Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a nation that often flickers in the news headlines, sometimes for its breathtaking natural beauty, other times for its complex political and economic realities. But before diving into the intricacies of its history and current affairs, it’s crucial to ground ourselves in the fundamental: Where exactly is Venezuela on the world map? Understanding its geographical location is paramount to comprehending its climate, resources, its historical connections, and its geopolitical significance.
South America: A Continental Context
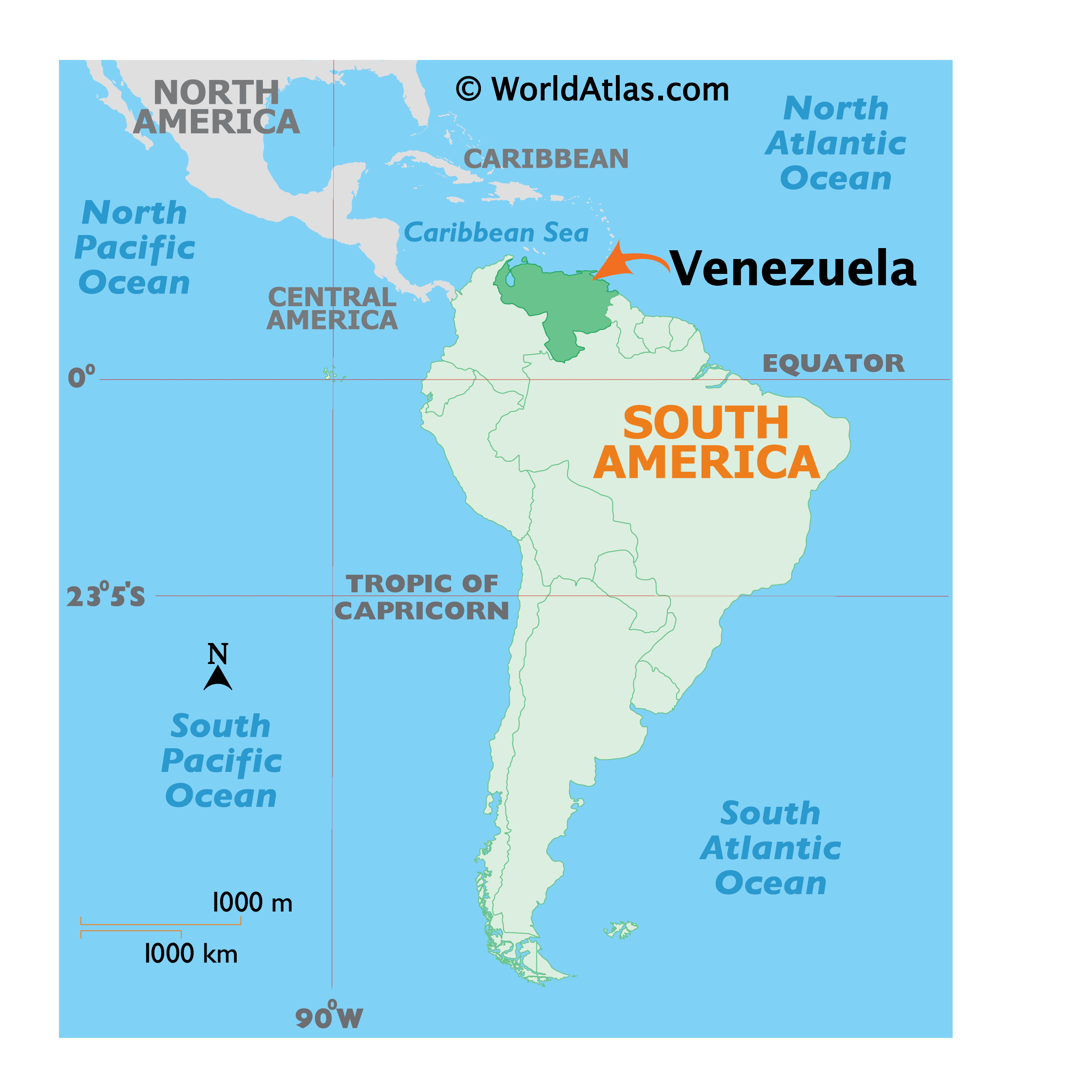
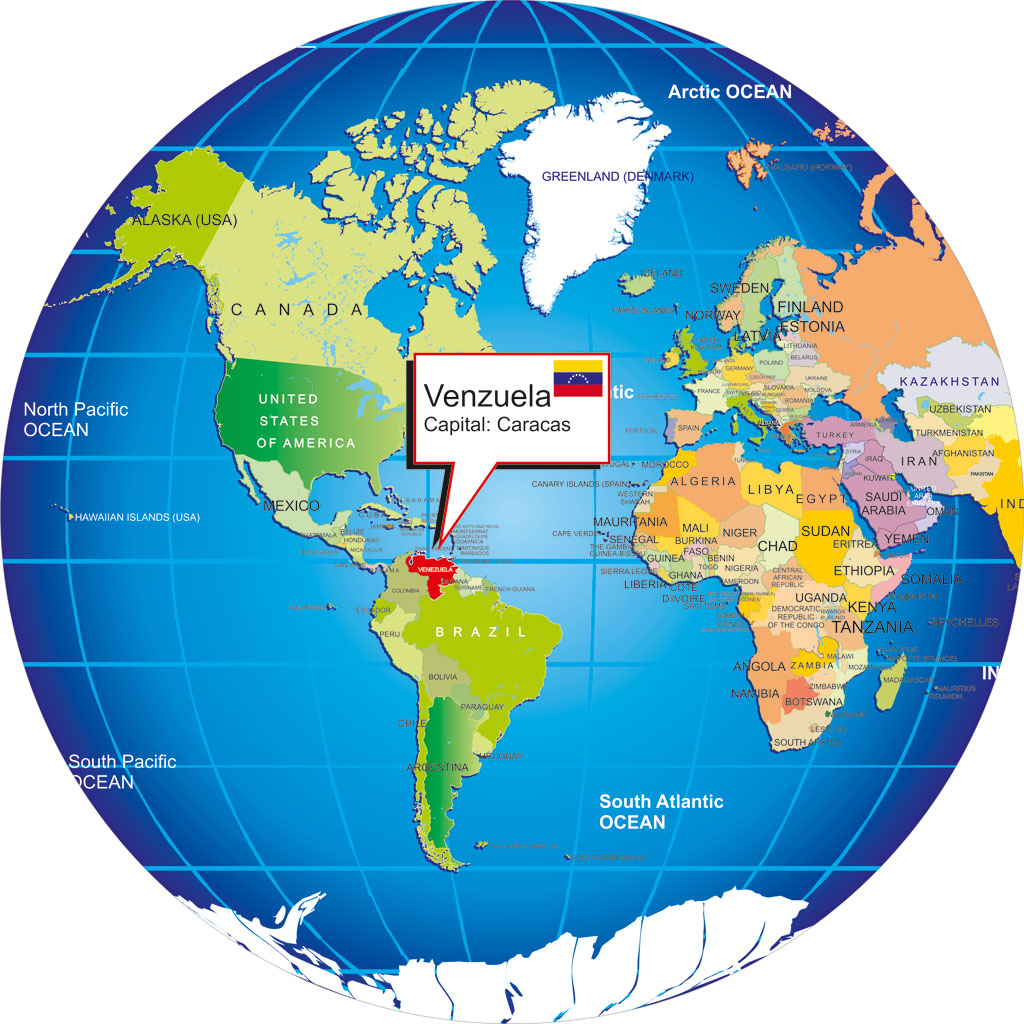
To pinpoint Venezuela, we must first zoom in on the continent of South America. This landmass, shaped somewhat like an inverted triangle, stretches from the Caribbean Sea in the north to the icy waters of the Drake Passage in the south. Venezuela sits prominently on the northern coast of this vibrant continent, facing the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.
Imagine South America as a face. Venezuela would be located towards the upper right cheek, nestled comfortably near the Caribbean coast. It’s a strategic location, granting the nation access to vital trade routes and proximity to key economic players in the region and beyond.
Cardinal Directions and Geographic Coordinates: Getting Specific
To be even more precise, we can use cardinal directions and geographic coordinates. Venezuela lies primarily north of the Equator, placing it in the Northern Hemisphere. It’s also located west of the Prime Meridian, firmly within the Western Hemisphere.
Geographic coordinates provide the most accurate way to locate any point on Earth. Venezuela’s approximate coordinates are:
- Latitude: Between 0° 38′ N and 12° 11′ N (meaning it stretches slightly north of the Equator)
- Longitude: Between 59° 47′ W and 73° 25′ W (situating it in the western part of the continent)
These coordinates place Venezuela in a region characterized by tropical and subtropical climates, influenced by its proximity to the Equator and the Caribbean Sea.
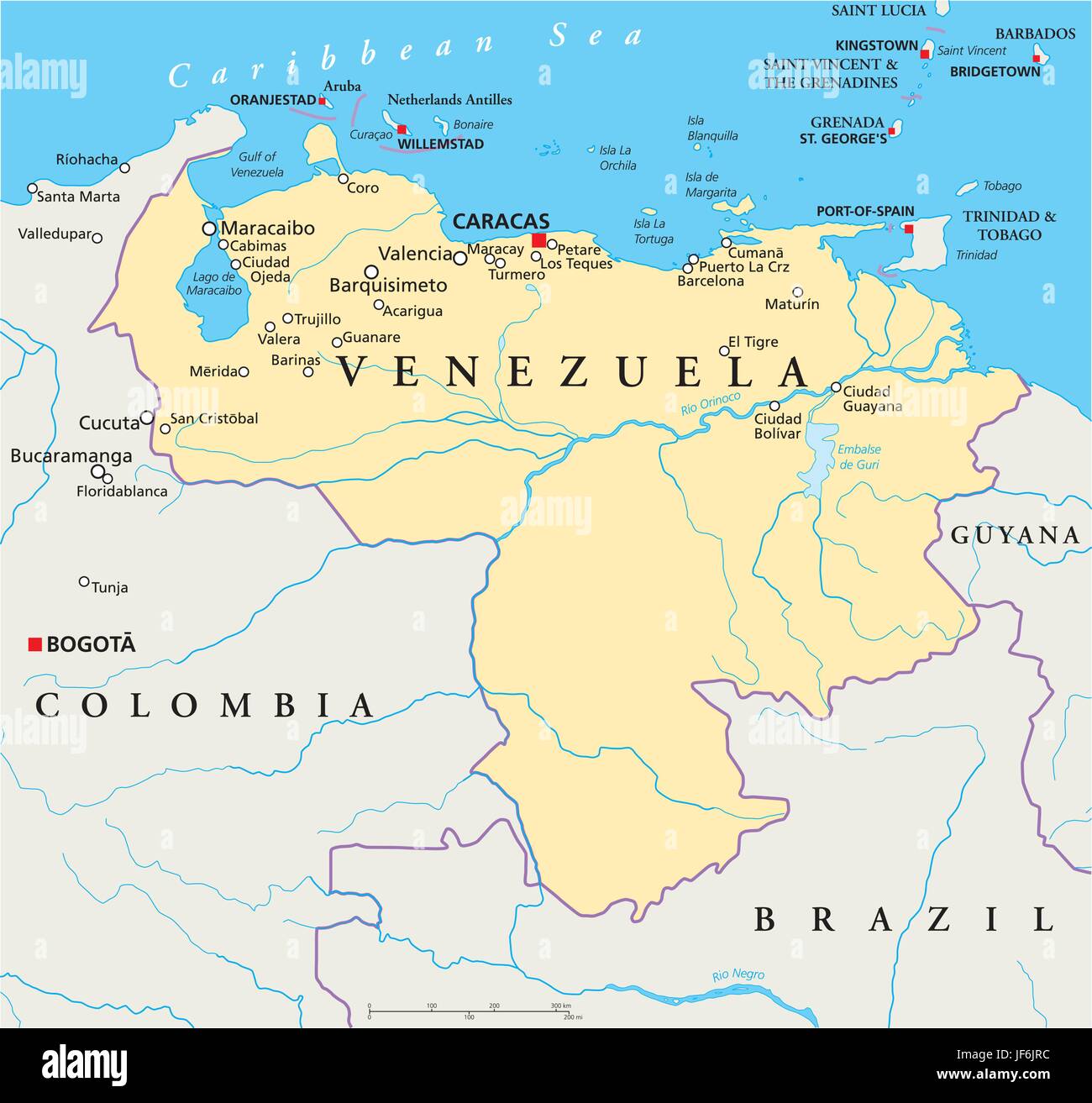
Neighboring Countries: Sharing Borders and Influences
A country’s neighbors significantly shape its history, culture, and economy. Venezuela shares land borders with three countries:
-
Colombia: To the west, Venezuela shares a long and porous border with Colombia. This border region has been historically characterized by trade, migration, and, unfortunately, conflict. The two nations have a complex and intertwined relationship, influenced by shared history, cultural similarities, and ongoing challenges related to security and border management.
-
Brazil: To the south, Venezuela borders Brazil, the largest country in South America. This border region is largely characterized by dense rainforest and sparsely populated areas. While trade and cooperation exist, the border’s remote nature presents logistical challenges.
-
Guyana: To the east, Venezuela shares a border with Guyana. This border is a source of ongoing territorial dispute, primarily concerning the Essequibo region, a large area west of the Essequibo River claimed by Venezuela. This long-standing dispute remains a significant point of contention between the two countries.
The Caribbean Connection: Islands and Sea Lanes
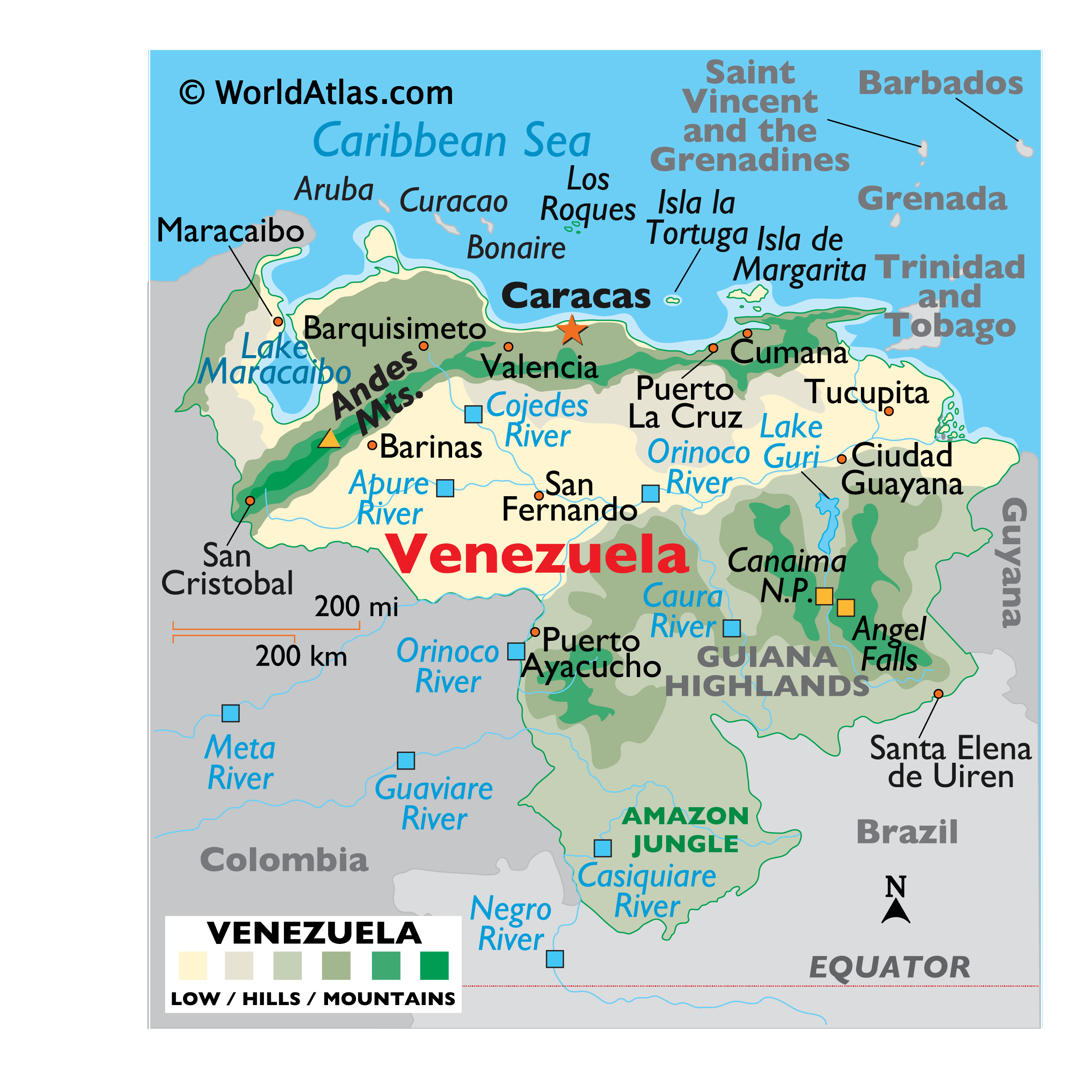
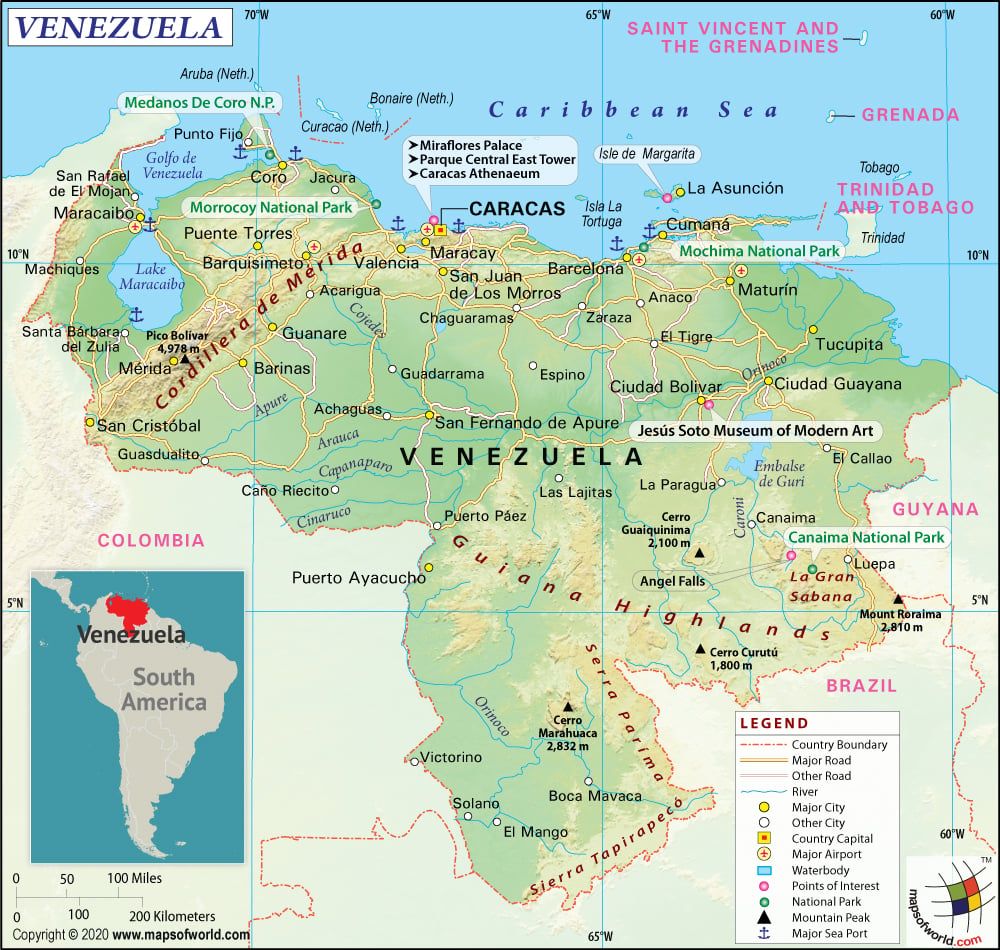
Venezuela’s northern coastline fronts the Caribbean Sea, giving it a strong connection to the islands of the Caribbean. Several island nations lie just a short distance from the Venezuelan coast, including:
-
Trinidad and Tobago: Located just off the northeastern coast of Venezuela, Trinidad and Tobago share close cultural and economic ties with the mainland nation. The proximity facilitates trade, migration, and cultural exchange.
-
Aruba, Curaçao, and Bonaire (the ABC Islands): These Dutch Caribbean islands lie north of Venezuela and have a long history of interaction with the mainland. Their economies are heavily reliant on tourism and trade, and they serve as important points of connection between Venezuela and the wider world.
-
Other Caribbean Islands: Numerous other islands, including Grenada, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, and Barbados, lie further east and northeast, contributing to a vibrant and interconnected Caribbean region.
Venezuela’s access to the Caribbean Sea provides crucial sea lanes for trade and commerce. Its ports, such as Puerto La Cruz, La Guaira, and Maracaibo, are vital hubs for the import and export of goods. The Caribbean Sea also plays a significant role in Venezuela’s tourism industry, attracting visitors to its beautiful beaches and coastal regions.
Geographic Features: Shaping the Landscape and Economy
Venezuela’s geography is incredibly diverse, contributing to its rich biodiversity and resource wealth. Key geographic features include:
-
The Andes Mountains: The northern and western parts of Venezuela are traversed by the Andes Mountains, providing dramatic landscapes, cooler climates, and sources of freshwater.
-
The Orinoco River Basin: A vast lowland area that dominates the central part of the country, the Orinoco River Basin is home to the Orinoco River, one of the longest rivers in South America. This region is vital for agriculture, transportation, and oil extraction.
-
Lake Maracaibo: Located in the northwest, Lake Maracaibo is the largest lake in South America and is rich in oil deposits. It’s a crucial economic resource but also faces environmental challenges due to pollution.
-
The Guiana Highlands: Located in the southeast, the Guiana Highlands are characterized by ancient rock formations, dense rainforests, and spectacular waterfalls, including Angel Falls, the world’s highest uninterrupted waterfall.
-
Coastal Plains: Venezuela’s extensive coastline provides access to valuable fisheries, tourist destinations, and strategic ports.
These diverse geographic features influence Venezuela’s climate, agriculture, resource distribution, and overall economic development.
Climate Zones: A Tropical Tapestry
Venezuela’s location near the Equator gives it a predominantly tropical climate. However, altitude and other geographic factors create variations in temperature and rainfall across the country. Generally, the climate can be categorized as:
-
Tropical Rainforest Climate: Found in the southern parts of the country, particularly in the Amazonian region, this climate is characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall throughout the year.
-
Tropical Savanna Climate: Dominates the central plains, with distinct wet and dry seasons.
-
Tropical Monsoon Climate: Influences the coastal areas, with heavy rainfall during certain months.
-
Highland Climate: Found in the Andes Mountains, with cooler temperatures and varying rainfall patterns depending on altitude.
Geopolitical Significance: A Nation at the Crossroads
Venezuela’s geographic location contributes to its geopolitical significance in several ways:
-
Strategic Location: Its position on the northern coast of South America gives it control over key trade routes and access to the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.
-
Oil Reserves: Venezuela possesses the world’s largest proven oil reserves, making it a crucial player in the global energy market. Its location near major shipping lanes facilitates the export of oil to international markets.
-
Regional Influence: As a relatively large and resource-rich nation, Venezuela has historically played a significant role in regional politics and integration efforts.
-
Border Security: Its shared borders with Colombia, Brazil, and Guyana present ongoing challenges related to security, migration, and territorial disputes.
Conclusion: A Land Defined by its Location
In conclusion, Venezuela’s location on the world map is far more than just a point of reference. It’s a key determinant of its climate, resources, cultural connections, and geopolitical significance. Situated on the northern coast of South America, bordering Colombia, Brazil, and Guyana, and facing the Caribbean Sea, Venezuela enjoys a strategic location that has shaped its history and continues to influence its future. Understanding this geographic context is essential for grasping the complexities of this vibrant and dynamic nation. From its diverse landscapes and tropical climate to its abundant natural resources and its role in regional and global affairs, Venezuela’s location on the world map provides a crucial lens through which to understand its past, present, and future. By recognizing its precise coordinates and appreciating its surrounding environment, we can better appreciate the intricate tapestry that makes up the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela.