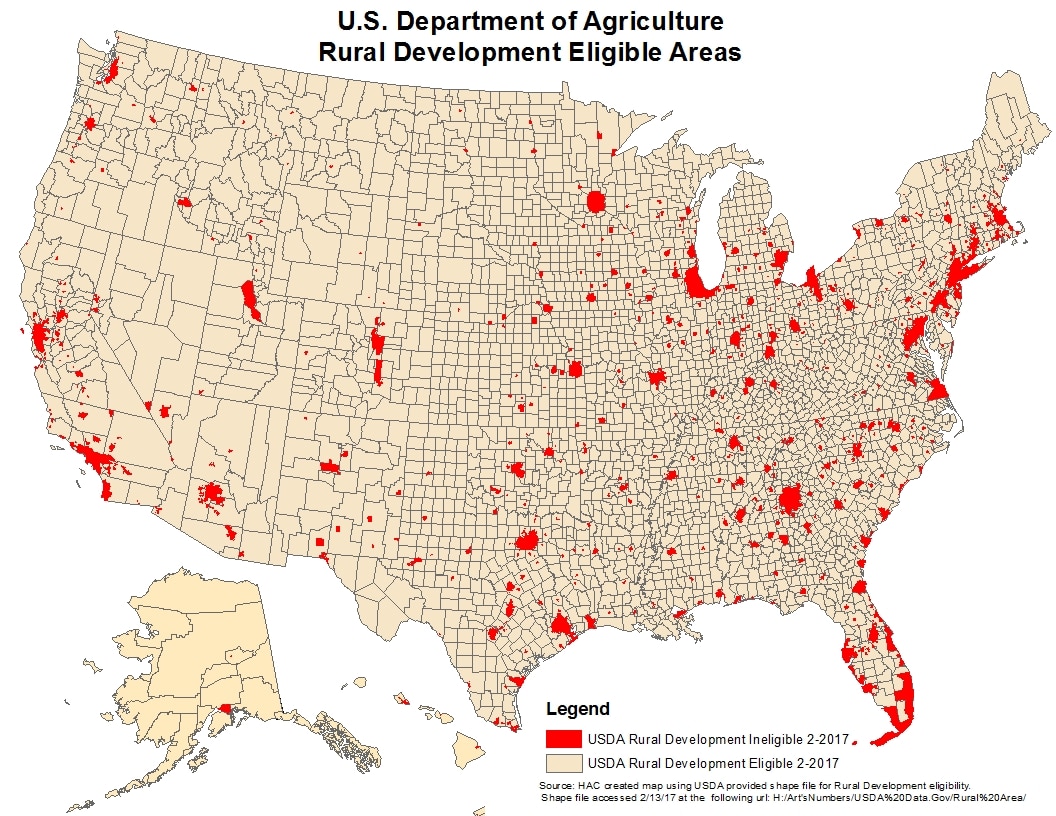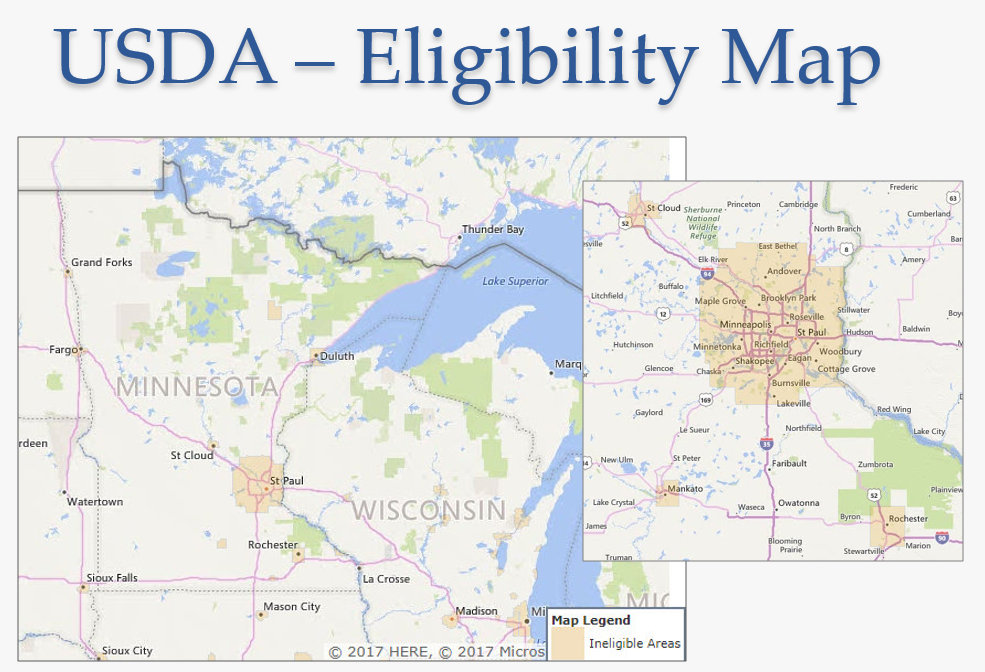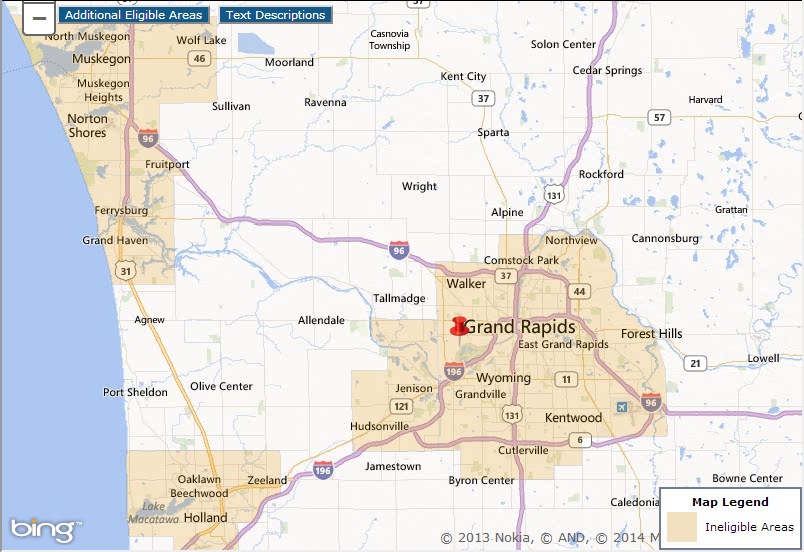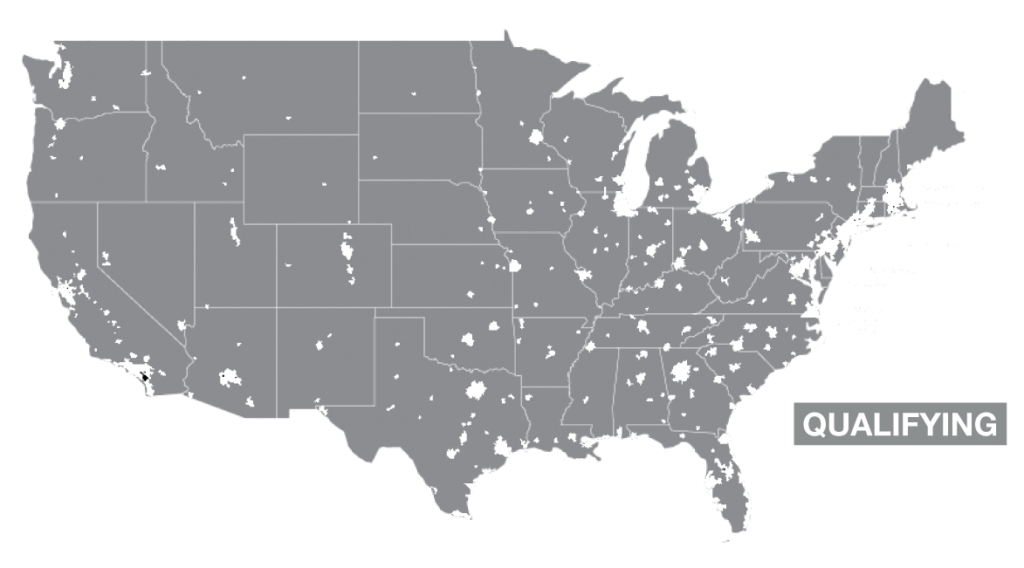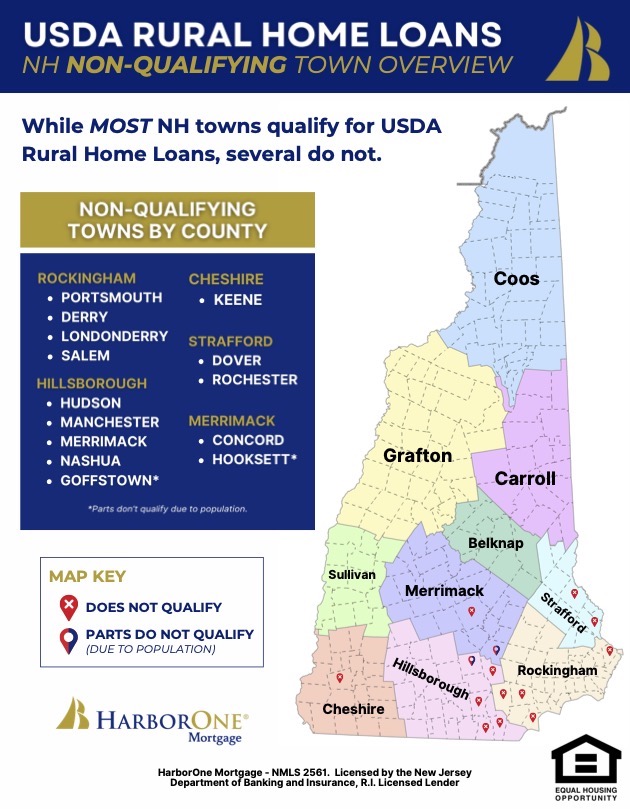
Rural areas are the backbone of many economies, providing essential resources, contributing to cultural heritage, and offering unique landscapes. However, these regions often face unique challenges, including limited access to capital, aging infrastructure, and population decline. To address these disparities, governments and organizations offer various rural development loan programs designed to stimulate economic growth, improve living standards, and foster sustainable development. Understanding the availability and distribution of these loan programs is crucial for individuals, businesses, and communities looking to thrive in rural settings. This is where the concept of a "Rural Development Loan Map" becomes invaluable.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Rural Development Loan Maps, their purpose, key features, the types of loans they often represent, how to interpret them, and their impact on rural communities.
What is a Rural Development Loan Map?
A Rural Development Loan Map is a visual representation, typically in the form of an interactive online tool or a static printed map, that displays the geographical distribution of rural development loans. It serves as a valuable resource for stakeholders seeking information about the availability and utilization of funding opportunities in rural areas. These maps often incorporate various layers of data, including:
- Loan Program Types: Identifying different types of loans, such as those for business development, housing, infrastructure, agriculture, or community facilities.
- Loan Amounts: Indicating the size and range of loans awarded in specific locations.
- Borrower Types: Differentiating between loans granted to individuals, small businesses, non-profit organizations, or government entities.
- Lender Information: Providing details about the organizations providing the loans, such as government agencies, banks, credit unions, or community development financial institutions (CDFIs).
- Geographic Boundaries: Clearly delineating rural areas eligible for specific loan programs.
- Project Outcomes: (Where available) Briefly summarizing the intended or actual impact of the funded projects.
The Purpose of Rural Development Loan Maps
Rural Development Loan Maps serve several crucial purposes:
- Transparency and Accessibility: They provide a transparent overview of where funding is being allocated, enabling stakeholders to understand the distribution of resources and identify potential opportunities.
- Resource Allocation Optimization: By visualizing the distribution of loans, policymakers and program administrators can identify areas where funding is lacking or where existing programs may need adjustments.
- Attracting Investment: Loan maps can attract potential investors and businesses to rural areas by showcasing the availability of financial support and the success of existing projects.
- Promoting Economic Development: By facilitating access to capital, these maps contribute to job creation, business growth, and overall economic development in rural communities.
- Empowering Rural Communities: By providing information about available resources, loan maps empower rural residents and businesses to take advantage of funding opportunities and improve their quality of life.
- Facilitating Collaboration: Loan maps can help connect lenders, borrowers, and community organizations, fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Measuring Program Effectiveness: By tracking the distribution and impact of loans, these maps can help evaluate the effectiveness of rural development programs and inform future policy decisions.
Key Features of a Comprehensive Rural Development Loan Map
A well-designed and comprehensive Rural Development Loan Map should incorporate the following key features:
- Interactive Functionality: Users should be able to zoom in and out of specific areas, filter data based on loan type, amount, borrower type, and lender, and access detailed information about individual loan projects.
- User-Friendly Interface: The map should be easy to navigate and understand, even for users with limited technical skills.
- Regular Updates: The data on the map should be updated regularly to reflect the most current information about loan availability and distribution.
- Data Accuracy: The information presented on the map should be accurate and reliable, sourced from reputable sources such as government agencies, lending institutions, and non-profit organizations.
- Detailed Project Information: For each loan project, the map should provide information about the borrower, the lender, the loan amount, the project description, and the anticipated or actual outcomes.
- Geographic Specificity: The map should accurately delineate rural areas eligible for specific loan programs, taking into account factors such as population density, economic indicators, and geographic boundaries.
- Search Functionality: Users should be able to search for specific locations, loan types, or lenders.
- Accessibility Features: The map should be accessible to users with disabilities, adhering to accessibility standards such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines).
- Data Export Options: Users should be able to export data from the map in various formats, such as CSV or Excel, for further analysis.
Types of Rural Development Loans Often Represented on the Map
Rural Development Loan Maps typically include information about a wide range of loan programs, catering to diverse needs within rural communities. Some common types of loans represented include:
- Business Loans: These loans are designed to support the establishment, expansion, or modernization of businesses in rural areas. They can be used for purposes such as purchasing equipment, acquiring real estate, or financing working capital. Examples include USDA Business & Industry Loans and SBA 7(a) loans targeted towards rural areas.
- Housing Loans: These loans help individuals and families purchase, build, or renovate homes in rural areas. They often come with favorable terms and interest rates to make homeownership more accessible. Examples include USDA Rural Housing Loans and loans from CDFIs specializing in affordable housing.
- Infrastructure Loans: These loans support the development and improvement of essential infrastructure in rural communities, such as water and sewer systems, roads, bridges, and broadband internet access. Examples include USDA Rural Development infrastructure loans and grants.
- Agricultural Loans: These loans provide financial assistance to farmers and ranchers for purposes such as purchasing land, equipment, or livestock, or for financing operating expenses. Examples include USDA Farm Service Agency loans and loans from agricultural credit associations.
- Community Facility Loans: These loans support the construction, renovation, or expansion of community facilities in rural areas, such as schools, hospitals, libraries, and fire stations. Examples include USDA Community Facilities Direct Loan & Grant Program.
- Energy Efficiency Loans: These loans help rural residents and businesses implement energy efficiency measures, such as installing solar panels or upgrading insulation.
- Water and Waste Disposal Loans: These loans finance the construction and improvement of water and waste disposal systems in rural areas.
- Telecommunications Loans: These loans support the development of broadband internet access and other telecommunications infrastructure in rural areas.
How to Interpret a Rural Development Loan Map
Interpreting a Rural Development Loan Map requires careful attention to the various data layers and features it presents. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify Your Area of Interest: Use the map’s zoom and navigation features to focus on the specific rural area you are interested in.
- Explore Loan Program Types: Utilize the map’s filtering options to view loans based on program type, such as business loans, housing loans, or infrastructure loans.
- Analyze Loan Amounts: Examine the loan amounts displayed on the map to understand the size and range of funding available in your area.
- Identify Borrower Types: Determine whether the loans in your area have been granted to individuals, small businesses, non-profit organizations, or government entities.
- Research Lenders: Identify the organizations providing loans in your area, such as government agencies, banks, credit unions, or CDFIs.
- Review Project Outcomes: If available, review the project descriptions and outcomes associated with the loans to understand the impact of the funding.
- Compare to Needs: Assess whether the available loan programs and funding levels adequately address the needs of your rural community.
- Contact Lenders: If you are interested in applying for a loan, contact the lenders listed on the map to learn more about their eligibility requirements and application process.
- Identify Gaps: Note any areas where funding is lacking or where specific types of loan programs are unavailable. This information can be used to advocate for increased funding or the development of new programs.
The Impact of Rural Development Loan Maps on Rural Communities
Rural Development Loan Maps have a significant positive impact on rural communities by:
- Increasing Access to Capital: By providing information about available loan programs, these maps help rural residents and businesses access the capital they need to thrive.
- Stimulating Economic Growth: By facilitating access to funding, loan maps contribute to job creation, business growth, and overall economic development in rural areas.
- Improving Living Standards: By supporting investments in housing, infrastructure, and community facilities, loan maps help improve the quality of life for rural residents.
- Promoting Sustainable Development: By encouraging investments in energy efficiency, renewable energy, and sustainable agriculture, loan maps contribute to the long-term sustainability of rural communities.
- Empowering Rural Residents: By providing information about available resources, loan maps empower rural residents to take control of their economic future and improve their communities.
- Strengthening Community Resilience: By supporting investments in essential infrastructure and community facilities, loan maps help rural communities become more resilient to economic and environmental challenges.
Conclusion
Rural Development Loan Maps are powerful tools for promoting economic development and improving living standards in rural communities. By providing a transparent and accessible overview of available funding opportunities, these maps empower individuals, businesses, and communities to access the capital they need to thrive. As technology continues to evolve, these maps are becoming increasingly sophisticated and user-friendly, making it easier than ever for stakeholders to navigate the rural landscape and unlock the potential of these vital regions. By understanding the purpose, key features, and interpretation of Rural Development Loan Maps, we can collectively work towards creating a more prosperous and sustainable future for rural communities across the globe. Continued investment in and improvement of these resources is crucial for ensuring that rural areas have the opportunity to flourish and contribute to the overall well-being of society.