Belize, a vibrant and biodiverse nation nestled on the eastern coast of Central America, often elicits curiosity about its precise location. While many are familiar with the general region, pinpointing Belize on a world map requires a deeper understanding of its geographical context. This article aims to illuminate the exact whereabouts of Belize, explore its surrounding geographical features, and delve into the significance of its strategic location.
Finding Belize: Latitude, Longitude, and Continental Context
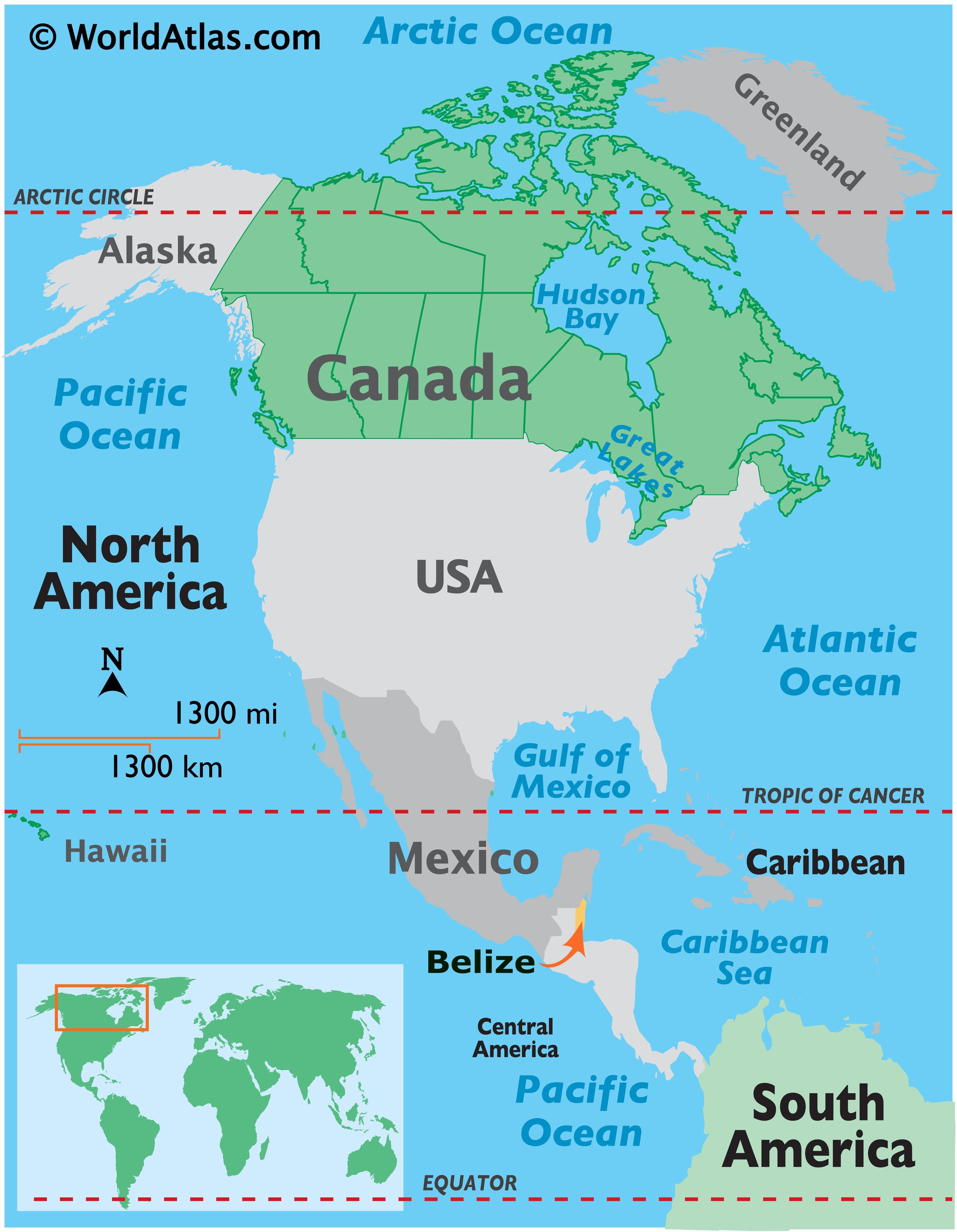
To accurately locate Belize on the world map, we must first understand the basics of geographical coordinates. Latitude measures the distance north or south of the equator, while longitude measures the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian. Belize sits at approximately 17.25 degrees North latitude and 88.75 degrees West longitude.
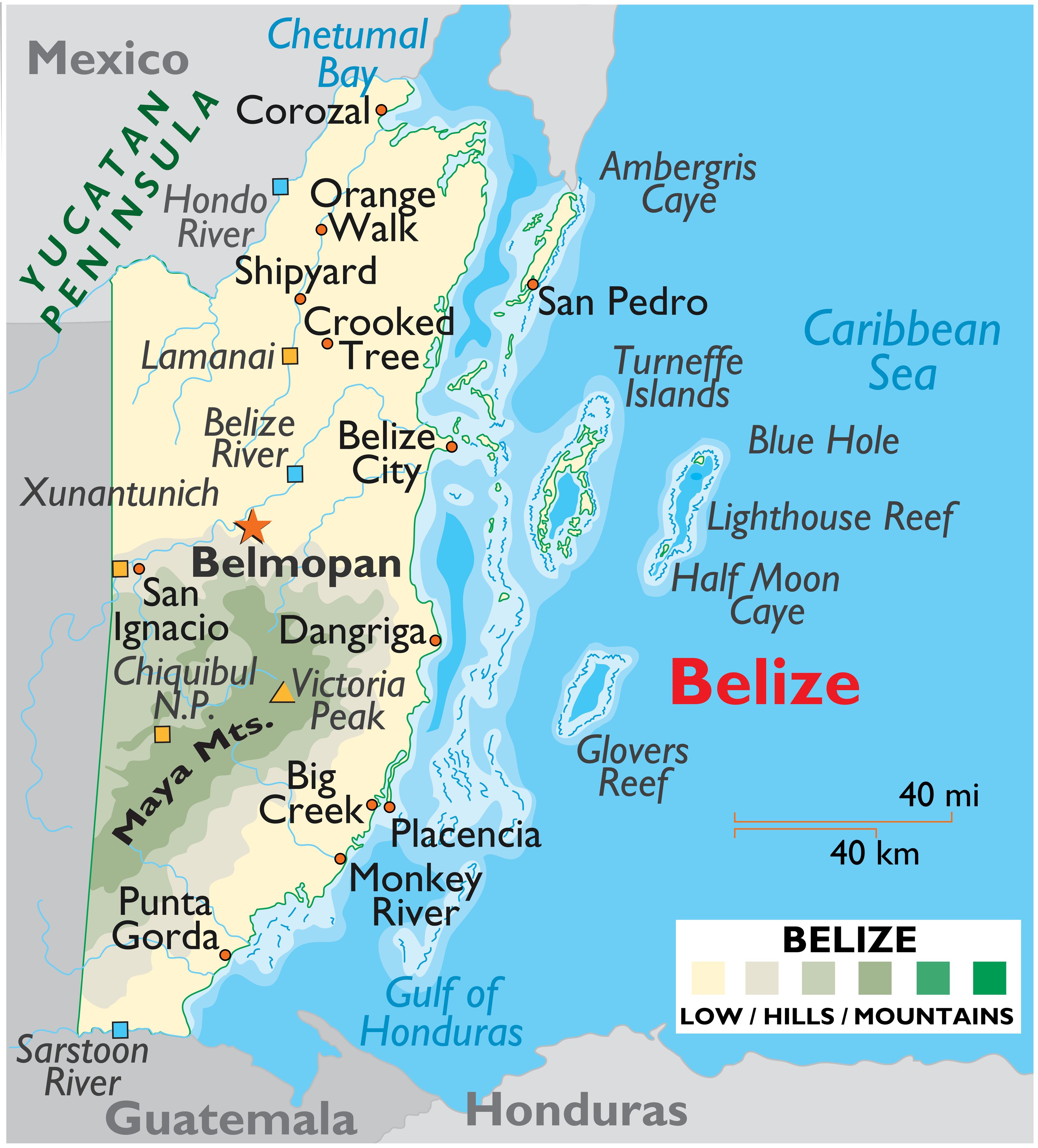
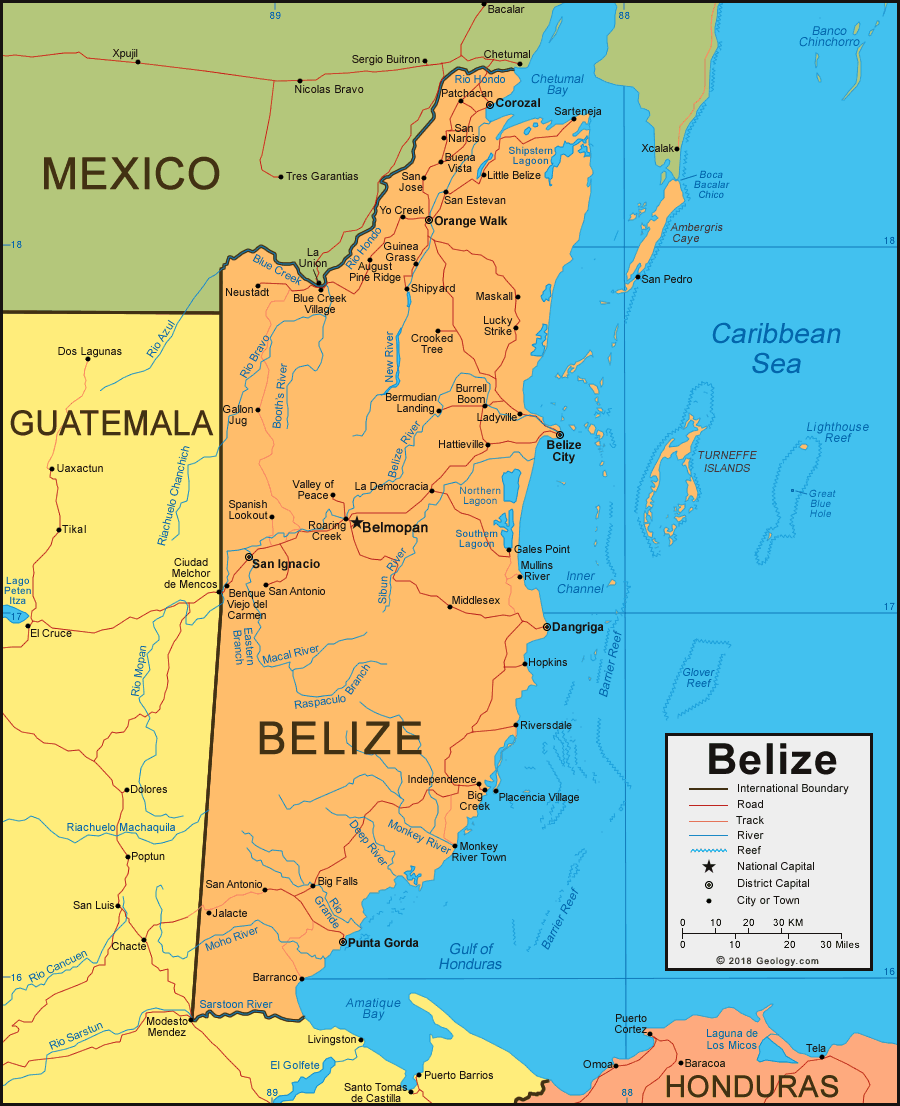
This places Belize squarely within Central America, a land bridge connecting North and South America. Specifically, Belize occupies the southeastern portion of the Yucatan Peninsula, bordered by Mexico to the north and Guatemala to the west and south. To the east, Belize boasts a stunning Caribbean Sea coastline, replete with islands, coral reefs, and turquoise waters.
Therefore, to find Belize on a world map:
- Locate Central America: Begin by identifying the Americas, then zoom in on the narrow isthmus connecting North and South America.
- Find the Yucatan Peninsula: Look for the large peninsula jutting out into the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea.
- Identify the Eastern Coast: Focus on the eastern coast of the Yucatan Peninsula, specifically the area where it meets the Caribbean Sea.
- Spot Belize: You’ll find Belize situated along this coastline, nestled between Mexico and Guatemala.
A Closer Look: Geographical Features and Borders
Beyond its continental context, Belize’s internal geography and borders further define its location and contribute to its unique identity.
-
Northern Border with Mexico: The northern border with Mexico is primarily defined by the Rio Hondo River, a natural boundary that meanders through lush rainforest. This border is relatively flat and low-lying, characterized by dense vegetation and occasional lagoons.
-
Western and Southern Border with Guatemala: The western and southern borders with Guatemala are more complex, marked by a combination of natural features and historical demarcations. The Sarstoon River partially defines the southern border, while other sections are delineated by a series of boundary markers and geographical coordinates. The terrain along this border is more varied, ranging from rolling hills to the rugged Maya Mountains in the south. It is important to note that Guatemala has historically made territorial claims on Belize, a dispute that has shaped the region’s political landscape.
-
Eastern Coastline and the Caribbean Sea: The eastern coastline of Belize is arguably its most defining feature. It stretches approximately 386 kilometers (240 miles) and is home to a stunning array of coastal ecosystems, including mangrove forests, lagoons, and sandy beaches. The most significant feature of this coastline is the Belize Barrier Reef, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and the second-largest barrier reef in the world after Australia’s Great Barrier Reef. This reef, dotted with hundreds of islands known as cayes, extends along the entire length of Belize’s coast and creates a unique maritime environment.
-
Internal Geography: The interior of Belize is characterized by diverse landscapes, ranging from coastal plains to the towering Maya Mountains. The Maya Mountains, located in the south, are the highest point in Belize, contributing to the country’s diverse ecosystems and providing crucial watersheds. The country is also traversed by numerous rivers and streams, contributing to its lush rainforests and fertile agricultural lands.
The Significance of Belize’s Location: History, Culture, and Economy
Belize’s geographical location has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and economy. Its position on the Caribbean coast has made it a strategic trading post for centuries, attracting European powers and influencing its cultural development.
-
Historical Significance: Belize’s location at the crossroads of Central America and the Caribbean has made it a point of contact for various cultures throughout history. The ancient Maya civilization flourished in this region, leaving behind impressive archaeological sites that continue to attract researchers and tourists. In the 17th century, British settlers arrived in Belize, drawn by the abundance of timber resources. Over time, Belize became a British colony, known as British Honduras. Its geographical proximity to other Central American nations, coupled with its unique colonial history, has given Belize a distinct identity within the region. Belize gained independence in 1981, but its historical ties to the United Kingdom continue to influence its legal and political systems.
-
Cultural Diversity: Belize’s geographical location has contributed to its remarkable cultural diversity. The country is a melting pot of ethnicities, including Maya, Mestizo, Creole, Garifuna, and European descendants. This cultural mix is reflected in Belize’s languages, cuisine, music, and traditions. The country’s official language is English, but Spanish, Creole, and various Maya languages are also widely spoken. Belizean cuisine is a delicious blend of Caribbean, Central American, and European influences, featuring dishes like rice and beans, stew chicken, and seafood. The music scene is equally diverse, incorporating elements of reggae, punta rock, and traditional Maya rhythms.
-
Economic Opportunities: Belize’s location provides significant economic opportunities, particularly in tourism and agriculture. The Belize Barrier Reef attracts divers and snorkelers from around the world, generating substantial revenue for the tourism industry. The country’s fertile lands and tropical climate are ideal for agriculture, with key exports including sugar, citrus fruits, and bananas. Belize’s location also facilitates trade with neighboring countries and access to international markets. The development of eco-tourism has become increasingly important, capitalizing on the country’s natural beauty and biodiversity while promoting sustainable practices.
Conclusion: A Strategic Jewel in the Caribbean
In conclusion, Belize’s location on the world map is far more than just a set of coordinates. Its position on the eastern coast of Central America, nestled between Mexico and Guatemala and bordering the Caribbean Sea, has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and economy. From its stunning coastline and the Belize Barrier Reef to its diverse interior landscapes and vibrant cultural mix, Belize offers a unique blend of natural beauty and cultural richness. Understanding its geographical context allows us to appreciate the strategic importance of this "Jewel of the Caribbean" and its role in the broader Central American and Caribbean region. So, the next time you look at a world map, remember to pinpoint Belize, not just as a location, but as a testament to the enduring power of geography to shape a nation’s destiny.