Deciphering the Landscape: The Essential Uses of Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Deciphering the Landscape: The Essential Uses of Topographic Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Landscape: The Essential Uses of Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Landscape: The Essential Uses of Topographic Maps

Topographic maps are more than just intricate drawings of hills and valleys. They are powerful tools that translate the three-dimensional landscape onto a two-dimensional surface, revealing a wealth of information critical for a diverse range of activities. From planning hiking trails to designing infrastructure, topographic maps provide a fundamental understanding of the terrain, facilitating informed decision-making and efficient execution.
Unveiling the Terrain: The Language of Contours
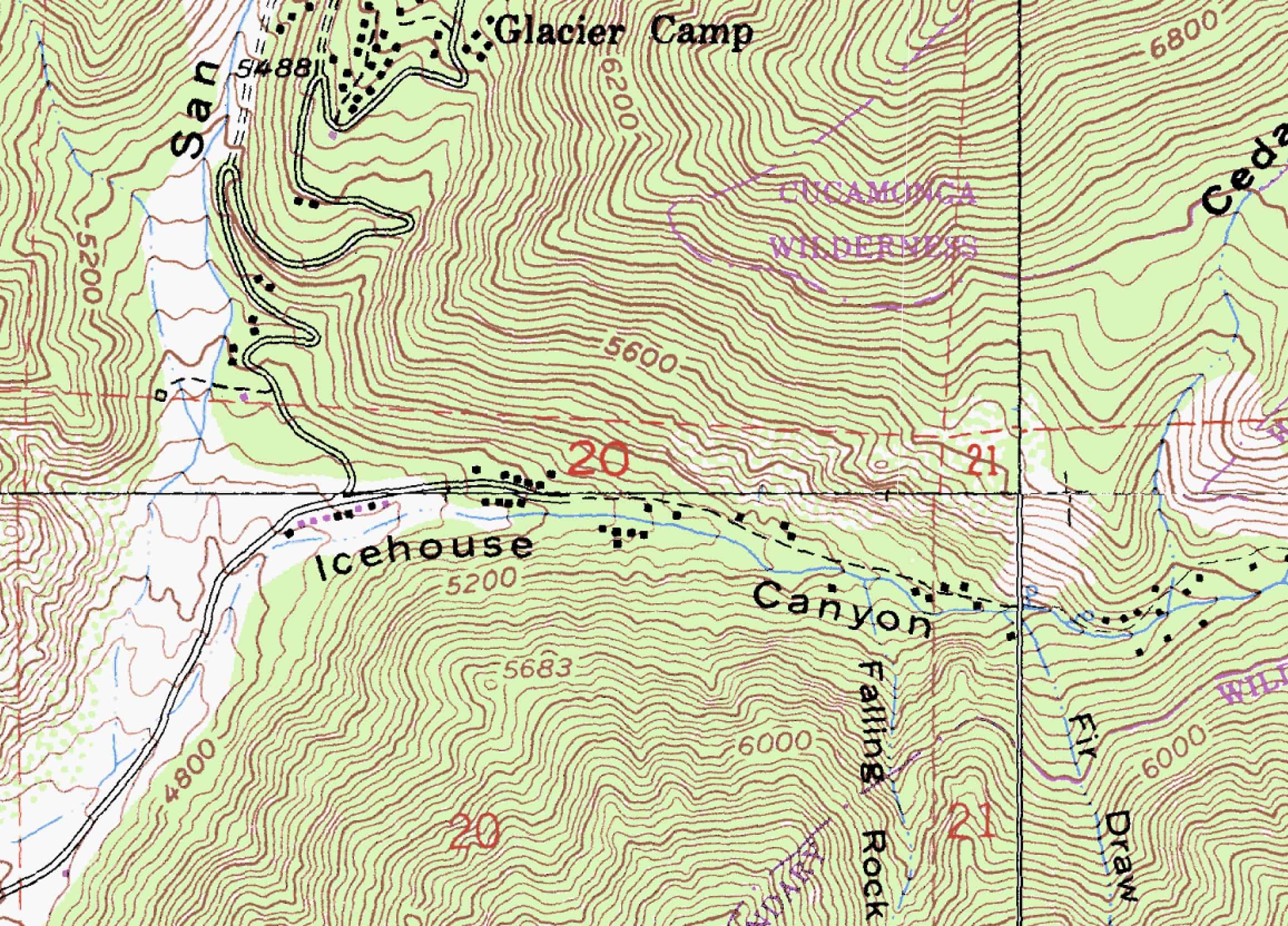
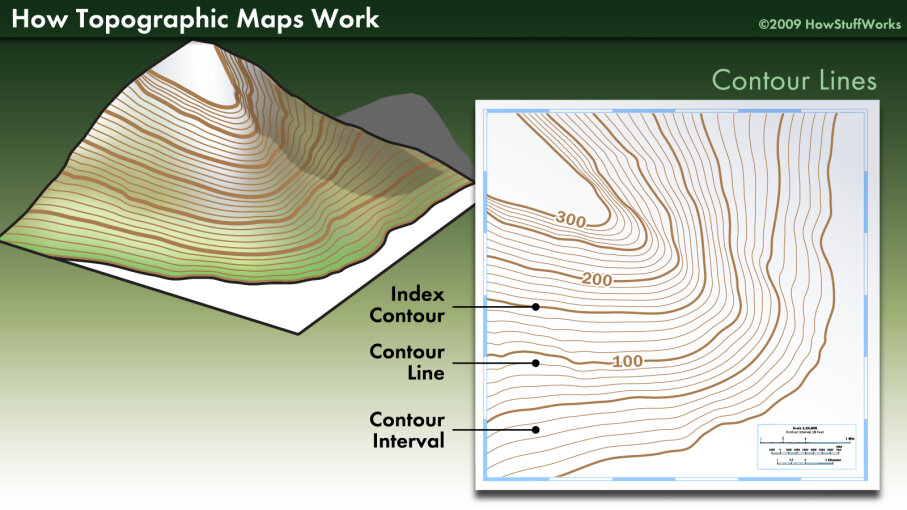
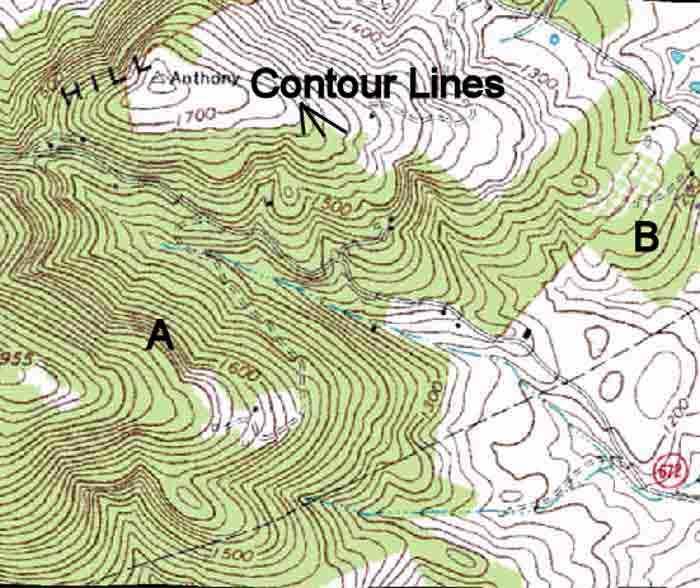
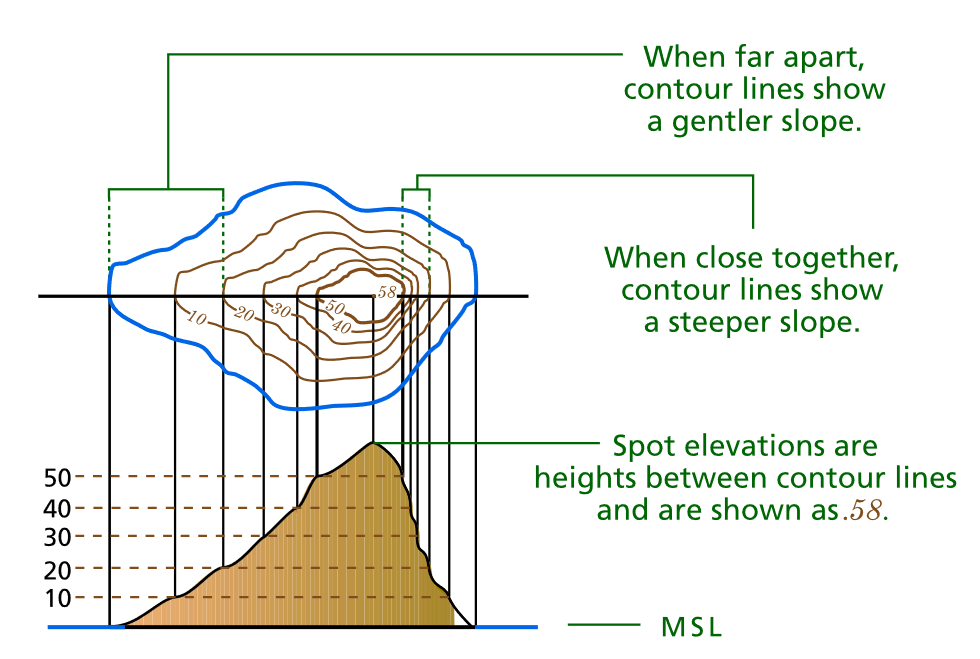
The hallmark of a topographic map is its use of contour lines. These lines connect points of equal elevation, effectively sketching the shape of the land. Imagine slicing through a landscape with a series of horizontal planes; each intersection with the ground would be represented by a contour line on the map. The closer the lines, the steeper the slope; the farther apart they are, the gentler the terrain. This system, combined with elevation points and other symbols, provides a comprehensive overview of the land’s topography, enabling users to visualize the landscape’s three-dimensional nature.
Beyond Elevation: A Wealth of Information
Topographic maps go beyond elevation, incorporating a plethora of data that enriches our understanding of the terrain. They depict features like:
- Hydrography: Rivers, streams, lakes, and wetlands are meticulously mapped, showcasing the flow of water and highlighting potential water sources or obstacles.
- Vegetation: Different types of vegetation are represented, providing insights into the ecological makeup of the area and potential challenges for construction or development.
- Cultural Features: Roads, bridges, buildings, and other human-made structures are included, offering a glimpse into the human footprint on the landscape.
- Land Use: Information about land use, such as agricultural areas, urban zones, or protected areas, helps understand the context of the terrain and its potential applications.
Navigating the Unknown: A Guide for Exploration
Topographic maps are indispensable for outdoor enthusiasts and professionals alike. They serve as reliable guides for:
- Hiking and Backpacking: Hikers and backpackers rely on topographic maps to plan routes, estimate distances, identify challenging terrain, and locate water sources, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
- Mountain Climbing: For climbers, topographic maps provide vital information about elevation changes, rock formations, and potential hazards, aiding in route planning and safety.
- Trail Building and Maintenance: Trail builders and maintainers use topographic maps to determine optimal routes, identify challenging sections, and plan for drainage and erosion control, ensuring accessible and sustainable trails.
- Wildlife Observation and Research: Biologists and wildlife researchers utilize topographic maps to study animal movements, habitat preferences, and the impact of environmental changes on species populations.
Building the Future: A Foundation for Development
Topographic maps play a crucial role in planning and executing various development projects, ensuring sustainability and minimizing environmental impact:
- Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development: Planners rely on topographic maps to assess the feasibility of building roads, bridges, and other infrastructure, taking into account terrain, water bodies, and existing structures.
- Construction and Engineering: Engineers use topographic maps to plan construction projects, optimize site layouts, and ensure structural stability, minimizing potential risks and optimizing resource utilization.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Topographic maps help assess the potential environmental impact of development projects, identifying sensitive areas and suggesting mitigation measures to protect natural resources.
- Resource Management: Topographic maps are essential for managing natural resources like water, timber, and minerals, enabling efficient extraction and sustainable use.
Beyond the Paper: The Digital Revolution
The advent of digital technologies has revolutionized topographic mapping, transforming it from static paper maps to dynamic digital platforms. Digital elevation models (DEMs) and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) allow for interactive visualization and analysis of terrain data, enabling:
- 3D Terrain Modeling: DEMs create realistic 3D representations of the landscape, facilitating virtual exploration and detailed analysis.
- Spatial Analysis and Modeling: GIS platforms allow for complex spatial analysis, overlaying various datasets like population density, soil types, and rainfall patterns to understand relationships and predict impacts.
- Real-time Data Integration: Digital topographic maps can be updated with real-time data, such as weather conditions, traffic updates, and emergency responses, enhancing situational awareness and decision-making.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a regular map?
A: A topographic map focuses on depicting the terrain’s elevation and features, using contour lines to represent changes in altitude. Regular maps, such as road maps or political maps, prioritize information like roads, cities, or political boundaries, without necessarily depicting elevation changes.
Q: How can I read a topographic map?
A: Understanding contour lines is key to reading a topographic map. The closer the lines, the steeper the slope; the farther apart they are, the gentler the terrain. Elevation points and other symbols provide additional information about the landscape.
Q: Where can I find topographic maps?
A: Topographic maps are available from various sources, including government agencies like the United States Geological Survey (USGS), online mapping platforms, and specialized retailers.
Q: What are the benefits of using topographic maps?
A: Topographic maps offer a comprehensive understanding of the terrain, enabling informed decision-making in various fields like outdoor recreation, construction, and environmental management.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps
- Choose the right scale: Select a map with a scale appropriate for your intended use.
- Study the legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and abbreviations used on the map.
- Identify key features: Locate significant features like rivers, mountains, and roads.
- Estimate distances and elevations: Use the scale and contour lines to determine distances and elevation changes.
- Plan your route carefully: Consider terrain, elevation changes, and potential hazards when planning your route.
Conclusion
Topographic maps are essential tools for navigating the landscape, understanding the terrain, and making informed decisions in various fields. Their ability to translate the three-dimensional world onto a two-dimensional surface, combined with their wealth of information, makes them invaluable for outdoor enthusiasts, professionals, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of the earth’s surface. As technology continues to advance, digital topographic maps will play an increasingly important role in shaping our understanding and interaction with the world around us.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Landscape: The Essential Uses of Topographic Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!