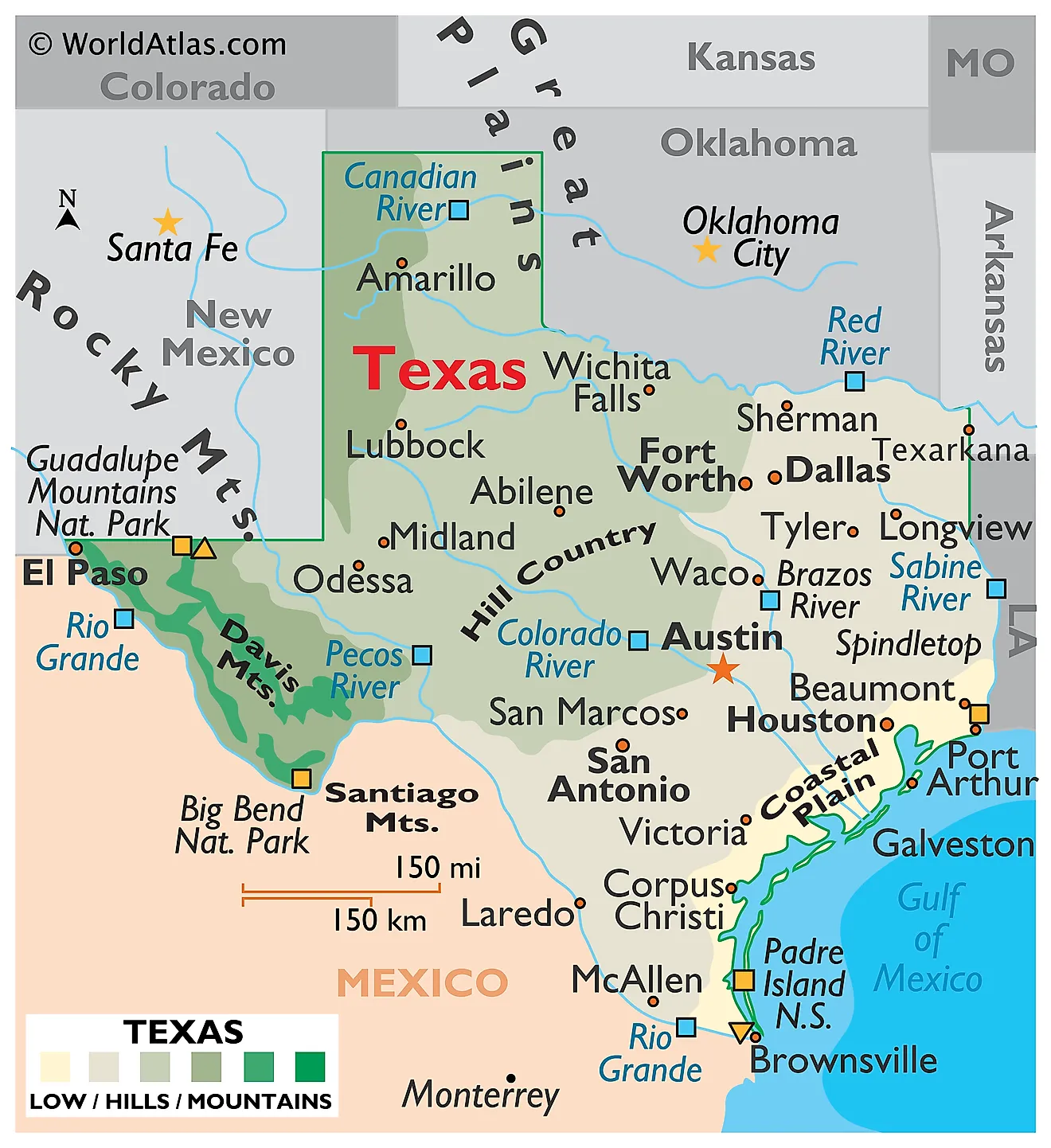
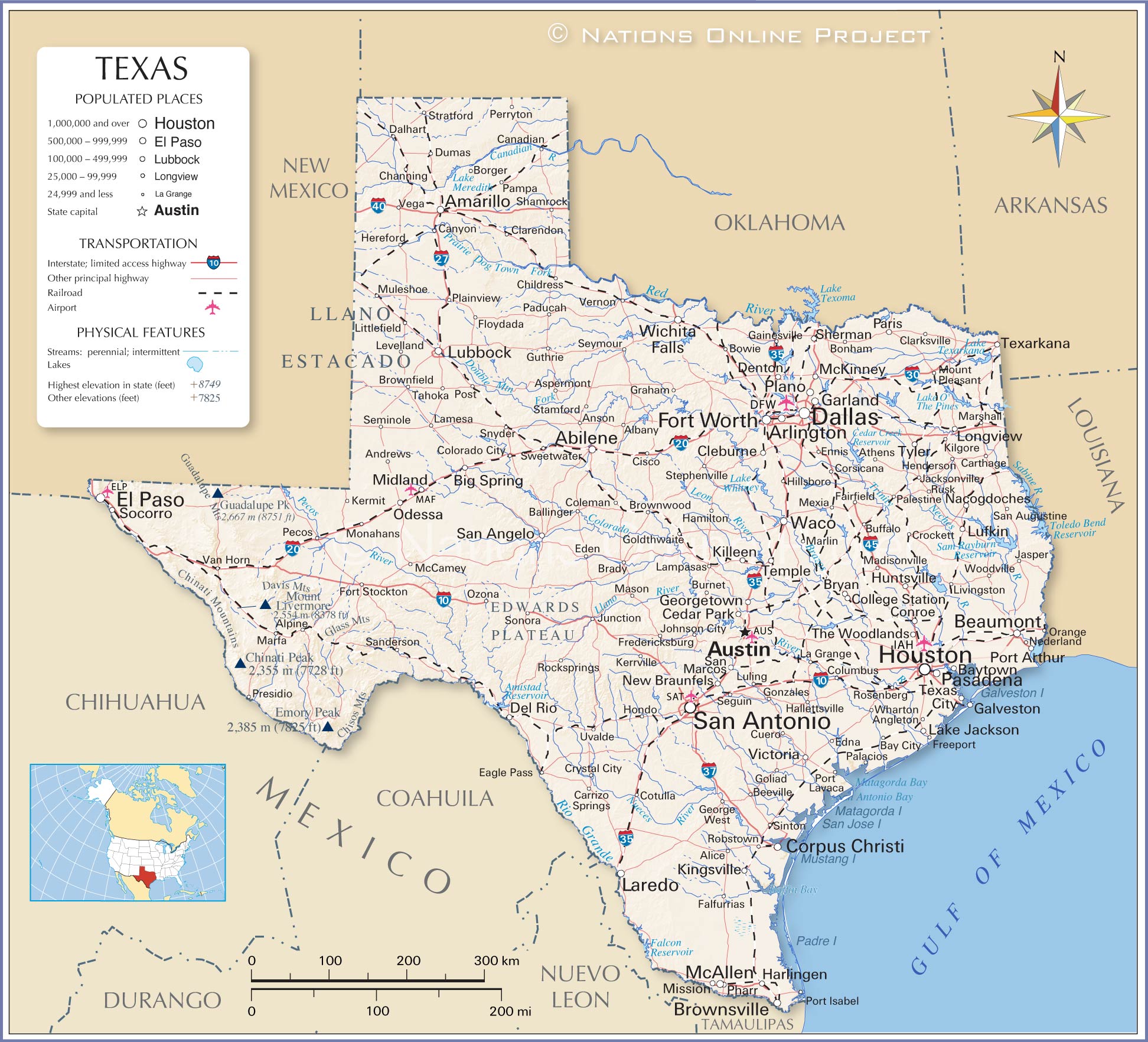
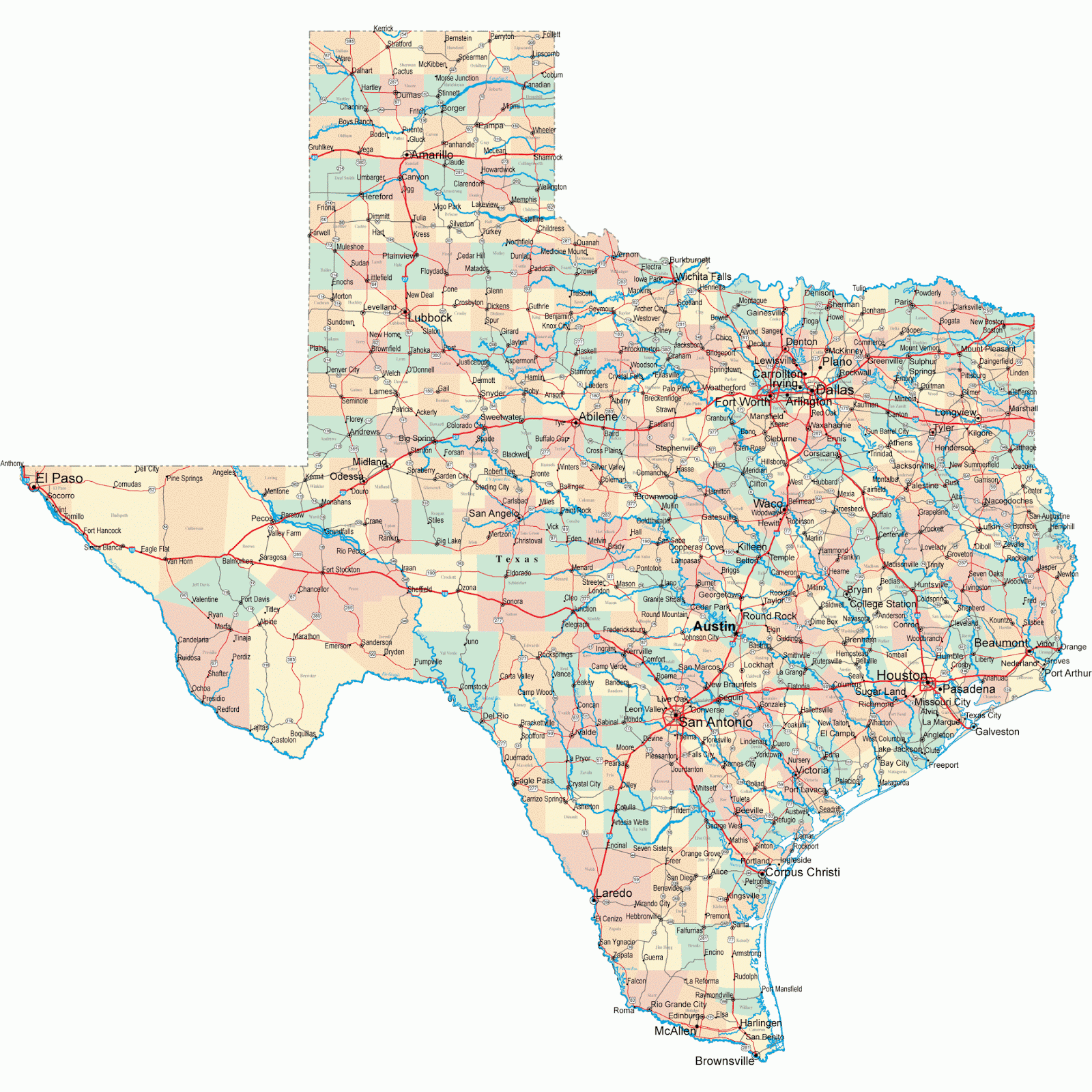
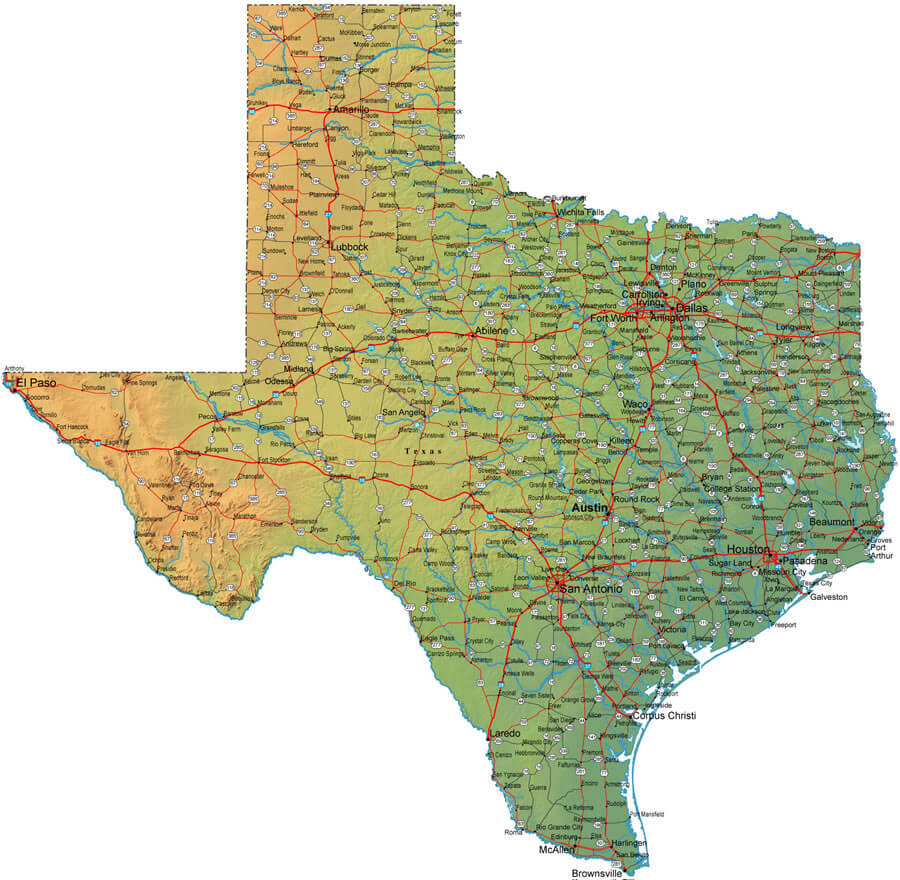
The Texas Gulf Coast, a vibrant tapestry woven from sandy beaches, sprawling bays, and bustling ports, holds a unique place in the state’s identity and economy. Understanding its geography is paramount to appreciating its beauty, navigating its complexities, and maximizing its potential. The Texas Gulf Coast map, therefore, becomes more than just a navigational tool; it’s a key to unlocking the region’s secrets and experiencing its rich offerings.
This article delves into the intricacies of the Texas Gulf Coast map, exploring its major features, regional variations, economic significance, and the environmental challenges it faces. We will traverse its iconic landmarks, unravel the layers of its coastal ecosystem, and understand the human impact on this dynamic landscape.
A Coastal Colossus: Defining the Texas Gulf Coast
The Texas Gulf Coast stretches for approximately 367 miles, from the Sabine River bordering Louisiana to the Rio Grande marking the boundary with Mexico. However, defining its exact boundaries on a map is more complex. Coastal counties are generally considered to be those bordering the Gulf of Mexico, including the barrier islands. Inland, the influence of the Gulf extends through brackish estuaries, salt marshes, and coastal prairies, making the “coastal zone” a broader, more ecologically defined area.
Major Features of the Texas Gulf Coast Map:
The Texas Gulf Coast map is characterized by a few dominant features that shape its environment and economy:
-
Barrier Islands: A defining characteristic of the Texas coast is its chain of barrier islands, elongated landforms running parallel to the mainland. These islands, including Galveston Island, Padre Island (both North and South), and Mustang Island, act as a natural buffer, protecting the mainland from storm surges and erosion. They also create shallow bays and lagoons behind them, providing crucial habitats for marine life. The map clearly delineates these islands, highlighting their varying lengths, widths, and the passes connecting them to the Gulf.
-
Bays and Estuaries: The landward side of the barrier islands is characterized by a complex network of bays and estuaries. These brackish water bodies, where freshwater rivers mix with saltwater from the Gulf, are vital nursery grounds for countless species of fish, shrimp, and other marine organisms. Major bays like Galveston Bay, Matagorda Bay, Aransas Bay, and Corpus Christi Bay are prominent features on the map. Their intricate shorelines, marked by marshes and mudflats, are visible and critical to understanding the coastal ecosystem.
-
Rivers and Drainage Basins: Numerous rivers flow into the Gulf of Mexico across the Texas coast. These rivers, including the Sabine, Trinity, Brazos, Colorado, and Nueces, carry freshwater and sediment from inland areas, shaping the coastal landscape and influencing salinity levels in the bays and estuaries. The map showcases these river systems and their associated drainage basins, highlighting the vital connection between the inland areas and the coastal zone.
-
The Gulf of Mexico: The vast expanse of the Gulf of Mexico is the dominant feature of the map. Its warm waters support a diverse range of marine life, and its currents play a significant role in the region’s weather patterns. The map often indicates shipping lanes, fishing grounds, and oil and gas platforms, highlighting the economic importance of the Gulf.
A Coast of Contrasts: Regional Variations Along the Texas Gulf Coast:
While unified by the Gulf, the Texas coast is not a monolithic entity. Distinct regional variations influence its landscape, economy, and culture. These variations are readily apparent when examining different sections of the map:
-
Upper Coast (Beaumont/Galveston/Houston): This region is dominated by the Houston metropolitan area, a major industrial and shipping hub. The map reflects this with the presence of large ports like the Port of Houston and the Port of Galveston, as well as numerous petrochemical plants and refineries. Galveston Island, with its historical charm and tourist attractions, is also a prominent feature. The region is characterized by flat coastal prairies and extensive marshlands.
-
Mid-Coast (Corpus Christi/Victoria): This area is characterized by a mix of agriculture, fishing, and tourism. Corpus Christi, a major port and naval air station, is a significant economic center. The map highlights Aransas National Wildlife Refuge, wintering ground for the endangered whooping crane, showcasing the region’s commitment to conservation. Smaller bays and estuaries, like Matagorda Bay and Aransas Bay, contribute to the region’s rich seafood industry.
-
Lower Coast (Brownsville/South Padre Island): This region, bordering Mexico, is known for its subtropical climate, pristine beaches, and diverse birdlife. South Padre Island, a popular tourist destination, is a prominent feature on the map. The Rio Grande Valley, a major agricultural area, contributes significantly to the region’s economy. The map also reveals the presence of numerous wildlife refuges and preserves, reflecting the region’s focus on conservation.
Economic Powerhouse: Mapping the Coastal Economy:
The Texas Gulf Coast is a vital economic engine for the state and the nation. The map visually represents the diverse industries that thrive along the coast:
-
Oil and Gas: The Gulf of Mexico is a major source of oil and gas, and the Texas coast is home to numerous offshore platforms, refineries, and petrochemical plants. The map often indicates the location of these facilities, highlighting the region’s role in energy production.
-
Shipping and Transportation: The Port of Houston is one of the busiest ports in the United States, handling a vast amount of cargo. Other major ports, such as Corpus Christi and Galveston, also contribute significantly to the region’s economy. The map depicts shipping lanes, port facilities, and major transportation routes, showcasing the region’s importance in global trade.
-
Fishing and Seafood: The Gulf of Mexico and its bays and estuaries support a thriving fishing industry. The map highlights fishing grounds, seafood processing plants, and marinas, reflecting the region’s dependence on marine resources.
-
Tourism: The Texas Gulf Coast attracts millions of tourists each year, drawn by its beaches, wildlife, and historical attractions. The map indicates popular tourist destinations, such as Galveston Island, South Padre Island, and the San Antonio Riverwalk, showcasing the region’s vibrant tourism industry.
Challenges and Conservation: Protecting the Coastal Ecosystem:
The Texas Gulf Coast faces numerous environmental challenges, including:
-
Coastal Erosion: The constant wave action and storm surges cause significant coastal erosion, threatening infrastructure and habitats. The map can illustrate areas particularly vulnerable to erosion, highlighting the need for coastal management strategies.
-
Pollution: Industrial activity, agricultural runoff, and urban development contribute to pollution of the Gulf and its bays. The map can identify potential sources of pollution and areas where water quality is impaired.
-
Habitat Loss: Coastal development and wetland drainage have resulted in significant habitat loss, impacting wildlife populations. The map can highlight areas where critical habitats are threatened and identify opportunities for restoration.
-
Sea Level Rise: Climate change is causing sea levels to rise, which could inundate low-lying coastal areas and exacerbate erosion. The map can be used to model the potential impacts of sea level rise and inform adaptation strategies.
Conservation efforts are crucial to protecting the Texas Gulf Coast’s unique ecosystem. The map can play a vital role in these efforts by identifying critical habitats, tracking pollution levels, and monitoring the effectiveness of conservation programs.
Conclusion: The Texas Gulf Coast Map as a Gateway to Understanding
The Texas Gulf Coast map is more than just a geographical representation; it is a key to understanding the region’s complex ecosystem, its vibrant economy, and the challenges it faces. By studying the map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and importance of this coastal landscape and work towards ensuring its long-term sustainability. From the bustling ports of the Upper Coast to the serene beaches of the Lower Coast, the Texas Gulf Coast map offers a window into a world of opportunity, beauty, and environmental responsibility. Its understanding is crucial for navigating, appreciating, and protecting this emerald embrace.