A Comprehensive Guide to Canada’s Diverse Regions: Understanding the Map
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Canada’s Diverse Regions: Understanding the Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Canada’s Diverse Regions: Understanding the Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Canada’s Diverse Regions: Understanding the Map
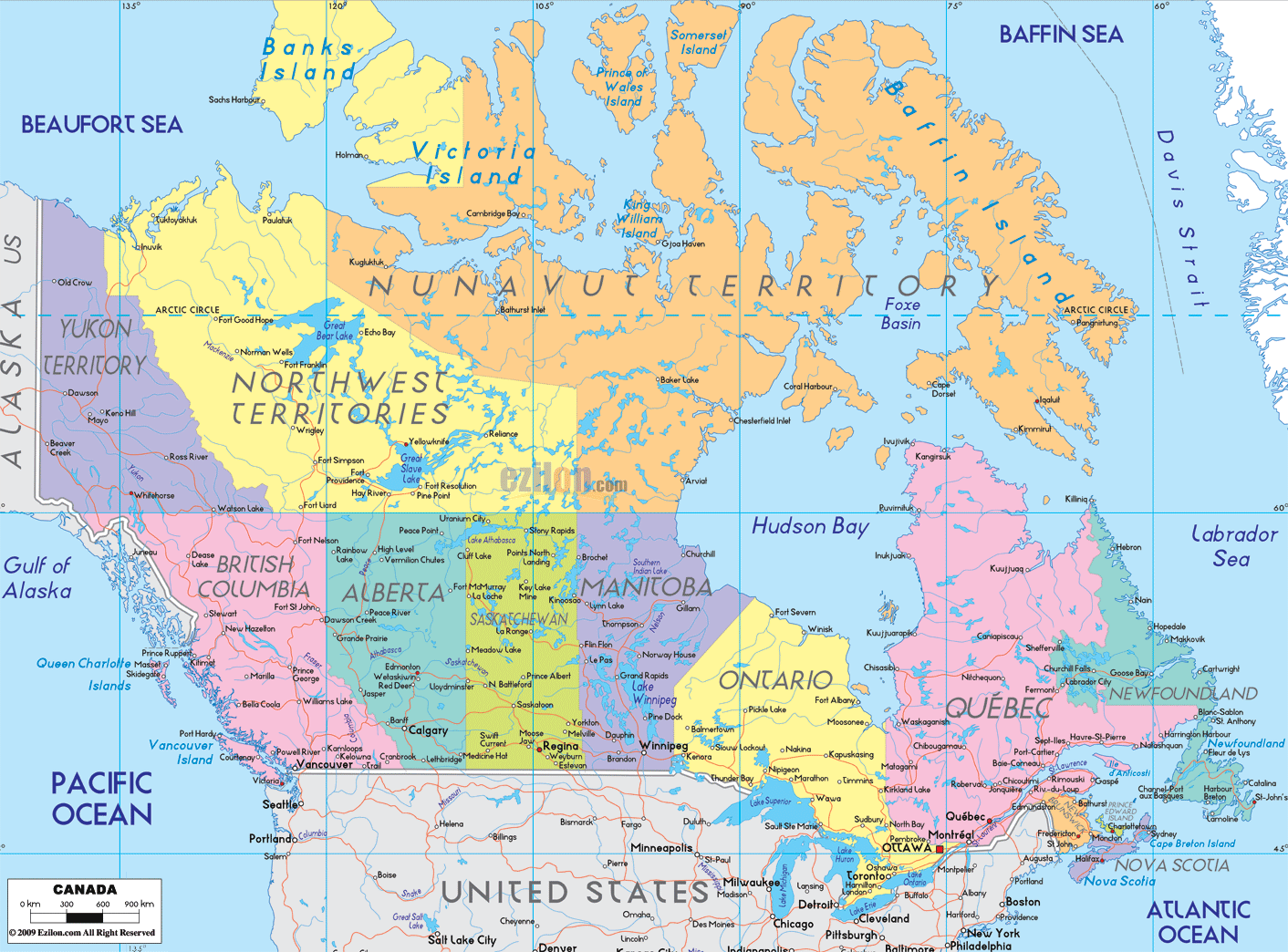
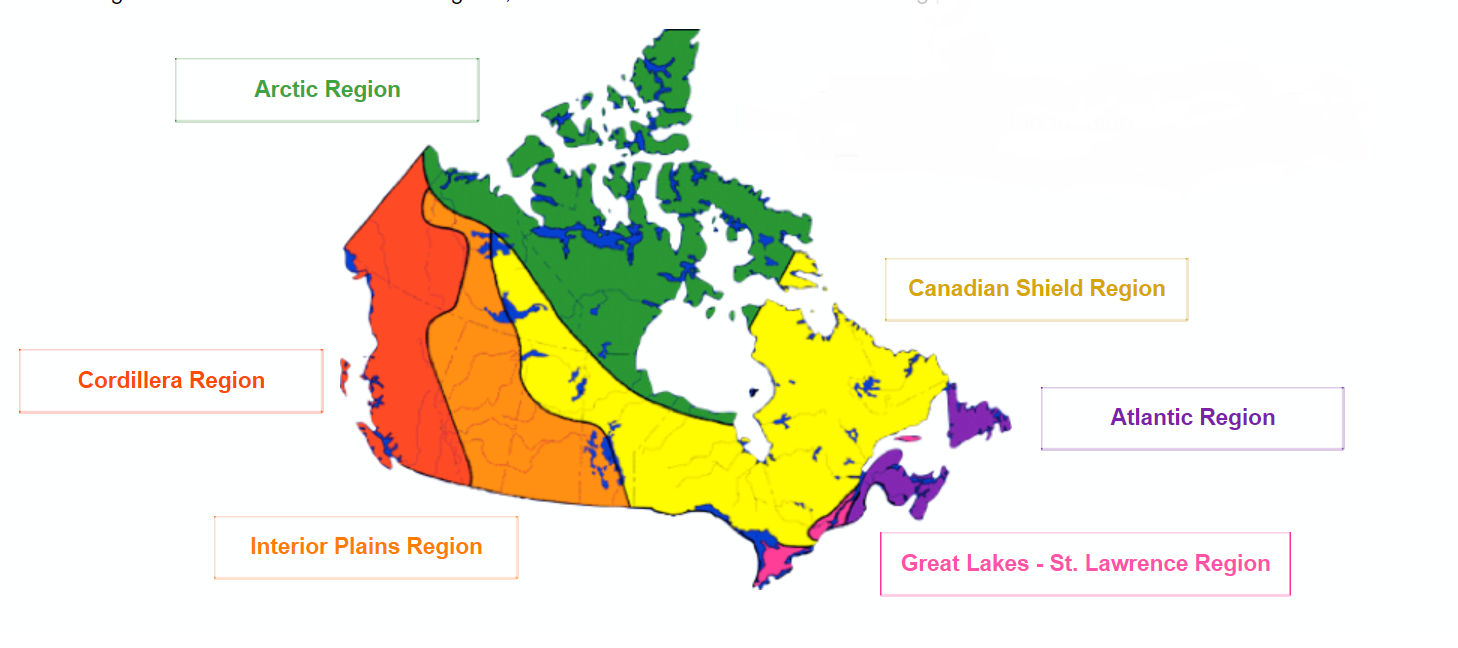
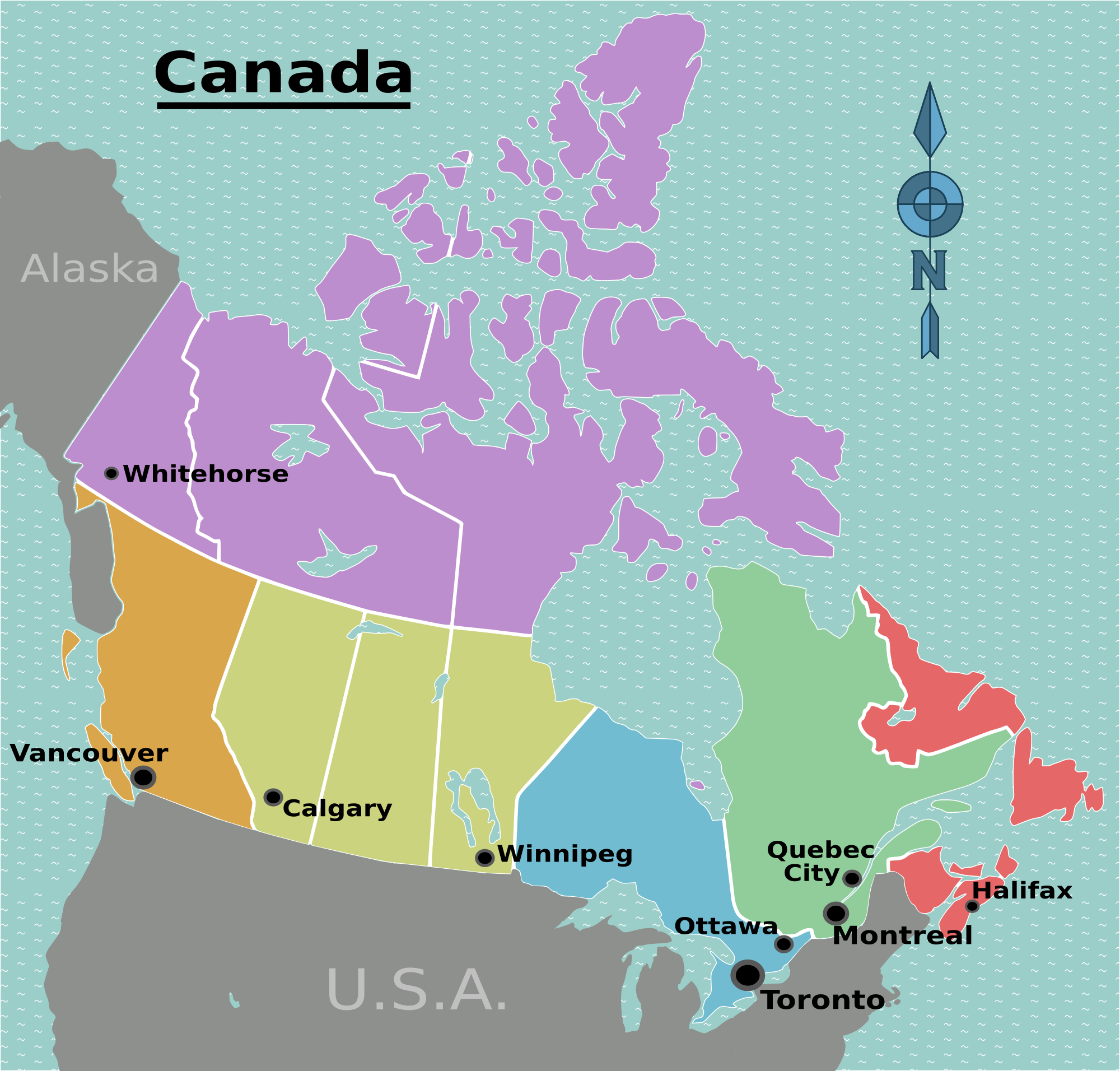
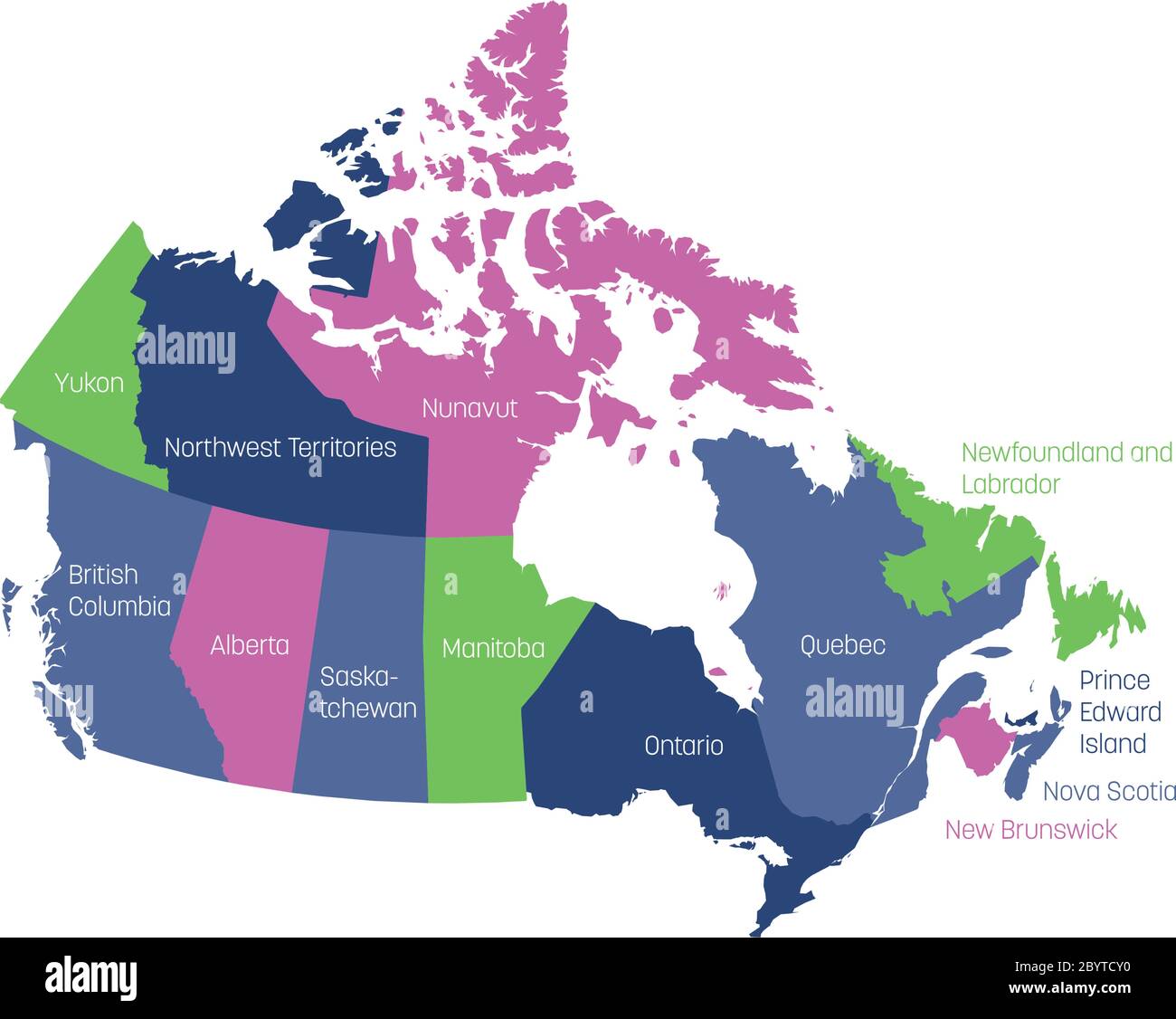
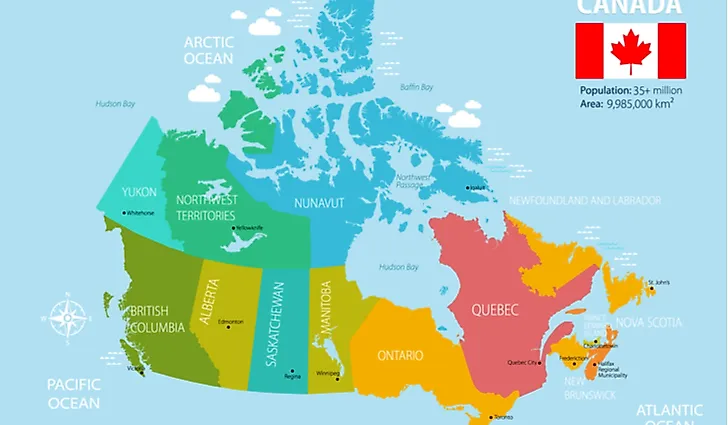
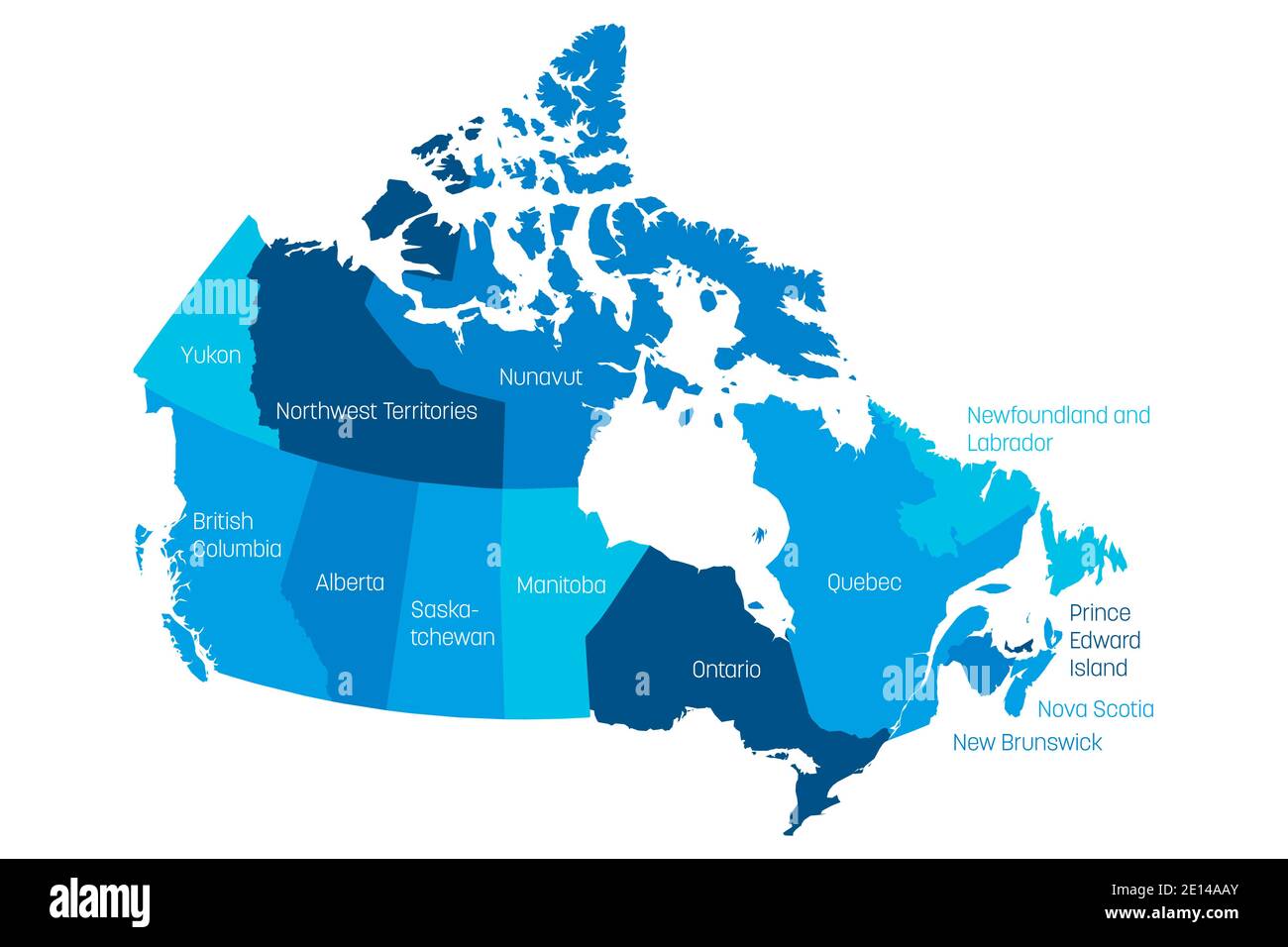
Canada, the second-largest country in the world, is a vast and diverse nation spanning ten provinces and three territories. Understanding the geographical and cultural nuances of each region is crucial for appreciating the country’s rich tapestry. This article delves into the distinct regions of Canada, exploring their unique characteristics, cultural heritage, and economic contributions.
The Atlantic Provinces: A Maritime Legacy
The Atlantic provinces, comprising New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, and Newfoundland and Labrador, occupy the easternmost corner of Canada. This region is renowned for its stunning coastline, rugged landscapes, and rich maritime history. The Atlantic provinces are home to numerous historical sites, charming fishing villages, and vibrant coastal cities.
- New Brunswick: Known for its bilingual heritage, New Brunswick offers a blend of French and English culture. It is also a major producer of lumber and forestry products.
- Nova Scotia: Renowned for its picturesque coastline and historic sites, Nova Scotia boasts a thriving tourism industry. It is also a significant center for seafood processing.
- Prince Edward Island: Often referred to as "Canada’s Cradle," Prince Edward Island is known for its rolling hills, red sandstone cliffs, and fertile farmland. It is a major agricultural producer, famous for its potatoes and seafood.
- Newfoundland and Labrador: This province is characterized by its dramatic coastline, rugged mountains, and vast wilderness. It is a significant center for oil and gas production, with a rich history of fishing and exploration.
Quebec: A French-Canadian Heritage
Quebec, the only province with a predominantly French-speaking population, holds a unique cultural and linguistic identity within Canada. Its landscape encompasses vast forests, rolling hills, and the majestic St. Lawrence River.
- Montreal: Canada’s second-largest city, Montreal is a vibrant cultural hub renowned for its architecture, cuisine, and artistic scene.
- Quebec City: The province’s capital, Quebec City is a historic gem known for its charming Old Town and its strategic location on the St. Lawrence River.
- The Eastern Townships: This region is characterized by its rolling hills, picturesque villages, and thriving agricultural industry.
- The Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean: Home to the majestic Saguenay Fjord and Lac Saint-Jean, this region offers breathtaking natural beauty and opportunities for outdoor recreation.
Ontario: The Heart of Canada
Ontario, Canada’s most populous province, is located in the heart of the country. It boasts a diverse landscape, ranging from the Great Lakes to the Canadian Shield. Ontario is a major economic powerhouse, with a strong manufacturing, technology, and financial services sector.
- Toronto: Canada’s largest city, Toronto is a global center for finance, culture, and innovation.
- Ottawa: The nation’s capital, Ottawa is home to Parliament Hill and numerous government institutions.
- Niagara Falls: This iconic natural wonder attracts millions of tourists annually.
- Muskoka: Known for its pristine lakes and forests, Muskoka is a popular destination for outdoor recreation and cottage living.
The Prairie Provinces: The Breadbasket of Canada
The Prairie provinces, consisting of Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Alberta, are known as the "breadbasket of Canada" due to their vast agricultural lands. The region’s landscape is characterized by flat plains, rolling hills, and vast stretches of grasslands.
- Manitoba: Located in the heart of the Canadian prairies, Manitoba is a major producer of wheat, canola, and other agricultural products. It is also home to significant mining and hydroelectric industries.
- Saskatchewan: Known for its vast wheat fields and its rich agricultural heritage, Saskatchewan is a major producer of grains, oilseeds, and potash.
- Alberta: Alberta is Canada’s leading energy producer, with significant oil and gas reserves. It also boasts a thriving agricultural sector and a growing tourism industry.
British Columbia: The Pacific Coast Gem
British Columbia, located on the Pacific coast, is known for its stunning mountain ranges, lush forests, and beautiful coastline. It is home to a diverse population, with a strong cultural heritage influenced by First Nations, Asian, and European communities.
- Vancouver: A vibrant coastal city, Vancouver is renowned for its natural beauty, cultural diversity, and thriving economy.
- Victoria: The provincial capital, Victoria is known for its charming historic district, its beautiful gardens, and its proximity to the Gulf Islands.
- The Okanagan Valley: This region is famous for its vineyards, orchards, and stunning scenery.
- The Rocky Mountains: Home to majestic peaks, glaciers, and pristine lakes, the Rocky Mountains offer unparalleled opportunities for outdoor recreation.
The Territories: A Vast and Untamed Wilderness
Canada’s three territories, Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut, occupy the northernmost regions of the country. These vast and sparsely populated regions are characterized by their rugged terrain, harsh climate, and stunning natural beauty.
- Yukon: Known for its majestic mountains, vast wilderness, and rich gold rush history, the Yukon is a popular destination for outdoor enthusiasts.
- Northwest Territories: This territory encompasses a vast expanse of tundra, boreal forests, and lakes. It is home to a diverse range of wildlife and is a major center for diamond mining.
- Nunavut: The largest and most northerly territory, Nunavut is home to a predominantly Inuit population and boasts a rich cultural heritage. It is known for its stunning Arctic landscapes and its unique wildlife.
The Importance of Regional Understanding
Understanding the distinct regions of Canada is crucial for appreciating the country’s diversity, history, and culture. Each region has its unique characteristics, contributing to the rich tapestry of Canadian life. This knowledge fosters a deeper understanding of the country’s past, present, and future.
FAQs
Q: What are the main geographical features of Canada?
A: Canada’s geography is diverse, encompassing vast plains, towering mountains, expansive forests, and a long coastline. The Canadian Shield, a vast expanse of Precambrian rock, covers a significant portion of the country. The Rocky Mountains, the Appalachian Mountains, and the St. Lawrence River are prominent geographical features.
Q: What are the major industries in each region of Canada?
A: Canada’s economy is diverse, with different industries dominating each region. The Atlantic provinces are known for their fishing, forestry, and tourism industries. Quebec is a major center for manufacturing, aerospace, and pharmaceuticals. Ontario is a powerhouse in manufacturing, finance, and technology. The Prairie provinces are the "breadbasket of Canada," with significant agricultural production. British Columbia is known for its forestry, mining, and tourism industries. The territories are rich in natural resources, with mining and tourism playing significant roles.
Q: What are some of the cultural differences between the regions of Canada?
A: Canada is a multicultural nation with distinct cultural influences in each region. Quebec has a strong French-Canadian heritage, while the Atlantic provinces have a rich maritime history. Ontario is a melting pot of cultures, while the Prairie provinces are known for their agricultural heritage. British Columbia is influenced by First Nations, Asian, and European cultures. The territories have unique cultural traditions rooted in their indigenous populations.
Q: How does the climate vary across Canada?
A: Canada experiences a wide range of climates due to its vast size and diverse geography. The Atlantic provinces have a humid continental climate with warm summers and cold winters. Quebec has a similar climate, but with colder winters. Ontario experiences a more moderate climate, with four distinct seasons. The Prairie provinces have a semi-arid climate with hot summers and cold winters. British Columbia has a temperate climate with mild winters and warm summers. The territories have a subarctic climate with long, cold winters and short, cool summers.
Tips
- Travel to different regions: Experience the diverse landscapes and cultures of Canada by visiting different regions.
- Learn about local history and culture: Immerse yourself in the unique history and culture of each region by visiting museums, historical sites, and cultural events.
- Support local businesses: Patronize local businesses and artisans to contribute to the regional economy and experience the unique products and services of each area.
- Engage with local communities: Connect with local residents to gain a deeper understanding of their perspectives and experiences.
Conclusion
Canada’s diverse regions are a testament to the country’s vast geography, rich history, and vibrant cultures. Understanding the unique characteristics of each region is essential for appreciating the complexity and beauty of this vast and diverse nation. From the rugged coastlines of the Atlantic provinces to the majestic mountains of British Columbia, each region offers a unique experience and contributes to the rich tapestry of Canadian life.
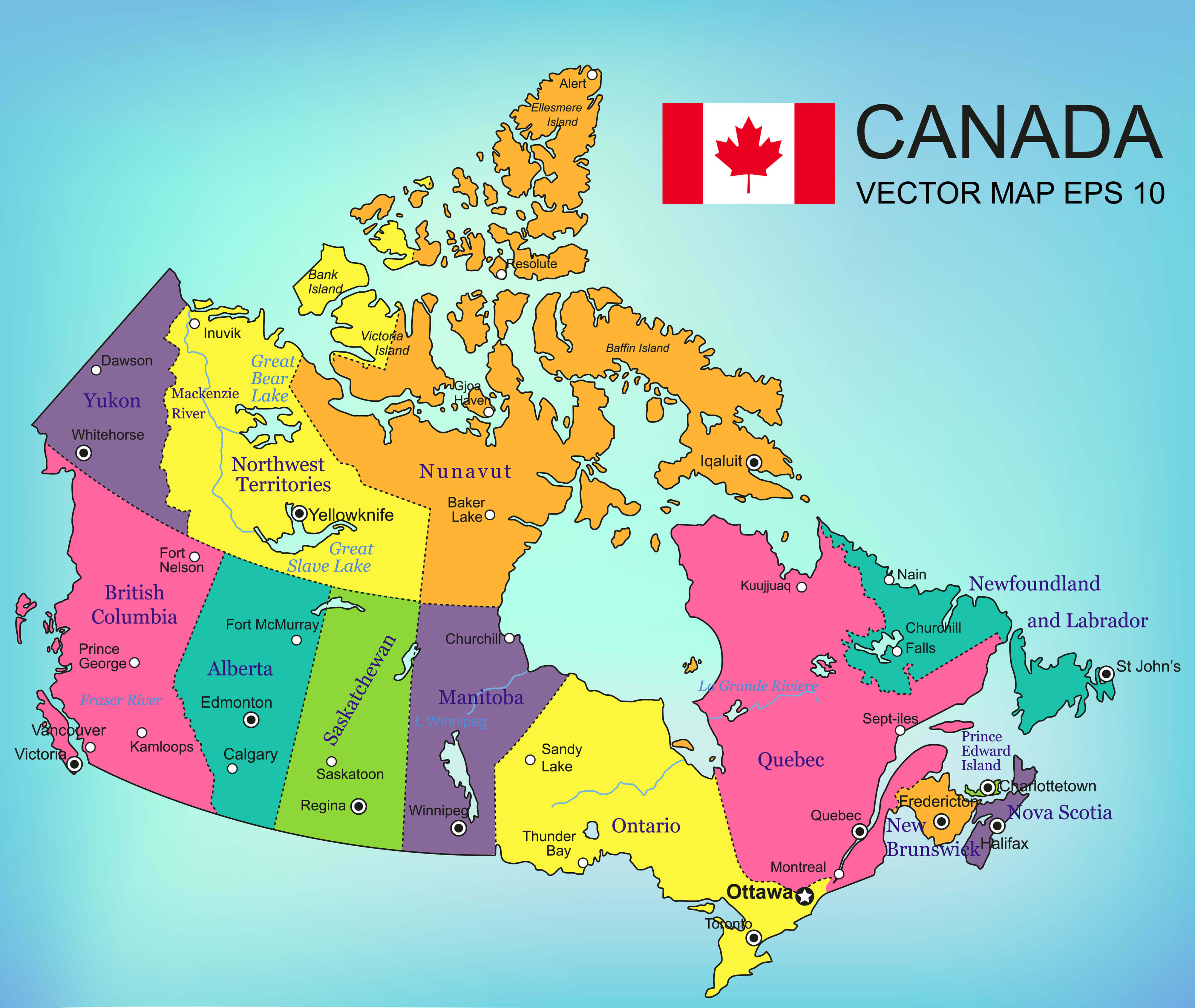
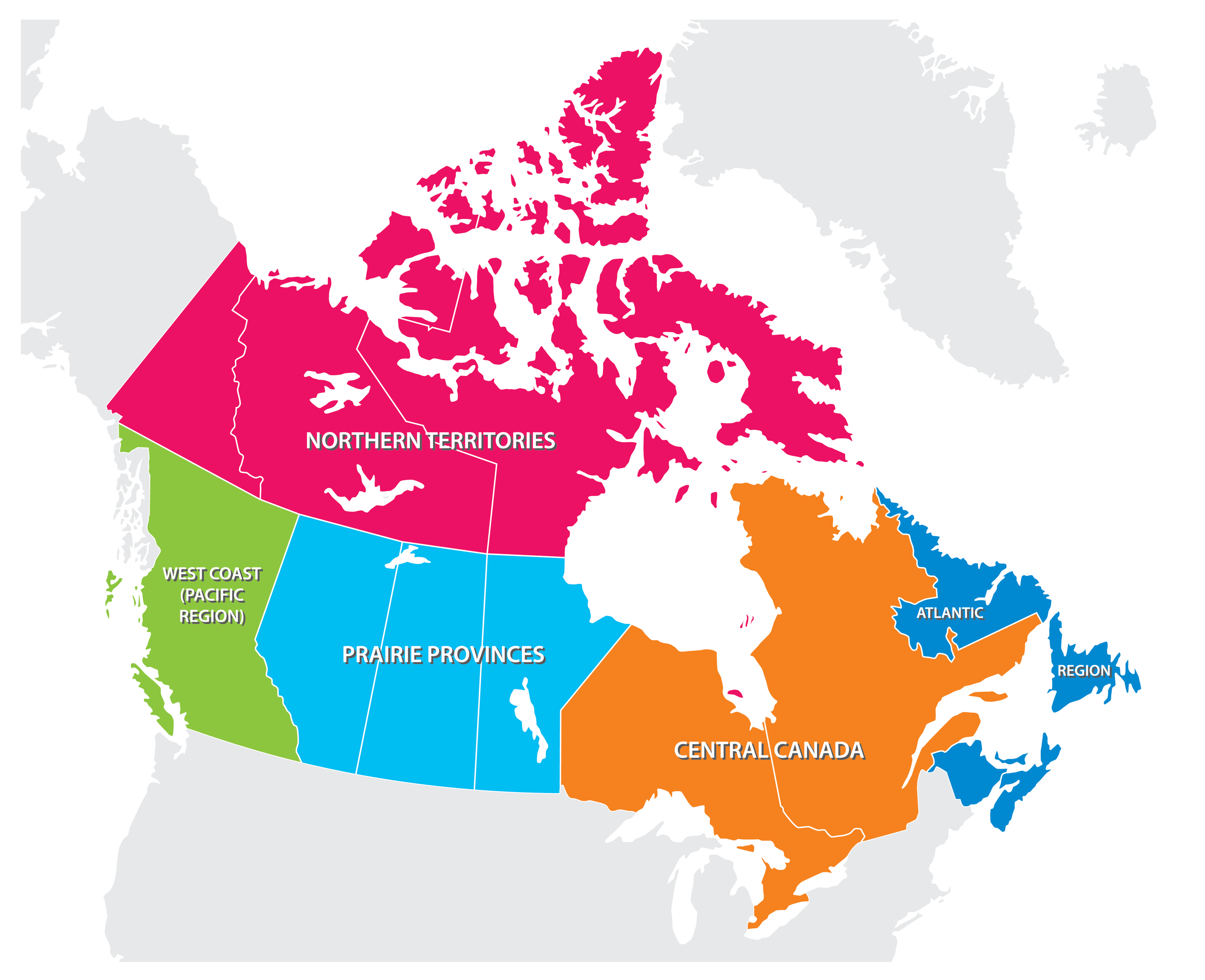
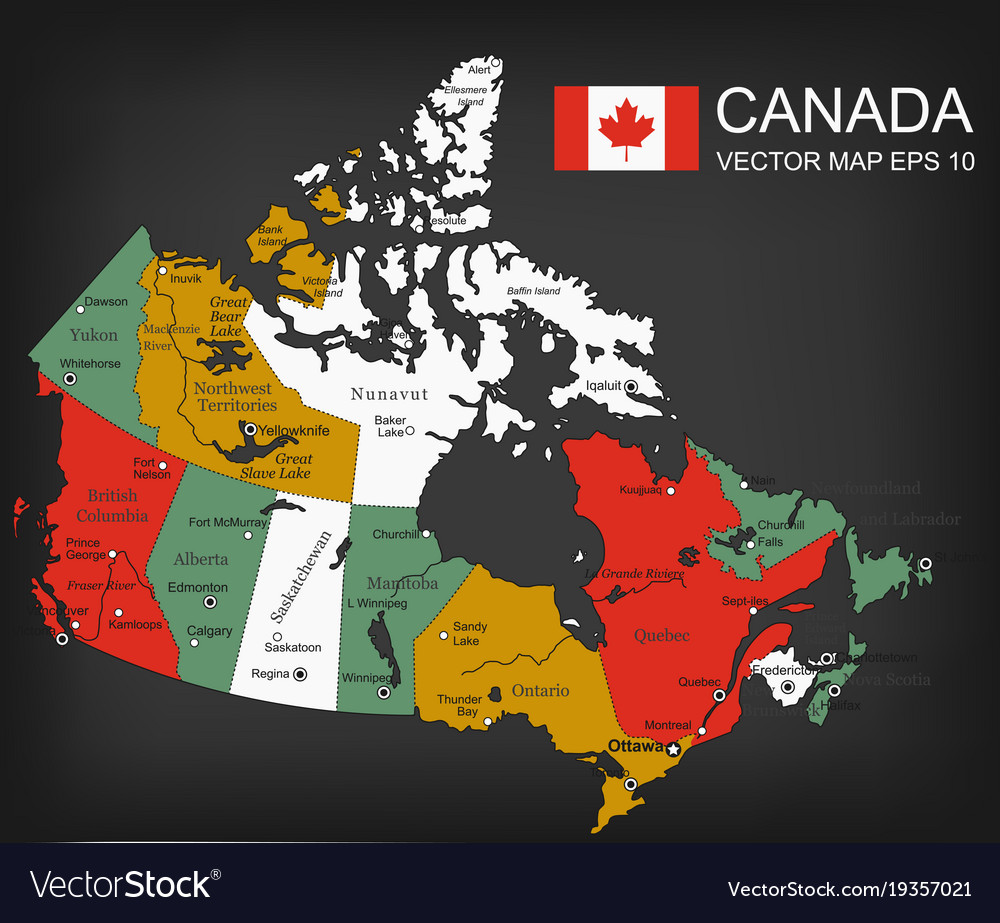
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Canada’s Diverse Regions: Understanding the Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!