contour interval. For instance, a map with a contour interval of 20 meters implies that every contour line represents a 20-meter change in elevation relative to the adjoining line.
Figuring out the Contour Interval: A Sensible Strategy
The contour interval isn’t arbitrarily chosen. It is fastidiously chosen based mostly on a number of elements:
-
Scale of the Map: Bigger-scale maps (displaying smaller areas in higher element) usually have smaller contour intervals, permitting for finer decision of elevation adjustments. Smaller-scale maps (masking bigger areas) typically use bigger contour intervals to take care of readability and keep away from overcrowding the map with quite a few contour strains. The connection between scale and contour interval is essential for efficient map design.
-
Terrain Reduction: The ruggedness or smoothness of the terrain considerably influences the contour interval. Areas with steep slopes and dramatic elevation adjustments require smaller contour intervals to precisely symbolize the topography. Conversely, comparatively flat areas can accommodate bigger contour intervals with out shedding important element. A mountainous area may need a 20-meter interval, whereas a gently rolling plain would possibly use a 10-meter and even bigger interval.
-
Map Function: The meant use of the map additionally performs a job. A map for mountain climbing would possibly require a smaller contour interval for detailed navigation, whereas a map for regional planning would possibly use a bigger interval to deal with broader elevation patterns.
-
Information Availability: The accuracy and determination of the elevation information used to create the map immediately affect the feasibility of a specific contour interval. If the info is proscribed or much less exact, a bigger contour interval could also be essential to keep away from creating deceptive or inaccurate representations.
Decoding Contour Strains and Intervals: A Visible Information
As soon as the contour interval is understood, deciphering the map turns into considerably simpler. A number of key options assist us perceive the terrain:
-
Intently Spaced Contour Strains: Point out steep slopes. The nearer the strains are collectively, the steeper the slope.
-
Broadly Spaced Contour Strains: Characterize light slopes or comparatively flat areas.
-
Contour Strains Forming Concentric Circles: Usually point out hills or mountains. The innermost circle represents the very best level (summit).
-
Contour Strains Forming a V-Form: Normally point out a valley or stream. The purpose of the V factors upstream.
-
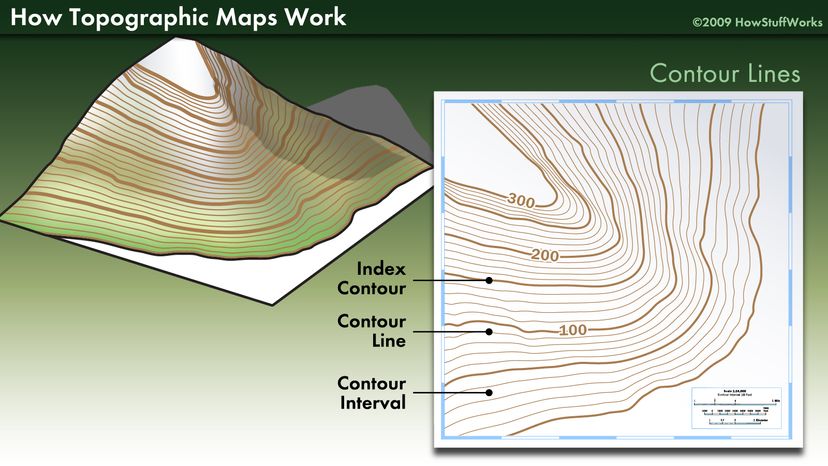
Index Contours: These are thicker strains, normally labeled with their elevation worth, making it simple to trace elevation adjustments throughout the map. They seem at common intervals, typically multiples of the contour interval (e.g., each fifth contour line is likely to be an index contour).
-
Supplementary Contours: Typically, half-interval contours are included to reinforce element in areas with light slopes. These strains are normally thinner than the common contours.
Purposes of Contour Intervals and Topographic Maps:
The correct illustration of elevation supplied by contour strains and their related intervals is significant in varied fields:
-
Civil Engineering: Contour maps are basic in planning and designing infrastructure initiatives like roads, dams, buildings, and pipelines. They assist engineers assess website suitability, decide earthwork volumes, and plan for drainage.
-
Environmental Science: Topographic maps help in understanding landforms, figuring out potential hazards (e.g., landslides, flooding), and analyzing ecological processes. They’re essential for environmental influence assessments and conservation planning.
-
Navy Operations: Contour maps are important for navy planning and navigation, enabling troops to grasp terrain options, plan routes, and assess potential vulnerabilities.
-
Agriculture: Farmers use contour maps to plan irrigation programs, optimize land use, and handle soil erosion.
-
Recreation and Out of doors Actions: Hikers, climbers, and different outside lovers depend on contour maps for navigation, route planning, and assessing the problem of trails.
-
City Planning: Contour maps inform city improvement choices, serving to planners account for topography, drainage, and potential hazards when designing city infrastructure and settlements.
Challenges and Limitations:
Whereas contour maps are invaluable instruments, it is essential to acknowledge their limitations:
-
Vertical Exaggeration: The vertical scale of a topographic map is commonly exaggerated relative to the horizontal scale to reinforce the visibility of elevation adjustments. This may result in a distorted notion of the particular terrain steepness.
-
Interpolation: Contour strains are drawn based mostly on restricted elevation information factors. The strains between these factors are interpolations, and inaccuracies can happen, significantly in areas with complicated terrain.
-
Information Decision: The accuracy of the contour strains immediately will depend on the decision of the elevation information used to create the map. Decrease-resolution information can result in much less exact representations of the terrain.
-
Visible Muddle: In areas with complicated topography and small contour intervals, the map can develop into visually cluttered, making interpretation tough.
Conclusion:
The contour interval is a crucial part of topographic maps, immediately impacting their accuracy, usability, and effectiveness throughout a broad spectrum of purposes. Understanding its calculation, interpretation, and limitations is crucial for anybody working with or deciphering topographic information. By fastidiously contemplating the dimensions, terrain aid, map function, and information availability, cartographers be certain that the chosen contour interval precisely displays the panorama and facilitates efficient communication of spatial info. The power to decipher the visible language of contour strains and their intervals unlocks a deeper understanding of the three-dimensional world, facilitating knowledgeable choices in varied fields, from engineering and environmental science to recreation and navy operations. Due to this fact, appreciating the importance of the contour interval isn’t merely a technical element; it is basic to understanding and using the ability of topographic maps.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Deciphering the Panorama: Understanding Contour Intervals and Their Significance. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!