In an era defined by increasingly unpredictable weather patterns, understanding and tracking these phenomena is more crucial than ever. Enter the "Elsa Tracking Map," a powerful tool used by meteorologists, researchers, and even the general public to monitor tropical cyclones, particularly those in the Atlantic basin. While named after the 2021 Tropical Storm Elsa, the term has become a general descriptor for detailed maps illustrating the path, intensity, and potential impact of any tropical system. This article will delve into the intricacies of the Elsa Tracking Map, exploring its components, how it’s interpreted, its limitations, and its significance in mitigating the risks associated with these powerful storms.
What is an Elsa Tracking Map?
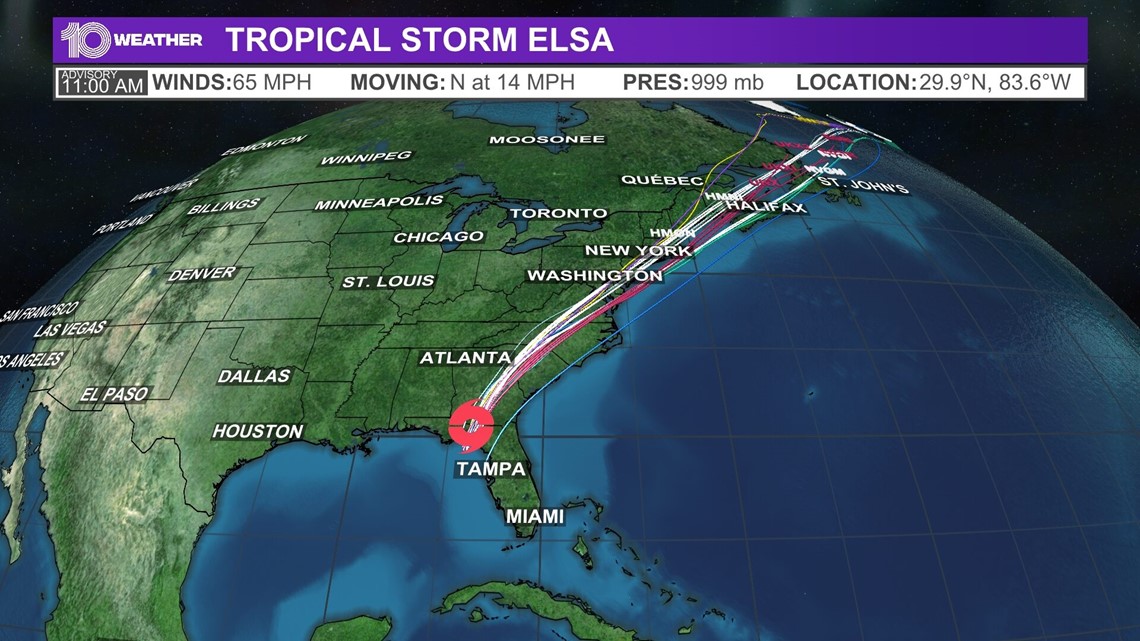
The Elsa Tracking Map is a visual representation of a tropical cyclone’s projected path and intensity over time. It’s not simply a line drawn on a map; it’s a sophisticated combination of meteorological data, forecasting models, and expert analysis. It aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the storm’s current location, predicted movement, potential strength, and the areas most likely to be affected.
Think of it as a roadmap for a dangerous weather system. It helps individuals, communities, and authorities prepare for potential impacts, from heavy rainfall and flooding to damaging winds and storm surges. The map is typically produced by national meteorological agencies like the National Hurricane Center (NHC) in the United States, and updated regularly as new data becomes available.
Components of the Elsa Tracking Map:
A typical Elsa Tracking Map incorporates several key elements that contribute to its overall information value:
-
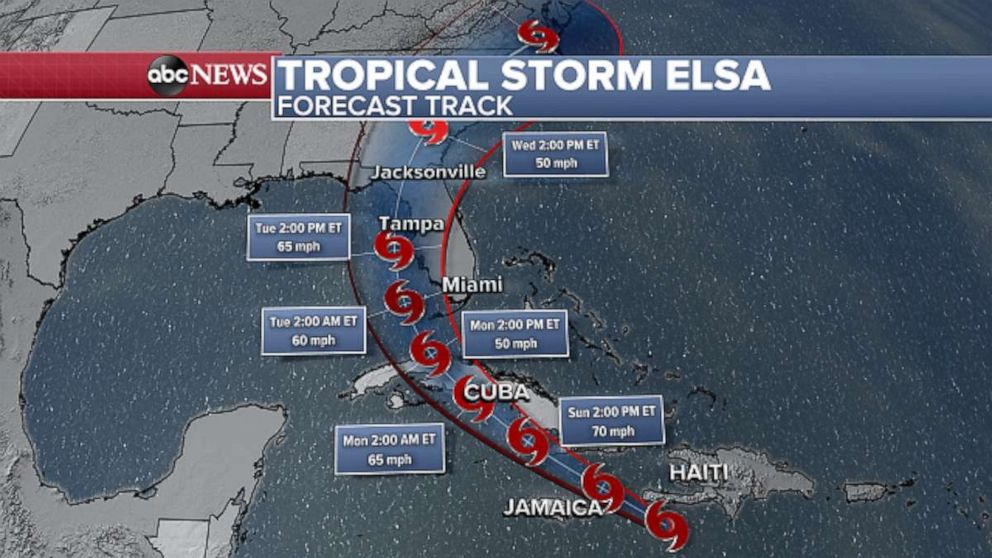
The Track Line (Cone of Uncertainty): This is perhaps the most prominent feature of the map. It’s a shaded area, often resembling a cone or fan, that represents the likely path of the storm’s center. This cone is not a guarantee of where the storm will go, but rather a statistical representation of where the storm is likely to go, based on historical data and forecast model performance. The width of the cone reflects the historical average errors in track forecasting over a 5-day period. A wider cone indicates greater uncertainty in the forecast.
-
The Best Track: A solid or dashed line, usually located within the cone of uncertainty, represents the observed or estimated past track of the storm. This line is derived from historical data and provides context for understanding the storm’s current trajectory.
-
Forecast Points (Symbols): Along the track line, you’ll find symbols (often circles, triangles, or squares) representing the predicted location of the storm’s center at specific time intervals (e.g., every 12 or 24 hours). These symbols are crucial for understanding the storm’s projected speed and direction of movement. Different symbols can also denote the forecast intensity of the storm at each point.
-
Intensity Forecast: The map often includes information about the projected intensity of the storm. This might be displayed through color-coded symbols, numerical wind speed values associated with the forecast points, or a separate graph showing the predicted maximum sustained winds over time. The intensity forecast is crucial for determining the potential severity of the storm’s impact.
-
Tropical Cyclone Watches and Warnings: These are geographical areas that are under threat from the storm’s effects. A "watch" indicates that tropical storm or hurricane conditions are possible within the specified area, typically within 48 hours. A "warning" indicates that tropical storm or hurricane conditions are expected within the specified area, typically within 36 hours. Watches and warnings are critical for prompting timely evacuations and preparations.
-
Isobars (Optional): Some advanced tracking maps may include isobars, which are lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. These lines provide information about the storm’s circulation pattern and can help to visualize the strength and extent of the pressure gradient.
-
Rainfall Forecasts (Optional): Increasingly, tracking maps are incorporating rainfall forecasts to indicate areas that are likely to experience significant rainfall and potential flooding. These forecasts can be crucial for planning flood mitigation strategies.
Interpreting the Elsa Tracking Map:
Successfully interpreting an Elsa Tracking Map requires a basic understanding of its components and their implications. Here are some key points to consider:
-
Focus on the Cone of Uncertainty: The most important aspect is to remember that the track line represents the likely path, not the definitive path. Any location within the cone of uncertainty is potentially at risk. Therefore, preparations should be made based on the possibility of impact, even if your location is on the edge of the cone.
-
Understand the Intensity Forecast: The intensity forecast, along with the track, is crucial for assessing the potential severity of the storm’s impact. A strong hurricane making landfall poses a significantly greater threat than a weak tropical storm.
-
Pay Attention to Watches and Warnings: Watches and warnings are issued when a specific area is under imminent threat. Heed the advice of local authorities and take necessary precautions if you are in a watch or warning area.
-
Consider the Storm’s Size: The Elsa Tracking Map typically focuses on the storm’s center, but the impacts can extend far beyond that point. The size and shape of the storm can significantly influence the area affected by strong winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surge. Consult additional resources, such as radar imagery and wind field forecasts, to get a better understanding of the storm’s overall size and impact area.
-
Stay Updated: Weather forecasts are constantly evolving as new data becomes available. It’s crucial to stay updated on the latest Elsa Tracking Map and related advisories from reputable sources like the NHC and your local weather service.
Limitations of the Elsa Tracking Map:
While the Elsa Tracking Map is a valuable tool, it’s essential to acknowledge its limitations:
-
Forecast Uncertainty: Tropical cyclone forecasting is inherently complex. Numerous factors influence a storm’s track and intensity, and even the most sophisticated models are subject to errors. The cone of uncertainty reflects this inherent uncertainty.
-
Impact Beyond the Cone: The Elsa Tracking Map focuses primarily on the storm’s center, but significant impacts can occur outside the cone of uncertainty. For example, heavy rainfall and flooding can extend far beyond the predicted track.
-
Storm Surge: While some maps now include storm surge potential, the prediction of storm surge is a complex process influenced by factors such as the coastline’s shape, the angle of approach of the storm, and the tide level. Understanding local storm surge vulnerabilities is crucial.
-
Data Availability: The accuracy of the Elsa Tracking Map depends on the availability and quality of meteorological data. Data gaps or inaccuracies can lead to forecast errors.
-
Communication Challenges: Effectively communicating the complexities of the Elsa Tracking Map to the public can be challenging. Misinterpretations can lead to complacency or panic.
The Significance of the Elsa Tracking Map:
Despite its limitations, the Elsa Tracking Map plays a vital role in mitigating the risks associated with tropical cyclones. Its significance lies in:
-
Early Warning System: Providing timely and accurate information about potential threats allows individuals, communities, and authorities to prepare for impending impacts.
-
Evacuation Planning: The Elsa Tracking Map helps to identify areas that are at risk and to plan for evacuations in a timely and orderly manner.
-
Resource Allocation: Authorities can use the map to allocate resources effectively, such as deploying emergency personnel and supplies to areas that are most likely to be affected.
-
Infrastructure Protection: Businesses and government agencies can use the map to take steps to protect critical infrastructure, such as power plants, hospitals, and transportation systems.
-
Public Awareness: The Elsa Tracking Map raises public awareness about the dangers of tropical cyclones and encourages people to take necessary precautions.
The Future of Tropical Cyclone Tracking:
The Elsa Tracking Map is a constantly evolving tool. Ongoing research and technological advancements are leading to improvements in forecasting accuracy and the presentation of information. Some key areas of development include:
-
Improved Forecasting Models: Scientists are continually working to develop more sophisticated forecasting models that can better predict the track and intensity of tropical cyclones. This includes incorporating data from new sources, such as satellites and ocean buoys, and improving the algorithms that drive the models.
-
Ensemble Forecasting: Ensemble forecasting involves running multiple simulations of a weather model with slightly different initial conditions. This allows forecasters to assess the range of possible outcomes and to quantify the uncertainty in the forecast.
-
High-Resolution Modeling: High-resolution models can capture more detail about the storm’s structure and the surrounding environment, leading to more accurate forecasts.
-
Enhanced Visualization: Developers are working to create more user-friendly and informative visualizations of tropical cyclone forecasts. This includes incorporating interactive maps, 3D displays, and augmented reality applications.
-
AI and Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being used to analyze vast amounts of weather data and to identify patterns that can improve forecasting accuracy.
Conclusion:
The Elsa Tracking Map, though named after a specific storm, represents a crucial tool for understanding and responding to the threat of tropical cyclones. While it’s essential to understand its limitations, its value in providing early warnings, facilitating evacuation planning, and promoting public awareness cannot be overstated. As technology continues to advance, the Elsa Tracking Map will undoubtedly become even more sophisticated and accurate, further contributing to our ability to mitigate the risks associated with these powerful storms and protect vulnerable communities. By understanding the map, staying informed, and heeding the advice of local authorities, individuals can play a vital role in minimizing the impact of tropical cyclones and ensuring their safety.