Navigating the Air We Breathe: A Comprehensive Look at Air Pollution Maps in the United States
Related Articles: Navigating the Air We Breathe: A Comprehensive Look at Air Pollution Maps in the United States
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Air We Breathe: A Comprehensive Look at Air Pollution Maps in the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Air We Breathe: A Comprehensive Look at Air Pollution Maps in the United States

The air we breathe is an invisible but essential component of our lives. Yet, it is often under threat from pollution, impacting our health and well-being. Air pollution maps, valuable tools for visualizing and understanding this threat, are becoming increasingly crucial for both individuals and policymakers.
Understanding the Landscape of Air Pollution:
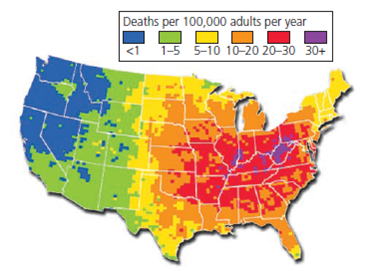
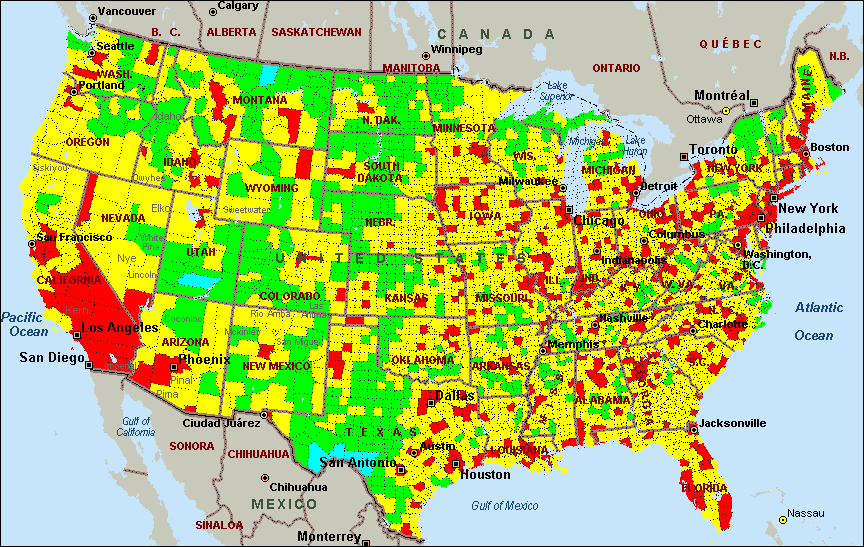
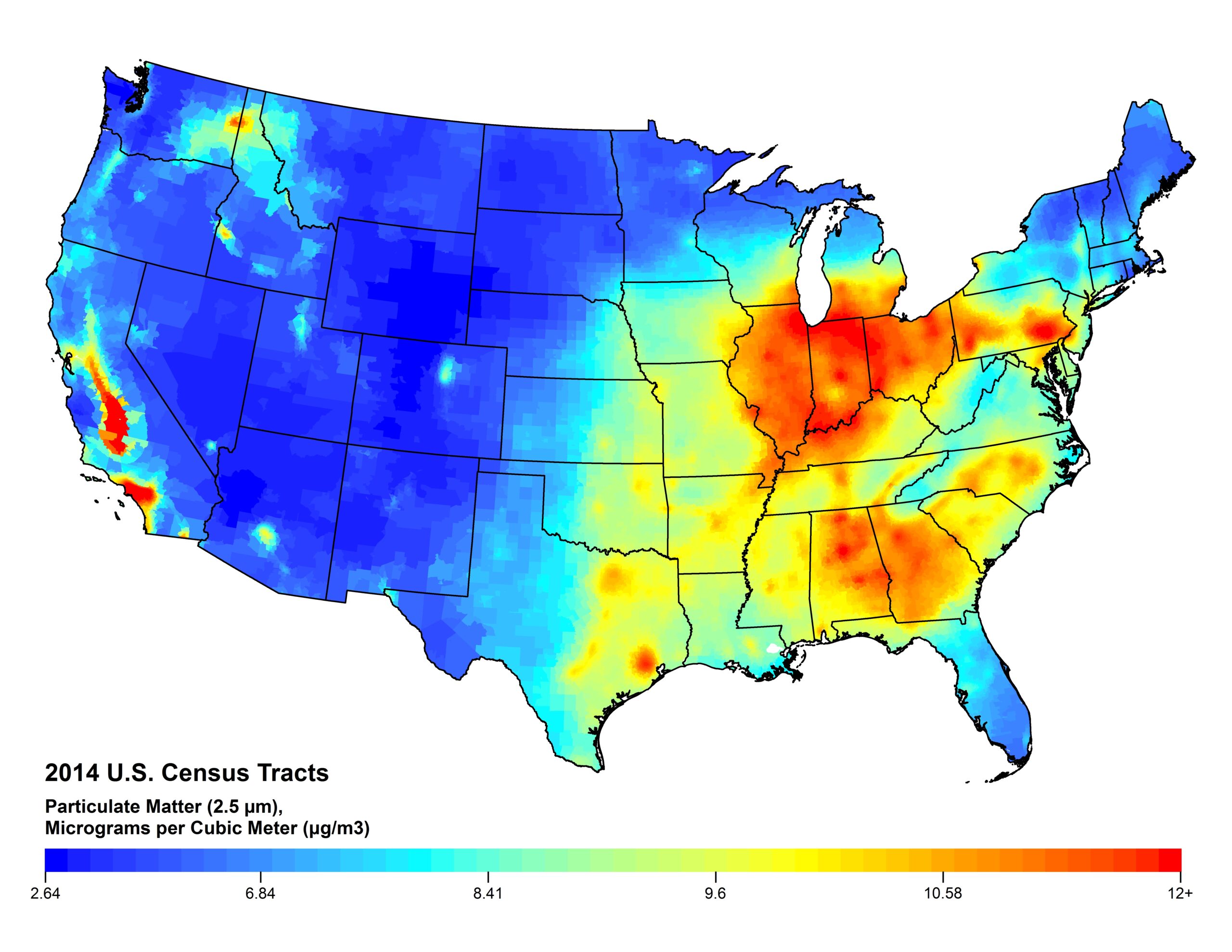
Air pollution maps, often presented as interactive online platforms, provide a visual representation of air quality across a specific geographic area. They utilize data from various sources, including ground-level monitoring stations and satellite imagery, to display real-time or historical information on air pollution levels. This data is typically presented using color-coded scales, with different colors representing varying levels of pollutants.
Key Pollutants and Their Impacts:
Air pollution maps generally focus on key pollutants that pose significant health risks. These include:
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): Microscopic particles, often emitted from vehicle exhaust, industrial processes, and wildfires, that can penetrate deep into the lungs and cause respiratory and cardiovascular problems.
- Ozone (O3): A gas formed by chemical reactions involving pollutants like nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds, primarily from vehicle emissions and industrial activities. Ozone can damage lung tissue and worsen respiratory conditions.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas mainly produced by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, primarily from vehicle emissions. It can reduce oxygen-carrying capacity in the blood, leading to cardiovascular issues.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): A gas released primarily from burning fossil fuels, particularly coal, in power plants and industrial processes. It can contribute to respiratory problems and acid rain.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): A gas primarily produced by combustion processes, mainly from vehicle emissions. It can irritate the lungs and contribute to respiratory problems.
Benefits of Air Pollution Maps:
Air pollution maps provide numerous benefits, empowering individuals, communities, and policymakers to address air quality issues effectively:
- Raising Awareness: By visually showcasing air pollution levels, maps increase public awareness of the issue and its potential health consequences.
- Personal Risk Assessment: Individuals can use maps to identify areas with higher pollution levels and adjust their activities accordingly, minimizing exposure.
- Supporting Health Decisions: Maps can assist healthcare professionals in identifying areas with elevated pollution levels, allowing them to better manage patients with respiratory or cardiovascular conditions.
- Policy and Planning: Air pollution maps provide valuable data for policymakers, helping them develop effective strategies to reduce emissions and improve air quality.
- Environmental Monitoring: Maps contribute to environmental monitoring efforts, enabling scientists to track pollution trends, identify sources, and evaluate the effectiveness of mitigation strategies.
Navigating Air Pollution Maps: A Guide for Users:
To effectively utilize air pollution maps, it is crucial to understand their features and limitations:
- Data Sources: Familiarize yourself with the data sources used by the map, including monitoring station locations and satellite coverage.
- Pollutants Measured: Understand the specific pollutants measured and their associated health risks.
- Timeframe: Determine whether the map displays real-time, hourly, daily, or historical data.
- Geographic Scope: Be aware of the map’s geographic coverage and its limitations in representing localized pollution hotspots.
- Interpretation: Learn to interpret the color-coded scales and understand the implications of different pollution levels.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: How accurate are air pollution maps?
A: The accuracy of air pollution maps depends on the density and reliability of monitoring stations and the quality of satellite data. While maps provide valuable insights, they may not capture localized pollution hotspots or transient events with high accuracy.
Q: What are the limitations of air pollution maps?
A: Maps typically focus on major pollutants, overlooking other potentially harmful substances. They may also struggle to accurately represent localized pollution sources or rapidly changing conditions.
Q: How can I use air pollution maps to protect my health?
A: Use maps to identify areas with elevated pollution levels and adjust your activities accordingly, such as avoiding strenuous exercise during high pollution periods or choosing indoor activities.
Q: What actions can I take to reduce air pollution?
A: Support policies promoting cleaner energy sources, reduce personal vehicle use, adopt energy-efficient practices, and advocate for stricter emission standards.
Tips for Using Air Pollution Maps Effectively:
- Consult multiple sources: Compare data from different maps and monitoring agencies to gain a comprehensive understanding of air quality.
- Consider local factors: Factor in local factors, such as traffic patterns, industrial activities, and weather conditions, when interpreting map data.
- Stay informed: Regularly check maps and follow local air quality alerts to stay informed about pollution levels.
- Engage with your community: Share information about air pollution and advocate for actions to improve air quality.
Conclusion:
Air pollution maps are powerful tools for visualizing and understanding the invisible threat of air pollution. By providing access to real-time and historical data, they empower individuals, communities, and policymakers to take informed actions to mitigate pollution and protect public health. As technology continues to advance, air pollution maps will play an increasingly crucial role in our collective efforts to create cleaner air for all.
![Air Quality in the contiguous United States [3500×2198] : r/MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/i3CuXwkonbxMyAjDJsBEqSJ_qMdv3_Dzwv1WtAlQF_w.gif?format=png8u0026s=d17f253bf79a8adb5fc36cb25cb8b5eede7bf531)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Air We Breathe: A Comprehensive Look at Air Pollution Maps in the United States. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
