Charting the Vastness: Understanding the Hudson Bay Map
Related Articles: Charting the Vastness: Understanding the Hudson Bay Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Vastness: Understanding the Hudson Bay Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Vastness: Understanding the Hudson Bay Map

The Hudson Bay, a vast inland sea nestled in the heart of Canada, is a geographical marvel that has shaped the history, culture, and environment of the country. Understanding the map of Hudson Bay is crucial for appreciating its diverse ecosystem, its historical significance, and its modern-day relevance. This exploration delves into the key features, historical context, and contemporary significance of the Hudson Bay map, offering insights into its profound impact on Canada.
Geographical Overview:
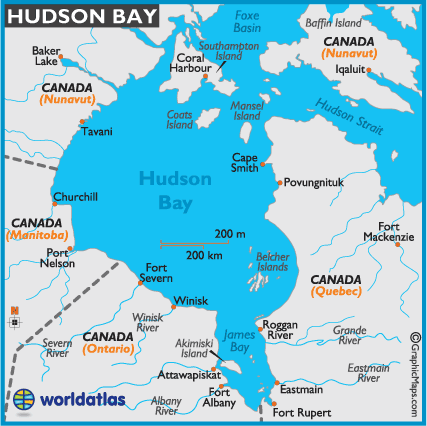
The Hudson Bay, the world’s largest inland sea, occupies a prominent position on the map of Canada. Its massive size, exceeding the combined area of several European countries, makes it a defining feature of the Canadian landscape. The bay is surrounded by the provinces of Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Quebec, and the territory of Nunavut. Its northern shores extend towards the Arctic Ocean, while its southern boundary meets the Canadian Shield.
Key Features on the Map:
The Hudson Bay map showcases a number of prominent features that contribute to its unique character:
- The James Bay: A large, shallow bay at the southern end of Hudson Bay, this area is known for its vast tidal flats and its significant role in hydroelectric power generation.
- The Foxe Basin: A large body of water situated north of Hudson Bay, the Foxe Basin is a major gateway to the Arctic Ocean. Its waters are rich in marine life and play a crucial role in the Arctic ecosystem.
- The Ungava Peninsula: A large peninsula located on the eastern side of Hudson Bay, the Ungava Peninsula is characterized by its rugged terrain, vast tundra, and significant mineral resources.
- The Belcher Islands: A group of islands located in the eastern part of Hudson Bay, these islands are known for their unique geology and their role as a nesting ground for seabirds.
- The Churchill River: This major river flows into Hudson Bay, providing a vital transportation route and contributing to the bay’s freshwater inflow.
- The Churchill, Manitoba: Located on the western shore of Hudson Bay, Churchill is a town renowned for its polar bear population and its role as a gateway to the Arctic.
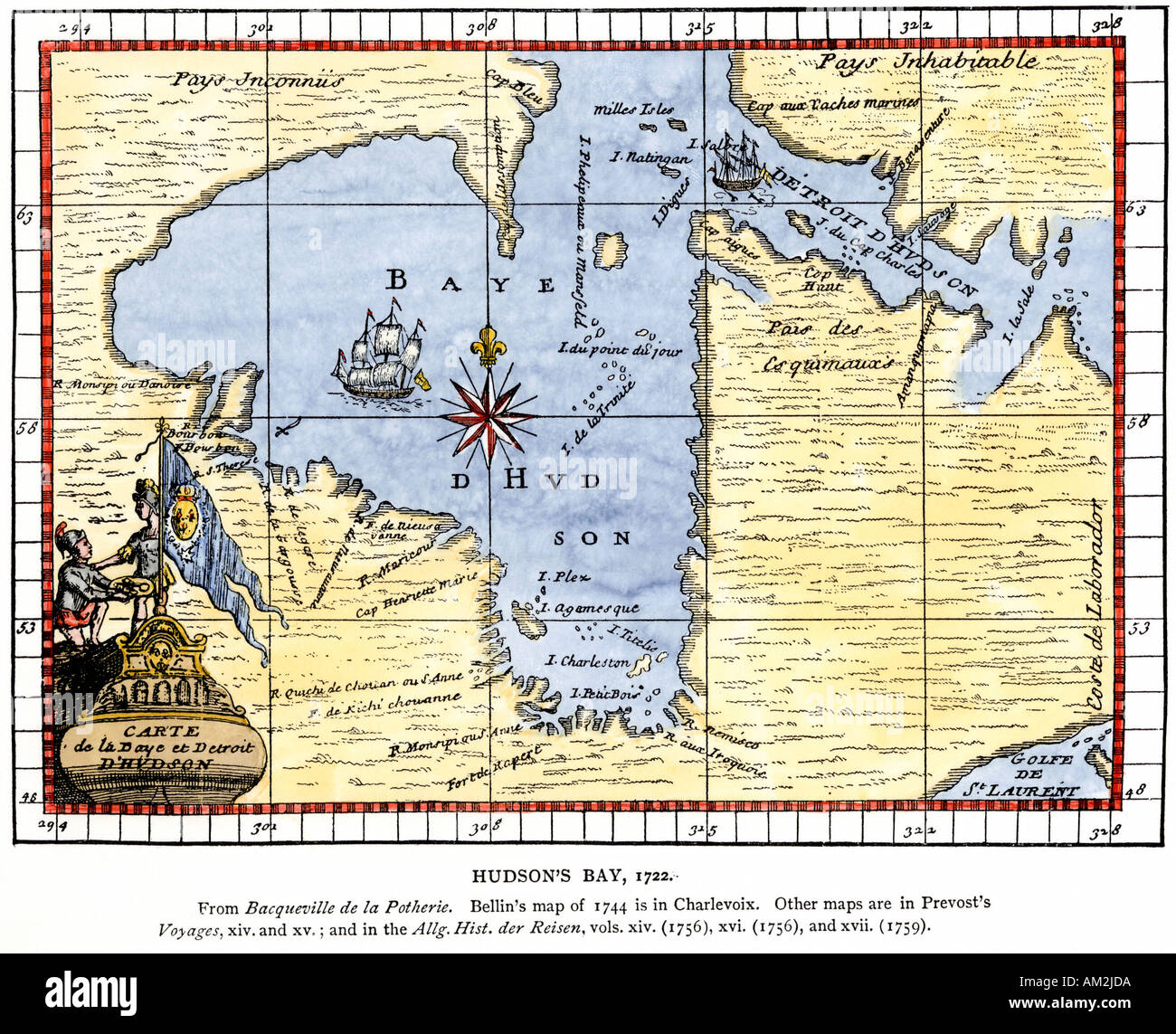
Historical Significance:
The Hudson Bay map is not merely a geographical representation; it embodies a rich history. The bay played a pivotal role in the fur trade, which profoundly shaped Canada’s early development. The Hudson’s Bay Company, established in 1670, established trading posts along the shores of the bay, connecting European markets to the vast resources of North America. These posts served as centers of trade and cultural exchange, influencing the lives of Indigenous communities and contributing to the expansion of European influence in the region.
Modern-Day Importance:
Beyond its historical significance, the Hudson Bay map remains crucial in understanding contemporary Canada. The bay’s vast resources, including its fisheries, mineral deposits, and potential for renewable energy, continue to hold economic importance. The region also plays a vital role in climate change research, as its sensitive ecosystem reflects the impacts of global warming.
Environmental Significance:
The Hudson Bay map reveals a delicate ecosystem that faces numerous challenges. The bay’s waters are home to a diverse array of marine life, including beluga whales, polar bears, and various species of fish. However, these populations are vulnerable to climate change, pollution, and overfishing. The region’s permafrost, a layer of permanently frozen ground, is also susceptible to thawing, which can have significant consequences for infrastructure and the environment.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The Hudson Bay map highlights both challenges and opportunities for Canada. The region’s remote location and harsh climate pose significant logistical and environmental challenges. However, the bay’s vast resources and its potential for sustainable development offer opportunities for economic growth and innovation.
FAQs on the Hudson Bay Map:
1. What is the significance of the Hudson Bay in Canadian history?
The Hudson Bay played a crucial role in the fur trade, shaping Canada’s early development. The Hudson’s Bay Company, established in 1670, established trading posts along the shores of the bay, connecting European markets to the vast resources of North America. These posts served as centers of trade and cultural exchange, influencing the lives of Indigenous communities and contributing to the expansion of European influence in the region.
2. What are the major environmental challenges facing the Hudson Bay?
The Hudson Bay’s ecosystem is vulnerable to climate change, pollution, and overfishing. Rising temperatures are impacting the region’s permafrost, leading to thawing and potential infrastructure damage. Pollution from industrial activities and shipping can also threaten the bay’s delicate marine life.
3. What are the economic opportunities associated with the Hudson Bay?
The Hudson Bay offers potential for economic growth in areas such as fisheries, mineral extraction, and renewable energy. The region’s vast natural resources can be sustainably developed to create economic opportunities while preserving the environment.
4. How does the Hudson Bay map contribute to our understanding of climate change?
The Hudson Bay is a sensitive indicator of climate change. The region’s permafrost thawing, sea ice retreat, and changes in marine ecosystems provide valuable data for understanding the impacts of global warming.
Tips for Understanding the Hudson Bay Map:
- Study the geographical features: Familiarize yourself with the major bays, rivers, and islands within the Hudson Bay region.
- Explore historical maps: Examine historical maps to understand the role of the Hudson Bay in the fur trade and the expansion of European influence.
- Consider environmental factors: Analyze the map in relation to climate change, pollution, and the region’s sensitive ecosystem.
- Research economic opportunities: Explore the potential for economic development in areas such as fisheries, mining, and renewable energy.
Conclusion:
The Hudson Bay map is more than just a geographical representation; it is a window into Canada’s history, culture, and environment. From its role in the fur trade to its significance in climate change research, the bay continues to shape the lives of Canadians and the future of the country. Understanding the map of Hudson Bay is essential for appreciating its unique character and its profound impact on the Canadian landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Vastness: Understanding the Hudson Bay Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!