Arizona, a state synonymous with stunning desert landscapes, dramatic canyons, and a rich tapestry of history, is also home to a significant amount of land managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM). Understanding the BLM land map of Arizona is crucial for anyone planning to explore the state’s wild and open spaces, whether for recreation, resource management, or research. This article delves into the intricacies of BLM land in Arizona, providing insights into its significance, how to access and interpret the maps, and the responsibilities that come with enjoying these public lands.
The Significance of BLM Land in Arizona
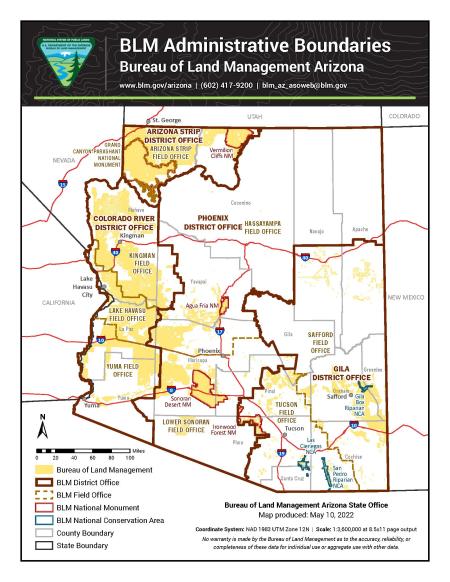
The BLM manages approximately 12.1 million acres of public land in Arizona, making it the largest landholder in the state after the state government itself. These lands are a diverse mosaic of ecosystems, ranging from the Sonoran Desert with its iconic saguaro cacti to the high-elevation forests of the Colorado Plateau. They encompass:
- Ecological Treasures: BLM land in Arizona supports a rich array of plant and animal life, including threatened and endangered species like the desert tortoise and the Gila topminnow. These lands provide critical habitat for wildlife, contribute to biodiversity conservation, and help maintain the ecological balance of the region.
- Recreational Opportunities: Millions of people visit BLM land in Arizona each year to engage in a wide range of outdoor activities. From hiking and camping to hunting, fishing, and off-roading, these lands offer unparalleled opportunities for recreation and adventure. The Grand Canyon-Parashant National Monument, managed jointly by the BLM and the National Park Service, is a prime example of the recreational draw of BLM land.
- Economic Importance: Beyond recreation, BLM land in Arizona plays a significant role in the state’s economy. It supports grazing, mining, and timber harvesting activities, providing livelihoods for many residents. The BLM also manages renewable energy resources on its lands, contributing to the state’s energy portfolio.
- Cultural Heritage: BLM land in Arizona is steeped in history and cultural significance. It contains numerous archaeological sites, representing the rich heritage of Native American tribes who have inhabited the region for thousands of years. These lands also bear witness to the history of early settlers, miners, and ranchers.
- Water Resources: The BLM plays a critical role in managing water resources on its lands in Arizona. This includes protecting watersheds, maintaining riparian areas, and ensuring the sustainable use of water for various purposes. The scarcity of water in the arid Southwest makes this role particularly important.
Accessing and Interpreting the BLM Land Map of Arizona
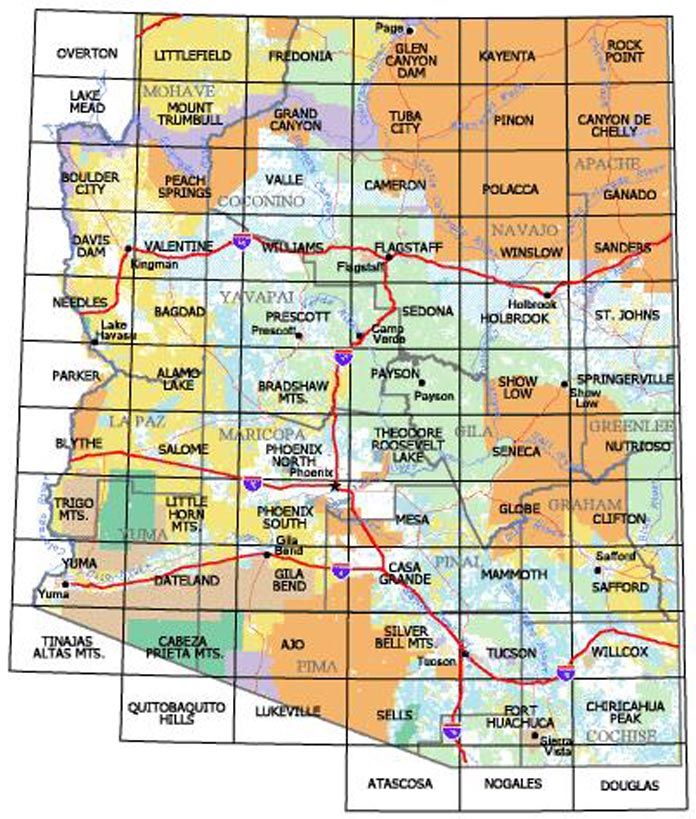
Navigating BLM land in Arizona effectively requires understanding how to access and interpret the available maps. Here’s a breakdown of the key resources and considerations:
- Official BLM Maps: The BLM provides a variety of maps for public use, including:
- Surface Management Maps: These maps show the ownership and management of land, distinguishing between BLM land, National Forest land, state land, private land, and other jurisdictions. They are essential for determining which agency manages a particular area.
- Recreation Maps: These maps highlight recreational opportunities, such as campgrounds, hiking trails, OHV routes, and scenic overlooks. They provide valuable information for planning outdoor adventures.
- Geographic Information System (GIS) Data: The BLM makes GIS data available online, allowing users to create custom maps and analyze spatial data. This is a valuable resource for researchers, resource managers, and anyone interested in detailed information about BLM land.
- Online Resources: The BLM website (www.blm.gov) is a primary source of information about BLM land in Arizona. The website provides access to maps, regulations, permits, and other important resources.
- Offline Resources: Paper maps are still useful, especially in areas with limited cell service. BLM offices in Arizona often have maps available for purchase.
- Map Interpretation: Understanding the symbols and legends on BLM maps is crucial. Key elements to look for include:
- Land Ownership Boundaries: Differentiating between BLM land and other ownership types is essential for knowing where you can legally access and recreate.
- Roads and Trails: Identifying roads and trails is important for navigation and planning routes. Pay attention to road classifications, as some roads may be suitable only for high-clearance vehicles.
- Water Sources: Locating water sources is critical, especially in the arid desert environment. Be aware that water sources may be unreliable and require purification.
- Restricted Areas: Some areas may be closed to certain activities or require permits. Pay attention to posted signs and regulations.
- Contour Lines: These lines indicate elevation changes and can help you understand the terrain.
Understanding Regulations and Responsibilities
Enjoying BLM land responsibly requires adhering to regulations and practicing Leave No Trace principles. Here are some key considerations:
- Permits and Fees: Some activities on BLM land may require permits or fees. This includes activities such as commercial filming, organized events, and certain types of resource extraction. Check with the local BLM office to determine if a permit is required.
- Fire Restrictions: Arizona is prone to wildfires, so it’s essential to be aware of fire restrictions. During dry periods, open fires may be prohibited. Always follow fire safety guidelines, such as clearing vegetation around campsites and using fire rings or stoves.
- Vehicle Regulations: Off-highway vehicles (OHVs) are popular on BLM land, but it’s important to follow vehicle regulations. This includes staying on designated routes, respecting speed limits, and avoiding sensitive areas.
- Camping Regulations: Dispersed camping is allowed on much of BLM land, but there are some restrictions. Follow camping regulations, such as camping at least 200 feet from water sources and packing out all trash.
- Leave No Trace Principles: These principles are essential for minimizing your impact on the environment. They include:
- Plan Ahead and Prepare: Know the regulations and conditions of the area you plan to visit.
- Travel and Camp on Durable Surfaces: Stay on established trails and campsites.
- Dispose of Waste Properly: Pack out everything you pack in.
- Leave What You Find: Avoid disturbing plants, animals, or cultural artifacts.
- Minimize Campfire Impacts: Use a stove for cooking whenever possible.
- Respect Wildlife: Observe wildlife from a distance and avoid feeding them.
- Be Considerate of Other Visitors: Minimize noise and respect the privacy of others.
Specific Areas of Interest on BLM Land in Arizona
Arizona’s BLM land offers a diverse range of experiences. Here are a few notable areas:
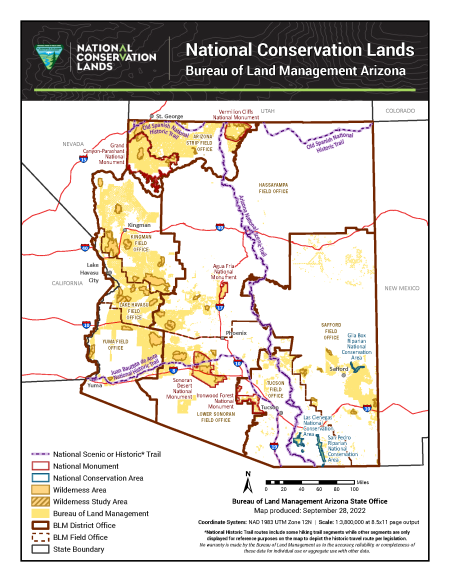
- Grand Canyon-Parashant National Monument: This monument showcases the dramatic landscape north of the Grand Canyon, offering hiking, camping, and scenic drives.
- Vermilion Cliffs National Monument: Known for its colorful sandstone cliffs and slot canyons, this monument is a popular destination for hiking and photography.
- Sonoran Desert National Monument: This monument protects a pristine example of the Sonoran Desert ecosystem, with its iconic saguaro cacti and diverse wildlife.
- San Pedro Riparian National Conservation Area: This area protects a critical riparian corridor along the San Pedro River, providing habitat for a wide variety of birds and other wildlife.
- Black Canyon National Recreation Trail: This historic trail follows a portion of the Black Canyon, offering hiking, mountain biking, and scenic views.
Conclusion
The BLM land map of Arizona is a gateway to exploring the state’s vast and diverse landscapes. By understanding the significance of these lands, learning how to access and interpret maps, and adhering to regulations and Leave No Trace principles, you can enjoy unforgettable experiences while helping to protect these valuable resources for future generations. Whether you’re a seasoned adventurer or a first-time visitor, remember that responsible stewardship is essential for preserving the beauty and ecological integrity of BLM land in Arizona. Embrace the opportunity to connect with nature, learn about the history and culture of the region, and contribute to the sustainable management of these public lands.