A Geographical Perspective: Exploring the Borders and Landscapes of Germany and Poland
Related Articles: A Geographical Perspective: Exploring the Borders and Landscapes of Germany and Poland
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Perspective: Exploring the Borders and Landscapes of Germany and Poland. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Perspective: Exploring the Borders and Landscapes of Germany and Poland

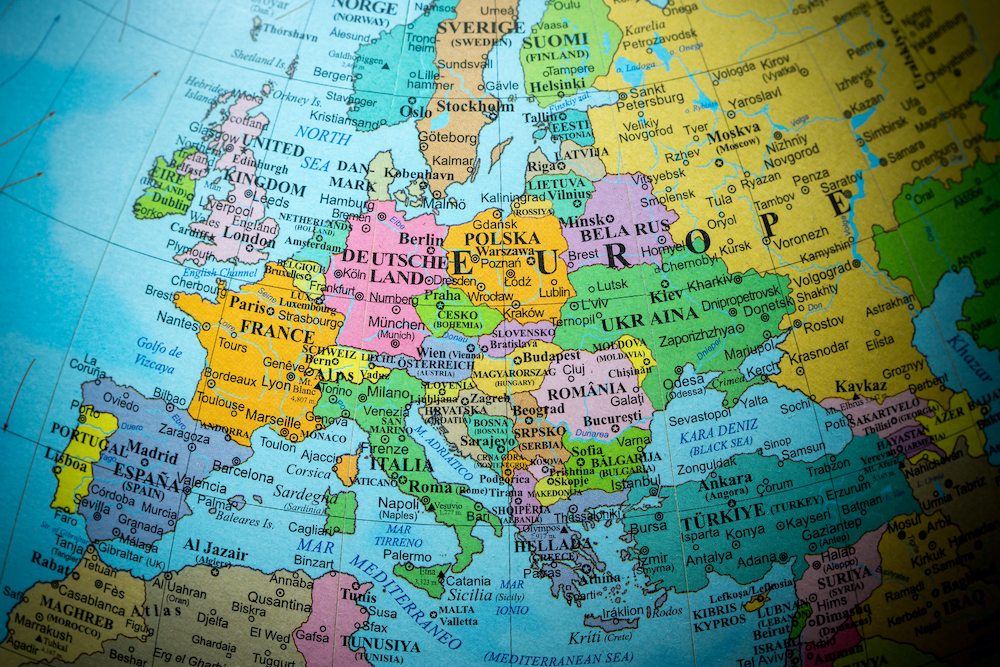
The maps of Germany and Poland, two neighboring nations in Central Europe, reveal a complex and fascinating geographical tapestry. Their intertwined histories, shared landscapes, and distinct cultural identities are intricately woven into the fabric of their respective territories. Understanding the geographical features of these nations offers a valuable lens through which to appreciate their unique characteristics and the historical forces that have shaped them.
A Shared Landscape:
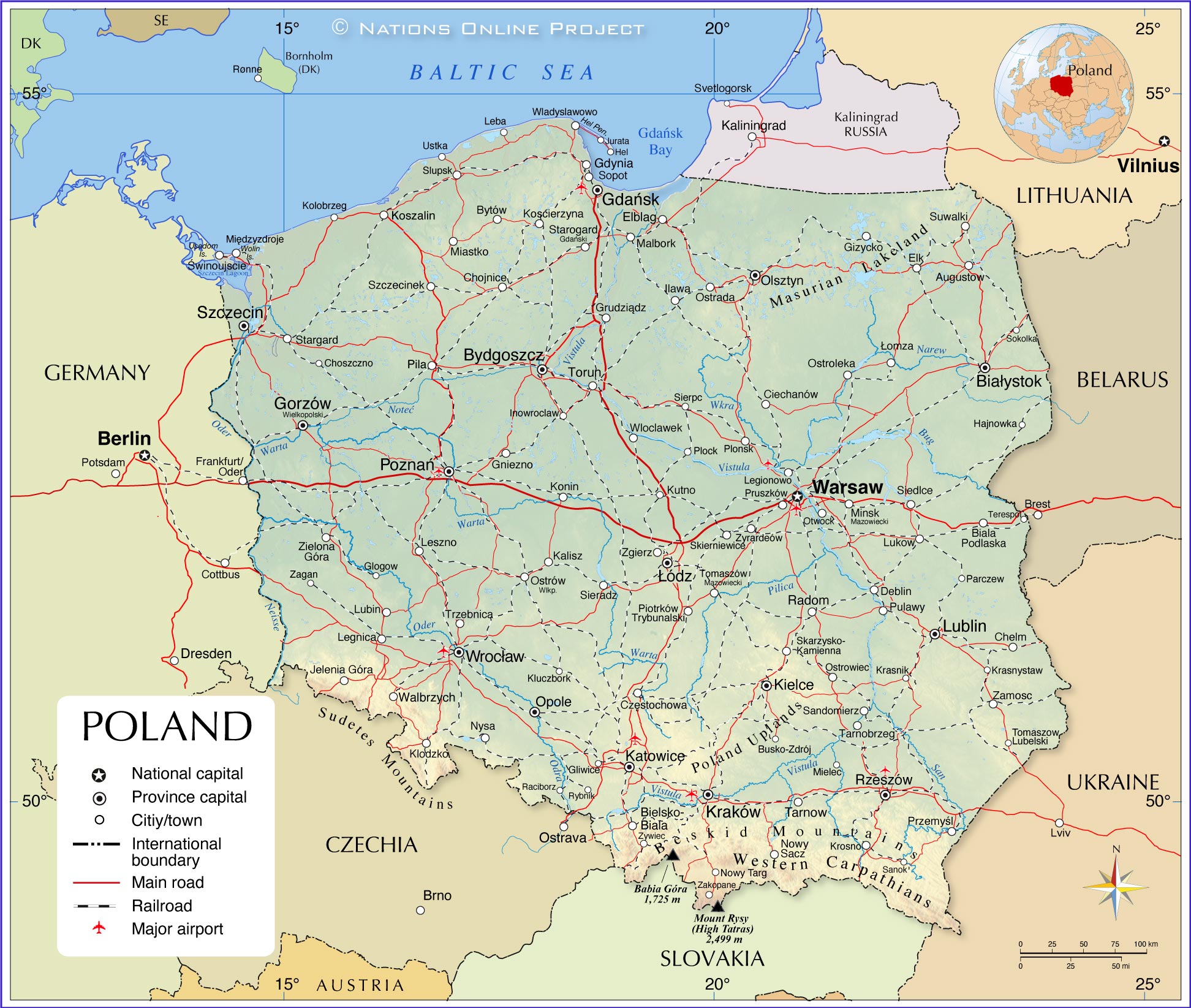
Germany and Poland share a long border stretching for approximately 456 kilometers, primarily along the Oder River. This border, a testament to historical shifts and political transformations, traverses diverse landscapes, from the rolling hills of the Sudeten Mountains to the fertile plains of the North German Lowland.
Germany’s Diverse Geography:
Germany, a nation of approximately 357,000 square kilometers, exhibits a remarkable geographical diversity. The country is broadly divided into three major regions:
- The Northern German Plain: This vast, flat expanse, stretching from the North Sea to the Baltic Sea, is characterized by fertile soil and extensive agricultural activity. It also encompasses major river systems like the Elbe, Weser, and Rhine, crucial for transportation and economic development.
- The Central German Uplands: This region, encompassing the Harz Mountains and the Thuringian Forest, features rolling hills, dense forests, and numerous historic towns and cities. Its diverse landscape fosters a range of industries, from mining to tourism.
- The Southern German Alps: This region, home to the Bavarian Alps, offers stunning mountain scenery, glacial lakes, and picturesque villages. It is a popular destination for outdoor activities and serves as a crucial source of hydroelectric power.
Poland’s Varied Terrain:
Poland, with a total area of approximately 312,000 square kilometers, boasts a similarly varied terrain. The country can be broadly divided into four major regions:
- The Baltic Sea Coast: This region, characterized by sandy beaches, coastal lagoons, and picturesque seaside resorts, offers a vibrant mix of tourism, fishing, and maritime industries.
- The North European Plain: This vast, flat expanse, stretching from the Baltic Sea to the Carpathian Mountains, encompasses fertile farmland, extensive forests, and major river systems like the Vistula and Oder.
- The Carpathian Mountains: This region, home to the Tatra Mountains, offers stunning mountain scenery, alpine meadows, and numerous ski resorts. It is a popular destination for outdoor activities and a vital source of mineral resources.
- The Silesian Lowlands: This region, located in southern Poland, is characterized by fertile soil and extensive coal deposits, making it a significant center for heavy industry.
Historical Influences on the Landscape:
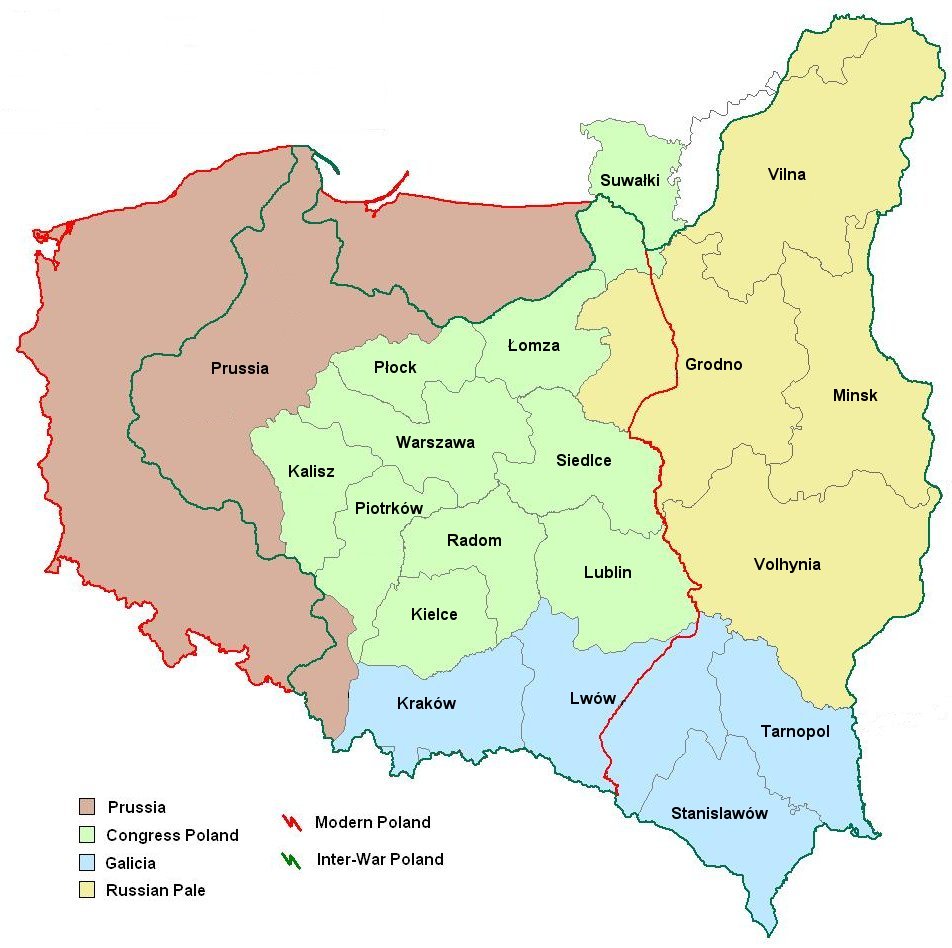
The maps of Germany and Poland reflect the impact of historical events on their respective landscapes. The division of Germany during the Cold War, for instance, left a lasting mark on the country’s infrastructure and economic development. The Polish-German border, frequently shifting throughout history, has influenced the cultural and linguistic identities of communities living along its course.
Understanding the Importance of the Maps:
The maps of Germany and Poland serve as invaluable tools for understanding the historical, cultural, and economic dynamics of these two nations. They provide a visual representation of the complex interplay between geography, history, and human activity. By studying the maps, we can gain insights into:
- The geographical factors influencing economic development: The fertile plains of Germany and Poland, for instance, have historically supported thriving agricultural industries.
- The historical forces shaping national identities: The shifting borders and political divisions have left a lasting impact on the cultural landscapes of both nations.
- The challenges and opportunities presented by the shared environment: The need for sustainable development, the management of shared resources, and the potential for cross-border cooperation are all issues highlighted by the maps.
FAQs about the Maps of Germany and Poland:
- What are the main geographical features of Germany and Poland? Both countries exhibit diverse landscapes, from coastal plains to mountainous regions, each with its unique characteristics and economic potential.
- How have historical events shaped the borders of Germany and Poland? The borders between the two nations have shifted frequently throughout history, reflecting political and cultural changes.
- What are the implications of the shared border between Germany and Poland? The shared border presents both challenges and opportunities, requiring cooperation on issues like environmental protection and economic development.
- How do the maps of Germany and Poland reflect their respective cultural identities? The geographical features of these countries, along with their historical experiences, have contributed to the development of distinct cultural identities.
- What are the major cities located on the border between Germany and Poland? Some of the major cities located on the border include Szczecin (Poland) and Frankfurt (Oder) (Germany).
Tips for Using the Maps of Germany and Poland:
- Focus on key geographical features: Identify the major rivers, mountain ranges, and coastal areas to understand the basic landscape structure.
- Consider historical context: Explore the historical shifts in borders and political divisions to appreciate the dynamics of the region.
- Analyze the economic implications: Examine the distribution of resources, infrastructure, and industries to understand the economic potential of each country.
- Think about cultural influences: Consider how the geographical features and historical experiences have shaped the cultural identities of Germany and Poland.
- Look for connections and contrasts: Compare and contrast the landscapes, cultural expressions, and economic activities of the two nations to gain a deeper understanding of their similarities and differences.
Conclusion:
The maps of Germany and Poland offer a valuable window into the rich geographical and cultural tapestry of these two nations. By understanding their landscapes, historical experiences, and shared border, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex interplay between geography, history, and human activity. The maps serve as a reminder of the interconnectedness of these two nations and the importance of cooperation in addressing shared challenges and harnessing mutual opportunities.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Perspective: Exploring the Borders and Landscapes of Germany and Poland. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!