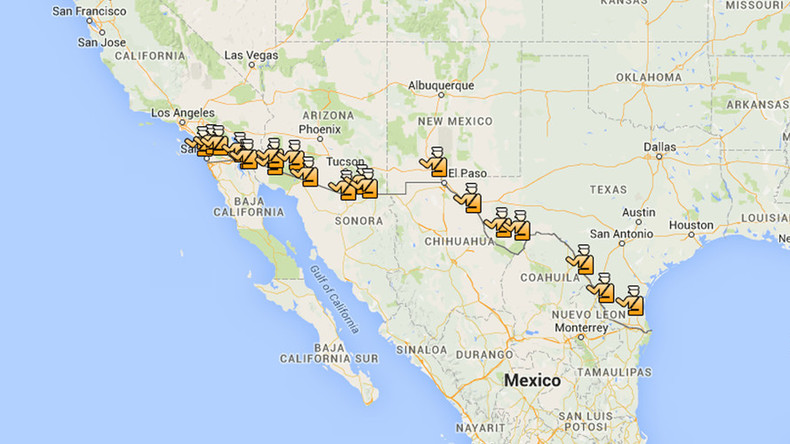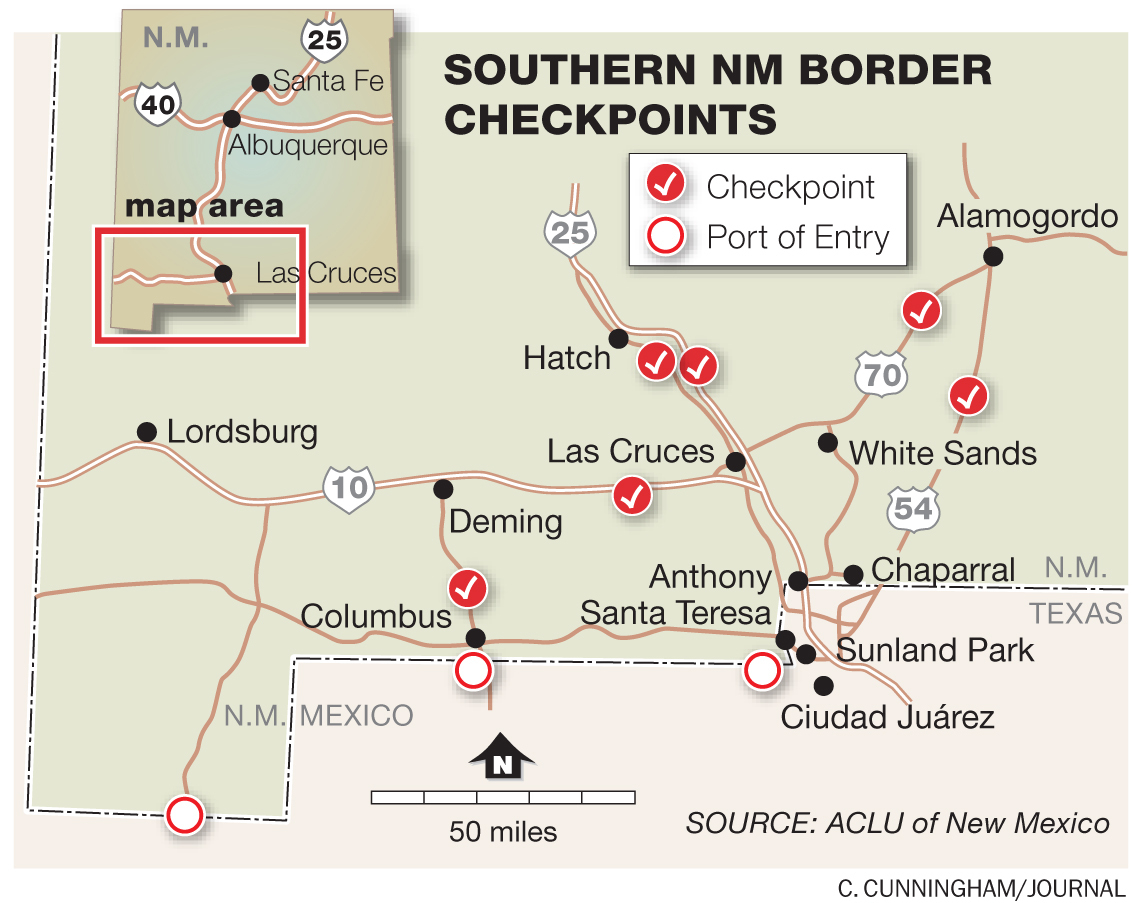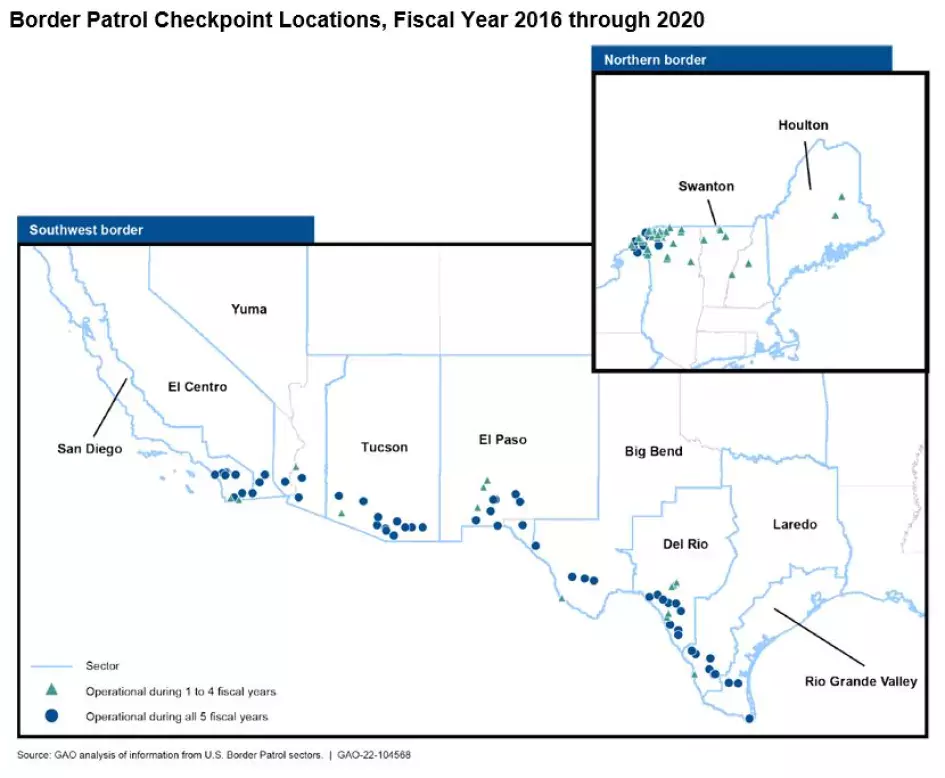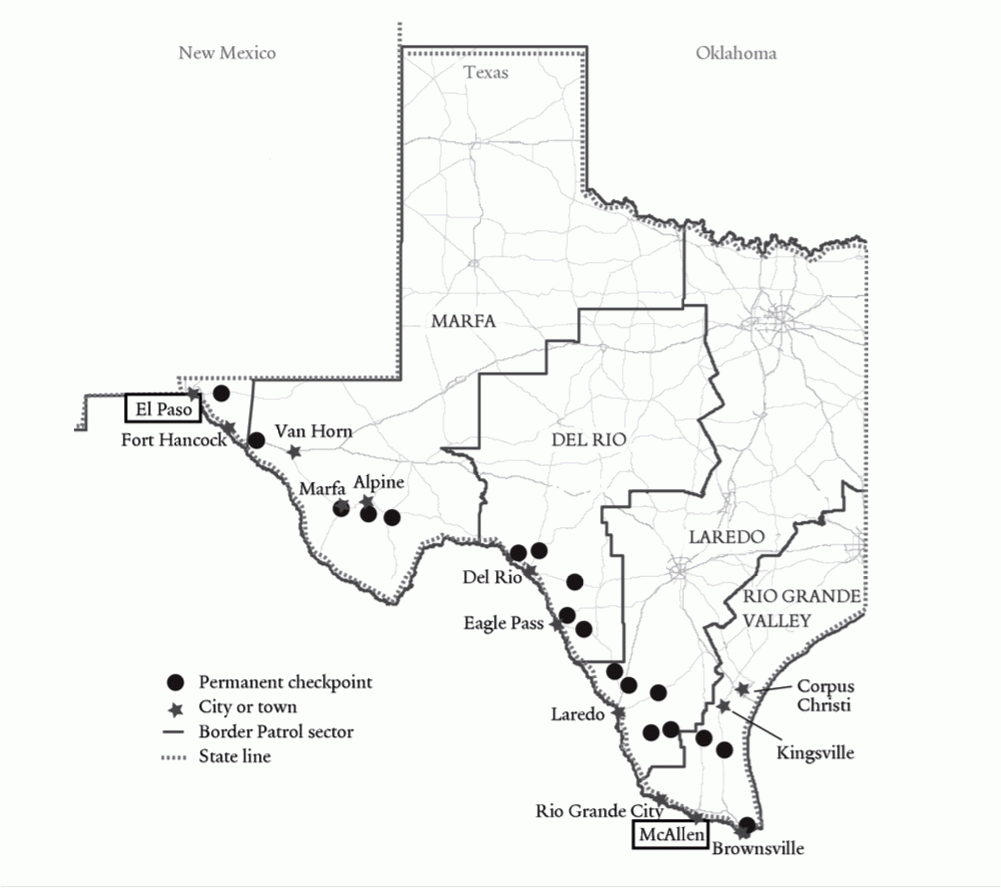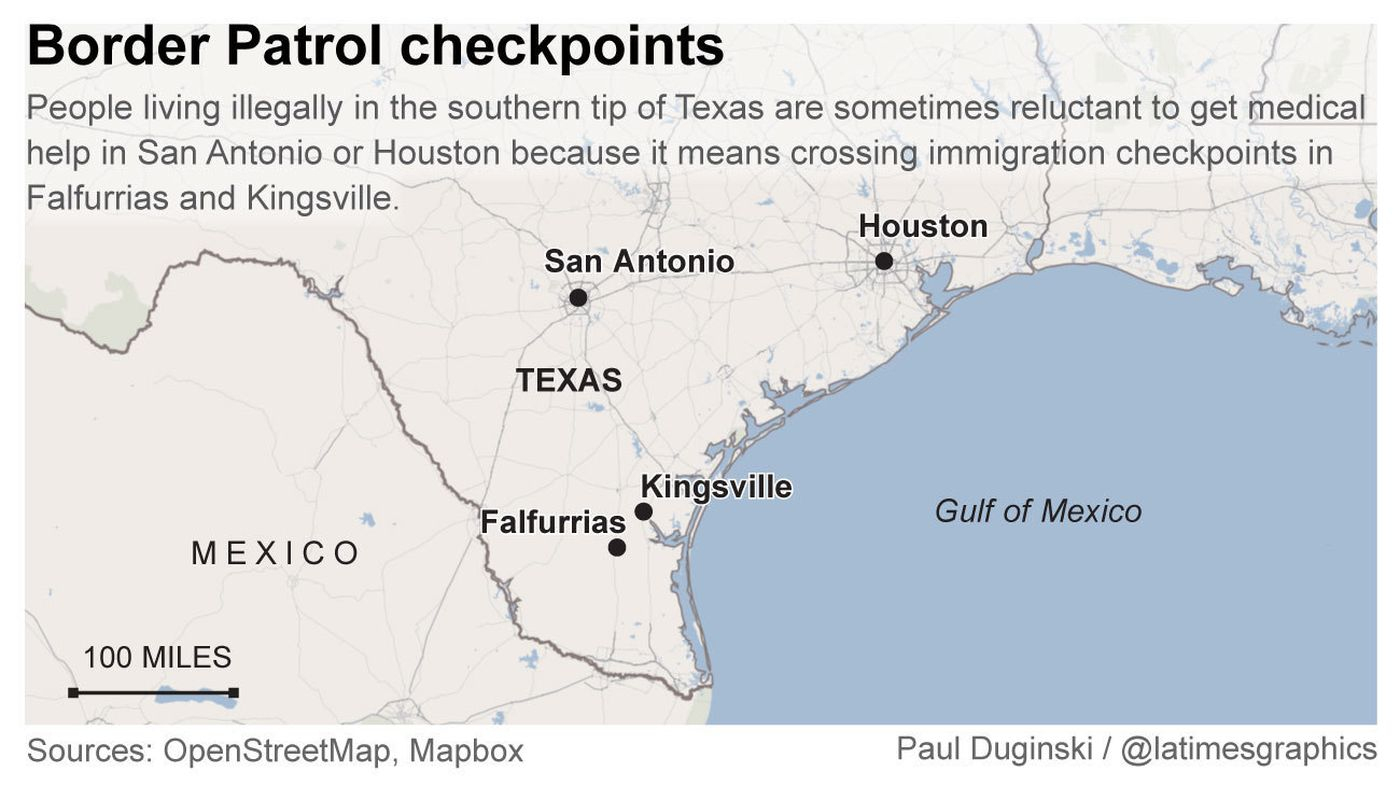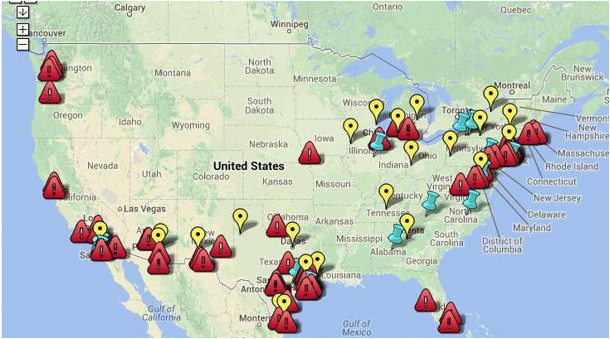
The immigration checkpoint map, a seemingly innocuous collection of dots and lines overlaid on a geographical representation of the United States, is a powerful and controversial symbol. It represents a complex web of enforcement strategies aimed at controlling the flow of people and goods across the nation’s borders. While proponents argue these checkpoints are crucial for national security and border control, critics contend they are ineffective, discriminatory, and infringe upon the rights of citizens and legal residents. Understanding the location, purpose, and impact of these checkpoints is crucial for engaging in informed discussions about immigration policy and its effects on American society.
This article delves into the intricacies of the immigration checkpoint map, exploring its historical context, the rationale behind checkpoint placement, the legal framework governing their operation, and the ongoing debates surrounding their effectiveness and ethical implications.
A Brief History of Immigration Checkpoints:
The history of immigration checkpoints in the United States is intertwined with the evolution of border control strategies. While the concept of border patrol dates back to the early 20th century, the formal establishment of permanent checkpoints emerged in the 1950s, largely in response to concerns about undocumented immigration from Mexico.
Initially, these checkpoints were primarily located along the immediate border region, focusing on preventing unauthorized entry into the country. However, over time, the enforcement strategy shifted, pushing the boundaries of immigration control further inland. This shift led to the establishment of "interior checkpoints," located dozens or even hundreds of miles away from the actual border.
The justification for this expansion rested on the argument that these interior checkpoints provided a "second line of defense" against undocumented immigrants who had already evaded border patrol agents. This strategy was particularly prominent in the Southwestern United States, with checkpoints strategically positioned along major highways leading away from the border.
The events of 9/11 further intensified the focus on border security and led to an increase in the number and operational intensity of immigration checkpoints. The perceived need to prevent terrorist entry into the country provided additional justification for expanding border control measures, including the use of checkpoints.
Understanding the Checkpoint Map: Location and Purpose:
The immigration checkpoint map reveals a network of permanent and temporary checkpoints operated by U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP). These checkpoints are strategically positioned along major highways and secondary roads, particularly in states like Arizona, California, New Mexico, and Texas.
-
Permanent Checkpoints: These are fixed locations, often equipped with sophisticated technology such as license plate readers, X-ray scanners, and canine units. They are typically staffed by armed Border Patrol agents who have the authority to stop and question individuals passing through. The primary purpose of permanent checkpoints is to detect and apprehend individuals who have entered the country illegally, as well as to interdict contraband such as drugs and weapons.
-
Temporary Checkpoints (Tactical Checkpoints): These are mobile checkpoints that can be set up in various locations for short periods. Their purpose is to provide increased surveillance and enforcement in specific areas, often in response to intelligence or perceived threats. The use of temporary checkpoints allows CBP to adapt its enforcement strategy to changing circumstances and target specific routes or areas.
The placement of checkpoints is often based on factors such as traffic patterns, historical data on illegal immigration, and proximity to known smuggling routes. CBP also considers the availability of infrastructure and the feasibility of establishing a secure and efficient checkpoint operation.
The Legal Framework Governing Checkpoint Operations:
The operation of immigration checkpoints is governed by a complex legal framework that attempts to balance the government’s interest in border security with the individual’s right to privacy and freedom from unreasonable search and seizure, as guaranteed by the Fourth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution.
The Supreme Court has addressed the legality of immigration checkpoints in several landmark cases. In United States v. Martinez-Fuerte (1976), the Court upheld the constitutionality of permanent immigration checkpoints, ruling that the government’s interest in preventing the entry of undocumented immigrants outweighed the minimal intrusion on individual liberty.
However, the Court emphasized that checkpoint stops must be brief and limited in scope. Agents can ask about citizenship and request identification, but they cannot conduct a search of a vehicle unless they have probable cause or reasonable suspicion of a crime.
-
Probable Cause: This refers to a reasonable belief, based on specific and articulable facts, that a crime has been committed or is being committed.
-
Reasonable Suspicion: This is a lower standard than probable cause, but it still requires more than a mere hunch or suspicion. Agents must have a reasonable belief, based on specific and articulable facts, that a person is involved in criminal activity.
The legal framework surrounding immigration checkpoints remains a subject of ongoing debate and litigation. Civil rights organizations and advocacy groups frequently challenge the legality of checkpoint operations, arguing that they are often conducted in a discriminatory manner and violate the constitutional rights of individuals.
The Debate: Effectiveness vs. Ethical Implications:
The effectiveness of immigration checkpoints is a hotly debated topic. Proponents argue that checkpoints are an essential tool for border security, helping to deter illegal immigration and interdict contraband. They point to statistics on apprehensions and seizures at checkpoints as evidence of their effectiveness.
However, critics argue that checkpoints are ineffective and inefficient, diverting resources from more effective border control strategies. They argue that checkpoints primarily apprehend low-level offenders and have little impact on the overall flow of undocumented immigrants.
Furthermore, critics raise serious concerns about the ethical implications of immigration checkpoints. They argue that checkpoints are often operated in a discriminatory manner, disproportionately targeting individuals based on their race, ethnicity, or appearance. Studies have shown that Hispanic individuals are more likely to be stopped and questioned at checkpoints, even when they are U.S. citizens or legal residents.
The practice of racial profiling at checkpoints raises serious questions about equal protection under the law and the potential for abuse of power. Critics also argue that checkpoints create a climate of fear and intimidation, particularly in border communities, where residents may feel constantly under surveillance.
The Impact on Border Communities:
The presence of immigration checkpoints has a significant impact on border communities, both economically and socially. While some businesses may benefit from the increased traffic and spending associated with checkpoint operations, others may suffer due to the perception that border communities are dangerous or unwelcoming.
Checkpoints can also create divisions within border communities, with some residents supporting their presence as a means of enhancing security and others opposing them as a symbol of government overreach and discrimination. The constant presence of law enforcement can create a sense of unease and distrust, particularly among minority communities.
Furthermore, the operation of immigration checkpoints can strain local resources, such as healthcare and social services, as apprehended individuals are processed and detained. This can place a burden on local communities and divert resources from other essential services.
Moving Forward: Finding a Balance:
The debate over immigration checkpoints reflects a broader struggle to balance the government’s interest in border security with the individual’s right to privacy and freedom from discrimination. Finding a solution that addresses both concerns is a complex and challenging task.
Some potential solutions include:
-
Increased Oversight and Accountability: Implementing stricter oversight mechanisms to ensure that checkpoint operations are conducted in a fair and non-discriminatory manner. This could involve body cameras for agents, increased data collection on checkpoint stops, and independent audits of checkpoint operations.
-
Focusing on Smarter Border Security Strategies: Investing in technology and intelligence gathering to improve border security without relying on intrusive and discriminatory tactics. This could include the use of drones, sensors, and other surveillance technologies to detect and apprehend individuals attempting to cross the border illegally.
-
Addressing the Root Causes of Illegal Immigration: Addressing the underlying economic and social factors that drive illegal immigration, such as poverty, lack of opportunity, and political instability in other countries. This could involve investing in economic development, promoting good governance, and addressing human rights abuses in countries that are major sources of undocumented immigrants.
Ultimately, finding a sustainable solution to the challenges posed by immigration checkpoints will require a comprehensive approach that addresses both the symptoms and the underlying causes of illegal immigration. It will also require a commitment to protecting the rights and dignity of all individuals, regardless of their immigration status. The immigration checkpoint map serves as a stark reminder of the complexities and challenges involved in managing borders and upholding the values of a just and equitable society. Ignoring the issues it highlights will only perpetuate the divisions and inequalities that undermine the fabric of American society.