Ohio, with its diverse population and varied economic landscape, boasts a complex and intricate network of school districts. Understanding the structure and organization of these districts is crucial for parents, educators, real estate professionals, and anyone interested in the state’s educational landscape. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Ohio’s school district map, exploring its key features, influencing factors, and practical implications.
Understanding the Basics: Types of School Districts in Ohio
Ohio’s school district system is not a monolithic entity. Instead, it comprises several types of districts, each with its own governance structure, funding mechanisms, and operational characteristics. These include:
- City School Districts: Typically found in larger urban centers, these districts serve the residents of a specific city. They often face unique challenges related to population density, socioeconomic disparities, and diverse student populations. Examples include Cleveland Metropolitan School District, Columbus City Schools, and Cincinnati Public Schools.
- Local School Districts: These districts serve primarily rural or suburban areas. They often encompass multiple townships or smaller municipalities. Due to their geographical spread and potentially smaller student populations, they may face challenges related to transportation, resource allocation, and attracting qualified teachers. Examples include Lakota Local School District, Olentangy Local School District, and Hilliard City School District (despite the "City" in the name, it operates as a local school district).
- Exempted Village School Districts: These districts are typically located in villages that have achieved a specific population threshold. They operate independently from the county educational service center, providing a higher degree of autonomy in curriculum development and resource management. Examples include Bexley City School District and Mariemont City School District.
- Joint Vocational School Districts (JVSDs): These specialized districts focus on providing career and technical education (CTE) programs to students from multiple surrounding school districts. They offer hands-on training in various trades and industries, preparing students for immediate employment or further technical education. Examples include Great Oaks Career Campuses and Polaris Career Center.
- Educational Service Centers (ESCs): While not technically school districts, ESCs play a vital role in supporting local school districts, particularly in rural areas. They provide a range of services, including professional development for teachers, curriculum support, special education services, and administrative assistance.
Mapping the Territory: Visualizing Ohio’s School District Boundaries
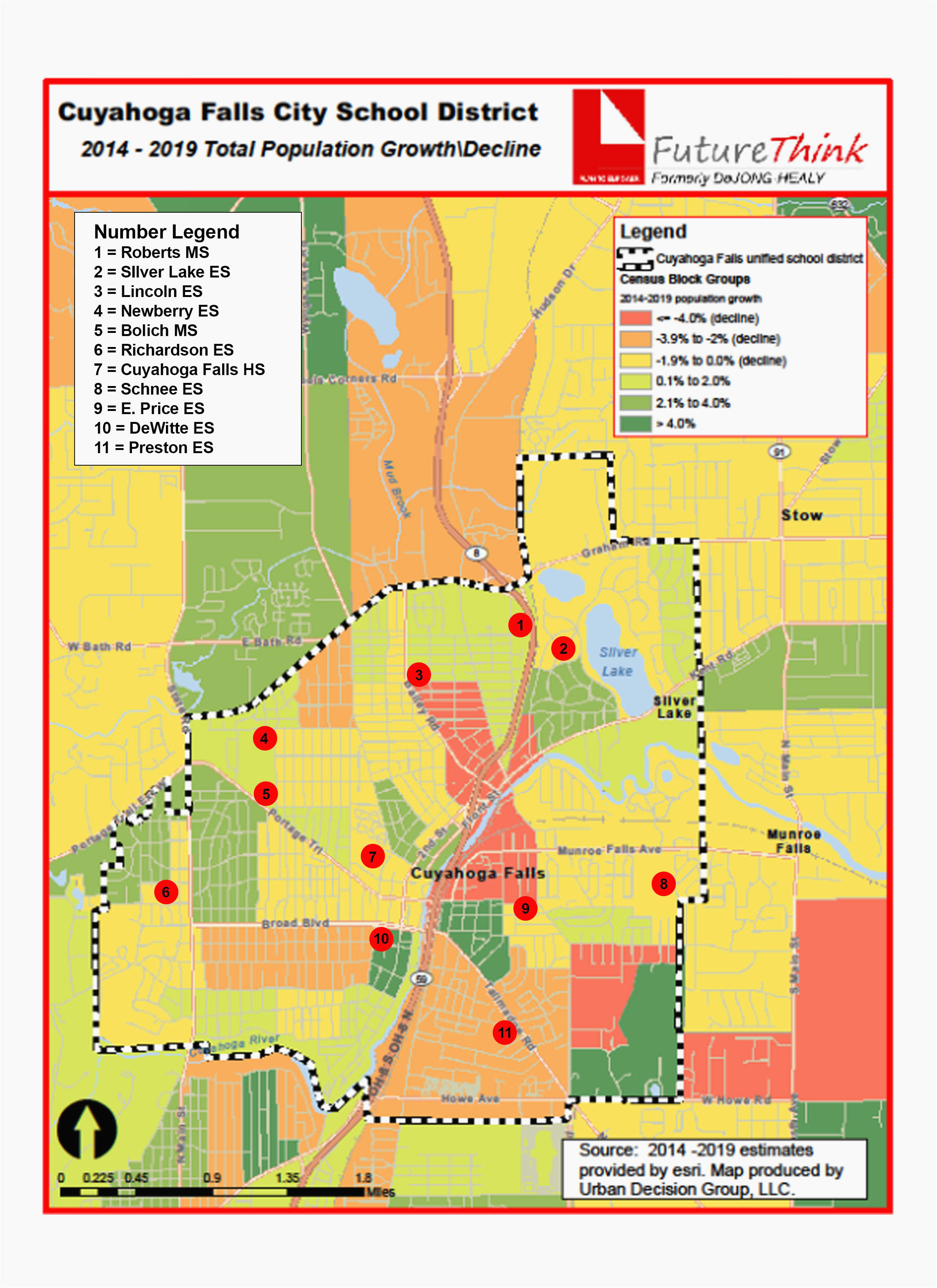
Visualizing Ohio’s school districts requires access to reliable and up-to-date mapping resources. Several organizations and agencies provide interactive maps and data sets that allow users to explore district boundaries, demographics, and performance metrics. These resources are invaluable for making informed decisions about education, housing, and community development.
- Ohio Department of Education (ODE): The ODE website is the primary source for official information on Ohio’s school districts. It provides interactive maps, searchable databases, and detailed reports on district performance, finances, and demographics.
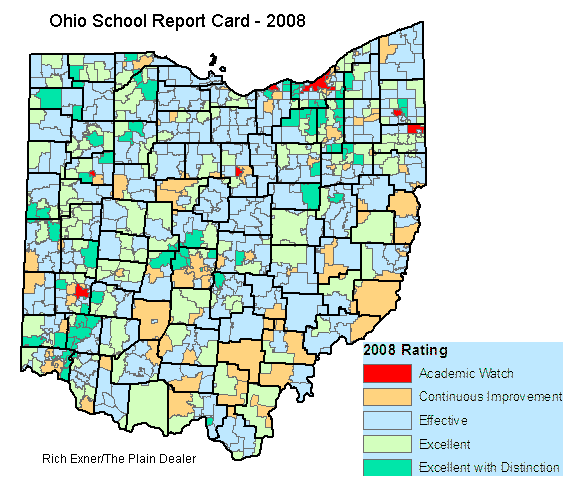
- Ohio School Report Cards: These annual reports, published by the ODE, provide a comprehensive overview of each school district’s performance on key indicators, such as graduation rates, standardized test scores, and student growth. The report cards often include maps showing the district’s boundaries and the location of its schools.
- County Auditor Websites: County auditors often maintain maps and data related to school district boundaries, property values, and tax levies. This information is particularly useful for understanding the financial aspects of school districts and their impact on local property taxes.
- Real Estate Websites: Many real estate websites integrate school district information into their property listings. These platforms allow users to search for homes within specific school districts and view school ratings and performance data.
- Third-Party Data Providers: Companies specializing in education data and analytics often offer subscription-based services that provide detailed maps, demographics, and performance metrics for Ohio’s school districts. These services can be particularly valuable for researchers, educators, and policymakers.
Factors Influencing School District Boundaries
The boundaries of Ohio’s school districts are not arbitrary. They are shaped by a complex interplay of historical, political, and demographic factors. Understanding these factors is essential for interpreting the school district map and its implications.
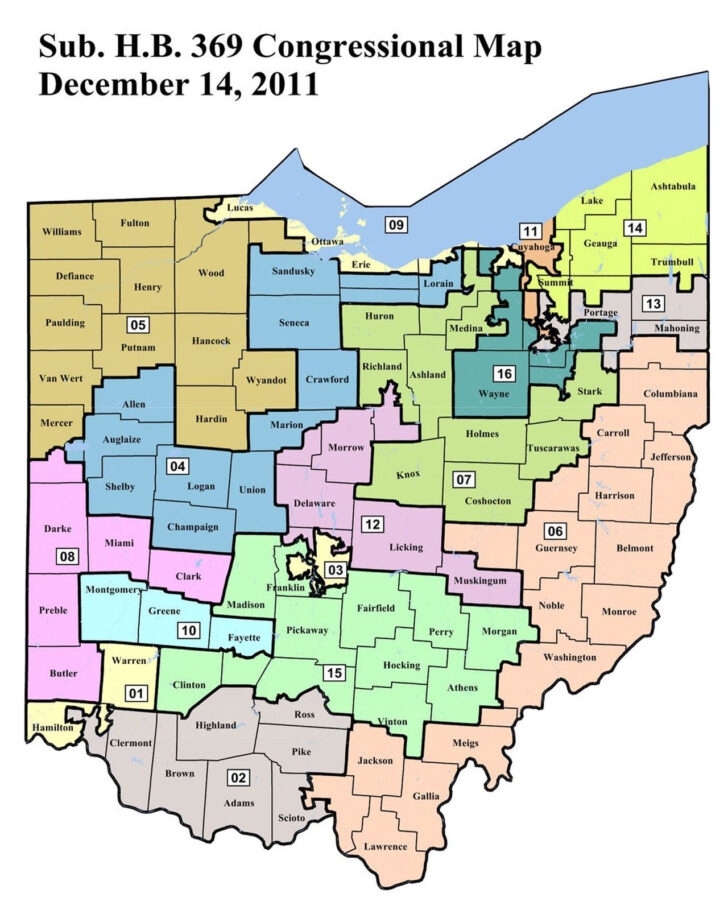
- Historical Development: The initial establishment of school districts in Ohio often followed existing political and geographical boundaries, such as townships and municipalities. Over time, these boundaries have been adjusted due to population growth, urbanization, and school consolidation.
- Population Density and Distribution: School district boundaries are often drawn to ensure a relatively equitable distribution of students and resources. However, disparities in population density can lead to imbalances in student-teacher ratios and per-pupil funding.
- Political Considerations: School district boundaries can be influenced by political factors, such as local government policies, voter preferences, and the lobbying efforts of interest groups. Consolidation efforts, in particular, can be highly contentious due to concerns about local control and community identity.
- Economic Factors: Property values and tax revenues play a significant role in school district funding. Districts with higher property values tend to have more resources to invest in education, while districts with lower property values may struggle to provide adequate funding for their schools.
- Desegregation Efforts: In the past, school district boundaries were sometimes used to perpetuate racial segregation. Court-ordered desegregation efforts have led to the redrawing of district lines in some areas to promote greater racial and socioeconomic integration.
Practical Implications of School District Maps
The Ohio school district map has significant practical implications for individuals, families, and communities. Understanding these implications is crucial for making informed decisions about education, housing, and community involvement.
- School Choice: The school district in which a family resides typically determines the public schools their children are eligible to attend. However, Ohio also offers various school choice options, such as open enrollment, charter schools, and voucher programs, which allow some students to attend schools outside their assigned district.
- Property Values: The quality of local schools is a major factor influencing property values. Homes located in highly rated school districts tend to command higher prices than those in less desirable districts.
- Community Identity: School districts often serve as important centers of community identity and social cohesion. Local schools provide opportunities for residents to connect with their neighbors, participate in community events, and support local businesses.
- Taxation: Property taxes are a primary source of funding for Ohio’s public schools. Residents of different school districts pay varying property tax rates, depending on the district’s funding needs and the value of their properties.
- Educational Equity: The Ohio school district map reflects disparities in wealth and resources across the state. Some districts have significantly more funding and resources than others, leading to inequities in educational opportunities for students.
Challenges and Future Directions
Ohio’s school district system faces several challenges, including funding disparities, declining enrollment in some areas, and the need to adapt to evolving educational needs. Addressing these challenges will require innovative solutions and collaborative efforts from policymakers, educators, and community stakeholders.
- Funding Reform: Ohio’s school funding system has been the subject of ongoing debate and litigation. Efforts to reform the system aim to address funding disparities and ensure that all students have access to a high-quality education, regardless of their zip code.
- Consolidation and Collaboration: As enrollment declines in some areas, school districts are exploring opportunities for consolidation and collaboration to share resources and improve efficiency. These efforts can be controversial, but they may be necessary to ensure the long-term sustainability of public education in Ohio.
- Innovation and Technology: Embracing innovation and technology is crucial for preparing students for the 21st-century workforce. School districts are investing in technology infrastructure, digital learning resources, and innovative teaching methods to enhance student engagement and achievement.
- Community Engagement: Building strong partnerships between schools, families, and communities is essential for fostering student success. Schools are working to engage parents, community organizations, and local businesses in supporting student learning and development.
Conclusion
The Ohio school district map is a complex and dynamic representation of the state’s educational landscape. Understanding its key features, influencing factors, and practical implications is essential for navigating the state’s education system and making informed decisions about education, housing, and community development. By addressing the challenges facing the system and embracing innovation and collaboration, Ohio can ensure that all students have access to a high-quality education and the opportunity to reach their full potential. As Ohio continues to evolve, so too will its school district landscape, requiring ongoing monitoring and adaptation to meet the changing needs of its students and communities. The resources provided by the Ohio Department of Education, county auditors, and other organizations are crucial tools for understanding and navigating this complex and vital aspect of Ohio’s society.