Discovering Cyprus: A Geographical Exploration of the Island Nation
Associated Articles: Discovering Cyprus: A Geographical Exploration of the Island Nation
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Discovering Cyprus: A Geographical Exploration of the Island Nation. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Discovering Cyprus: A Geographical Exploration of the Island Nation

Cyprus, a charming island nation within the jap Mediterranean Sea, holds a novel place on the planet’s geopolitical panorama. Its location, an interesting mix of East and West, has formed its historical past, tradition, and financial system for millennia. Understanding the place Cyprus sits on the map requires exploring not simply its coordinates but in addition its relationship to its neighboring international locations and continents, its geological formation, and its strategic significance.
Geographical Coordinates and Regional Context:
Cyprus is located on the crossroads of three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa. Its geographical coordinates are roughly 35° North latitude and 33° East longitude. This places it south of Turkey, west of Syria and Lebanon, and north of Egypt. The island is separated from the Turkish mainland by a comparatively quick stretch of water, the Cilician Sea, whereas the gap to the Syrian and Lebanese coasts is barely higher. Its proximity to Egypt is extra substantial, with the Mediterranean Sea separating the 2.
This strategic location has been a double-edged sword. It has facilitated commerce and cultural alternate all through historical past, connecting the island to main civilizations and empires. Concurrently, it has made Cyprus a extremely sought-after territory, resulting in quite a few conquests and intervals of overseas rule. Its central place within the jap Mediterranean made it an important node in historic commerce routes, linking the East and West, and this continues to be a big think about its fashionable financial system and geopolitical standing.
Island Morphology and Geology:
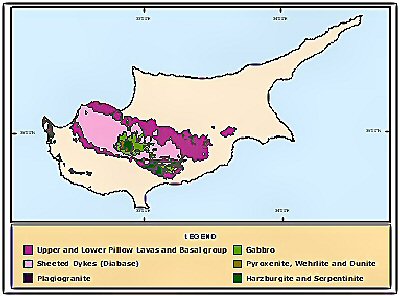
Cyprus is the third-largest island within the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily and Sardinia. Its form is roughly rectangular, with a most size of roughly 240 kilometers and a most width of round 100 kilometers. The island is mountainous, with two foremost mountain ranges dominating its panorama: the Troodos Mountains within the southwest and the Kyrenia Mountains within the north. These ranges are separated by a central plain, the Mesaoria Plain, which is the island’s most fertile agricultural area.
Geologically, Cyprus is a part of the African Plate, however its location close to the boundary with the Eurasian Plate has resulted in important tectonic exercise all through its historical past. The Troodos Mountains are of ophiolite origin, that means they’re fashioned from oceanic crust that has been uplifted onto the continental crust. This geological formation is comparatively uncommon and makes Cyprus an interesting topic for geological research. The island’s numerous geology contributes to its assorted landscapes, from rugged mountains and dense forests to sandy seashores and fertile plains. This variety is mirrored in its wealthy biodiversity, with a variety of wildlife, a few of that are endemic to the island.
Neighboring International locations and Maritime Boundaries:
Cyprus’s rapid neighbors are Turkey to the north, Syria and Lebanon to the east, and Egypt to the south. Its maritime boundaries are outlined by worldwide agreements, and these boundaries are essential for managing its Unique Financial Zone (EEZ) and its offshore sources, significantly pure gasoline. The delimitation of maritime boundaries within the jap Mediterranean has been a topic of ongoing negotiations and disputes, significantly between Cyprus and Turkey. These disputes spotlight the complexities of managing sources and sovereignty in a area with competing claims and pursuits.
The island’s relationship with Turkey is especially advanced and traditionally fraught. Turkey’s army presence within the northern a part of the island, following the 1974 Turkish invasion, stays a significant level of competition and a big issue within the ongoing Cyprus drawback. The division of the island right into a Greek Cypriot-administered south and a Turkish Cypriot-administered north has profound implications for its geography and its geopolitical standing.
Political Geography and the Cyprus Drawback:
The political geography of Cyprus is deeply intertwined with its historical past and its location. The island’s division into two self-governing entities, the Republic of Cyprus (acknowledged internationally besides by Turkey) and the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (acknowledged solely by Turkey), is a significant impediment to its full integration into the worldwide neighborhood. The continued Cyprus drawback, a fancy subject involving territorial disputes, refugee points, and differing nationwide identities, considerably impacts the island’s political geography and its potential to totally make the most of its strategic location for financial and social improvement.
Efforts in direction of reunification have been ongoing for many years, mediated by the United Nations. Nevertheless, important variations stay between the 2 sides, hindering progress in direction of a long-lasting and mutually acceptable resolution. The political division of the island impacts its infrastructure, its financial system, and its social cloth, creating challenges for its inhabitants and limiting its potential for development and improvement.
Strategic Significance and Geopolitical Significance:
Cyprus’s strategic location on the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa continues to carry important geopolitical significance. Its proximity to main power pipelines, its potential for offshore power exploration, and its function as a transit level for transport and air journey make it an important participant in regional dynamics. The island’s strategic worth has attracted the eye of main powers all through historical past, and its geopolitical significance stays outstanding within the twenty first century.
The invention of serious offshore pure gasoline reserves has additional enhanced Cyprus’s strategic significance. The exploration and exploitation of those reserves have generated important curiosity from worldwide power firms and have additionally contributed to the continuing disputes with Turkey over maritime boundaries. The administration of those sources and the balancing of financial pursuits with geopolitical concerns are essential challenges for Cyprus.
Conclusion:
Finding Cyprus on a map entails greater than merely figuring out its coordinates. It requires understanding its advanced relationship with its neighbors, its distinctive geological formation, and the lasting impression of its historic and political evolution. The island’s strategic location, its wealthy historical past, and its ongoing challenges make it an interesting case research in geography, politics, and worldwide relations. Its place on the crossroads of continents, its numerous landscapes, and its unresolved political standing proceed to form its future and its place on the planet. Understanding Cyprus’s geographical context is important to greedy its current and its potential for the longer term.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered worthwhile insights into Discovering Cyprus: A Geographical Exploration of the Island Nation. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!