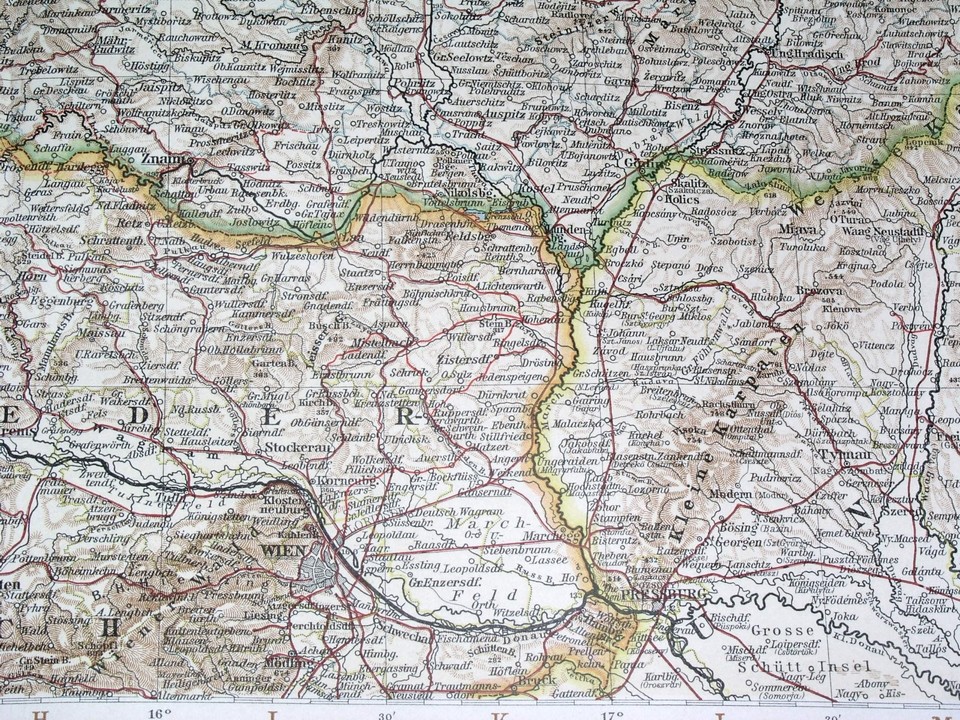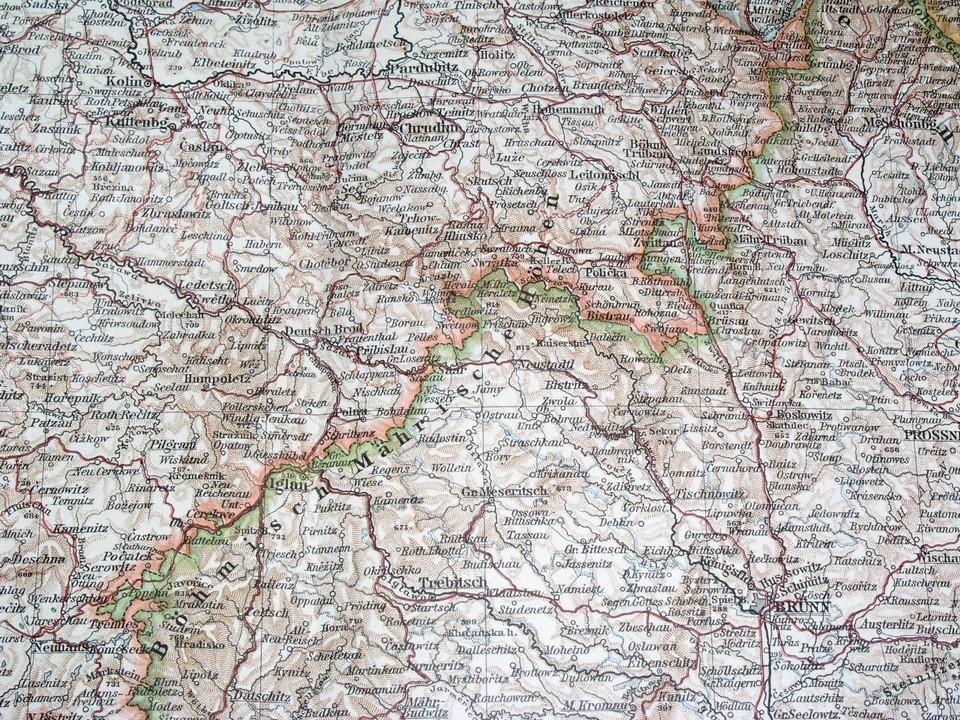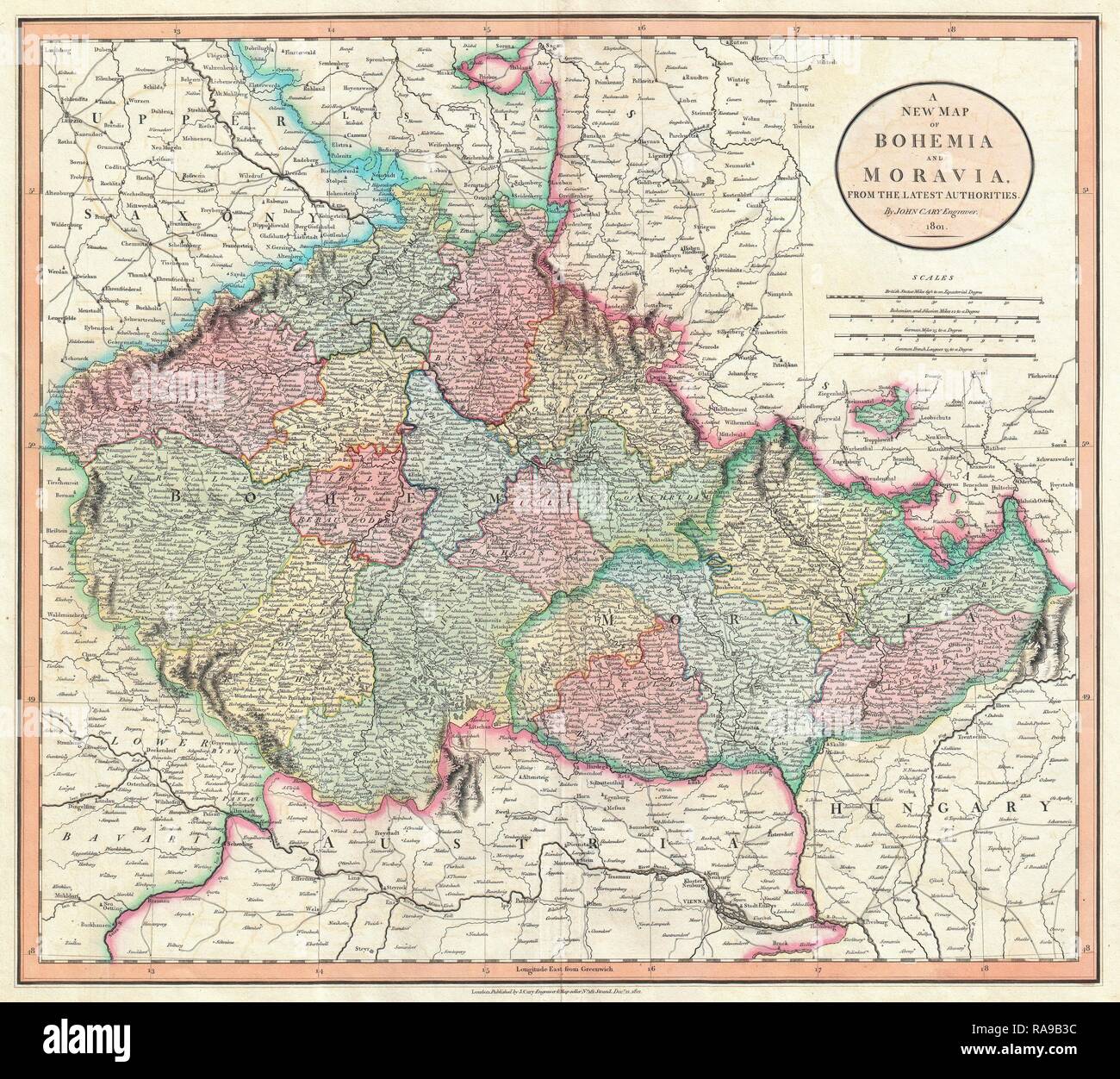
Bohemia, a name that resonates with romance, resilience, and a distinctive cultural identity, exists not just in the realm of imagination, but firmly etched upon the map of Central Europe. More than just a geographic location, Bohemia is a region steeped in history, a cradle of innovation, and a battleground where empires clashed and ideas blossomed. Understanding Bohemia requires more than pinpointing its coordinates; it demands an exploration of its geographical contours, its historical evolution, and the profound influence it has exerted on the surrounding world.
Looking at a map of modern Europe, Bohemia corresponds roughly to the western two-thirds of the Czech Republic. It’s a landlocked territory, cradled by mountain ranges that define its borders and shaped its character. These mountains – the Ore Mountains (Krušné hory) to the northwest, the Sudetes (Krkonoše) to the northeast, the Bohemian Forest (Šumava) to the southwest, and smaller ranges like the Brdy Highlands to the south – have served as both protection and insulation, fostering a distinct Bohemian identity while simultaneously influencing its economic and political development.
The geographical heart of Bohemia is the Bohemian Basin, a fertile plain drained by the Elbe (Labe) and Vltava (Moldau) rivers, both vital arteries for trade and agriculture. This basin, with its rich soil and temperate climate, has been the breadbasket of the region, supporting a thriving agricultural economy for centuries. It’s also home to Prague, the magnificent capital city that sits astride the Vltava, its spires and bridges a testament to Bohemia’s rich history and cultural significance.
A Tapestry of History Woven onto the Landscape:
The story of Bohemia is intimately intertwined with its geography. The presence of the mountain ranges provided natural defenses, attracting early settlers and contributing to the region’s relative isolation. Archaeological evidence suggests human habitation dating back to the Paleolithic era, but it was the arrival of the Celtic Boii tribe in the 4th century BC that gave the region its name. "Bohemia" is derived from "Boiohaemum," meaning "the home of the Boii."
The Boii were eventually displaced by Germanic tribes, followed by the arrival of the Slavs in the 6th century AD. These Slavic tribes, gradually coalescing into the Czechs, laid the foundation for the Kingdom of Bohemia, which would rise to prominence under the Přemyslid dynasty. The Přemyslids, consolidating power through strategic alliances and military prowess, established a strong and independent Bohemian state, building fortresses and towns that are still visible on the map today.
The 13th and 14th centuries marked a golden age for Bohemia. King Ottokar II expanded Bohemian territory and influence, while his grandson, Charles IV, transformed Prague into a major European center of culture and learning. Charles, who also served as Holy Roman Emperor, founded Charles University in 1348, one of the oldest universities in Europe, cementing Prague’s position as a hub of intellectual and artistic innovation. The architectural legacy of this era, including Charles Bridge and St. Vitus Cathedral, continues to dominate the Prague skyline, a visible reminder of Bohemia’s imperial grandeur.
However, Bohemia’s prosperity and influence were not without their challenges. The Hussite Wars, ignited by the religious reformer Jan Hus in the early 15th century, plunged the region into decades of conflict. Hus, a staunch advocate for religious reform and national identity, was burned at the stake for heresy, sparking a fierce rebellion among his followers. The Hussite armies, employing innovative military tactics and fueled by religious fervor, successfully defended Bohemia against repeated crusades launched by the Holy Roman Empire. The Hussite Wars, while devastating, solidified a sense of Bohemian national identity and laid the groundwork for future religious and political movements.
Following the Hussite Wars, Bohemia entered a period of relative stability under the Jagellon dynasty. However, this period was short-lived. In 1526, the Habsburgs ascended to the Bohemian throne, marking the beginning of a long and often turbulent relationship. The Habsburgs, staunch Catholics, sought to re-Catholicize Bohemia, leading to escalating tensions with the Protestant Bohemian nobility. This culminated in the Defenestration of Prague in 1618, an event that triggered the Thirty Years’ War, a devastating conflict that engulfed much of Europe.
The Thirty Years’ War had a profound impact on Bohemia. The Bohemian nobility was decimated, Protestantism was suppressed, and the region was subjected to harsh Habsburg rule. Bohemia became an integral part of the Habsburg Empire, losing much of its autonomy and independence. The landscape of Bohemia, once dotted with bustling towns and thriving agricultural communities, bore the scars of war and religious persecution.
From National Revival to Modern Statehood:
Despite the hardships imposed by Habsburg rule, the spirit of Bohemia remained unbroken. The 19th century witnessed a surge in Bohemian national consciousness, fueled by the Romantic movement and a renewed interest in Czech language, literature, and history. Intellectuals and artists like Josef Jungmann, František Palacký, and Bedřich Smetana played a crucial role in reviving Czech national identity and promoting Bohemian culture. This national revival movement laid the foundation for the eventual creation of an independent Czechoslovakia after the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1918.
Czechoslovakia, comprising Bohemia, Moravia, and Slovakia, represented the fulfillment of centuries of Bohemian aspirations for self-determination. Prague once again became a capital city, a vibrant center of culture and politics. However, this period of independence was tragically cut short by the Nazi occupation during World War II. Bohemia, along with the rest of Czechoslovakia, suffered immensely under Nazi rule, its cultural heritage plundered and its population subjected to brutal oppression.
Following the war, Czechoslovakia was liberated, but soon fell under the influence of the Soviet Union. Bohemia became part of the Eastern Bloc, subjected to communist rule for over four decades. Despite the political repression, the spirit of Bohemian resistance remained alive, finding expression in art, literature, and music. The Prague Spring of 1968, a brief period of liberalization and reform, was brutally crushed by Soviet forces, but it served as a powerful symbol of Bohemian resistance to totalitarian rule.
The Velvet Revolution of 1989, a peaceful transition to democracy, marked the end of communist rule in Czechoslovakia. In 1993, Czechoslovakia peacefully dissolved into two independent states: the Czech Republic and Slovakia. Bohemia became the heartland of the Czech Republic, its historical legacy and cultural identity playing a vital role in shaping the new nation.
Bohemia Today: A Legacy of Resilience and Innovation:
Today, Bohemia is a thriving region, a testament to its resilience and its ability to adapt to changing circumstances. Prague is a major European capital, a popular tourist destination renowned for its stunning architecture, rich history, and vibrant cultural scene. The Bohemian landscape, dotted with castles, chateaux, and picturesque towns, attracts visitors from around the world.
Beyond its historical and cultural attractions, Bohemia is also a modern and innovative region, with a thriving economy and a strong focus on technology and innovation. The legacy of Bohemian craftsmanship, particularly in fields like glassmaking and brewing, continues to thrive.
Looking at a map of Bohemia today, one sees not just a geographical region, but a living testament to centuries of history, struggle, and cultural achievement. From its ancient roots to its modern-day success, Bohemia stands as a powerful symbol of resilience, innovation, and the enduring power of cultural identity. The map of Bohemia is more than just lines and coordinates; it is a story etched onto the landscape, a story that continues to unfold with each passing year. It’s a story of a land that has weathered countless storms, emerged stronger each time, and continues to captivate the world with its unique charm and enduring spirit. Bohemia, a name that continues to resonate with history, legend, and the unwavering spirit of a people.