Navigating the Ancient World: A Comprehensive Look at Greek and Roman Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Ancient World: A Comprehensive Look at Greek and Roman Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Ancient World: A Comprehensive Look at Greek and Roman Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Ancient World: A Comprehensive Look at Greek and Roman Maps

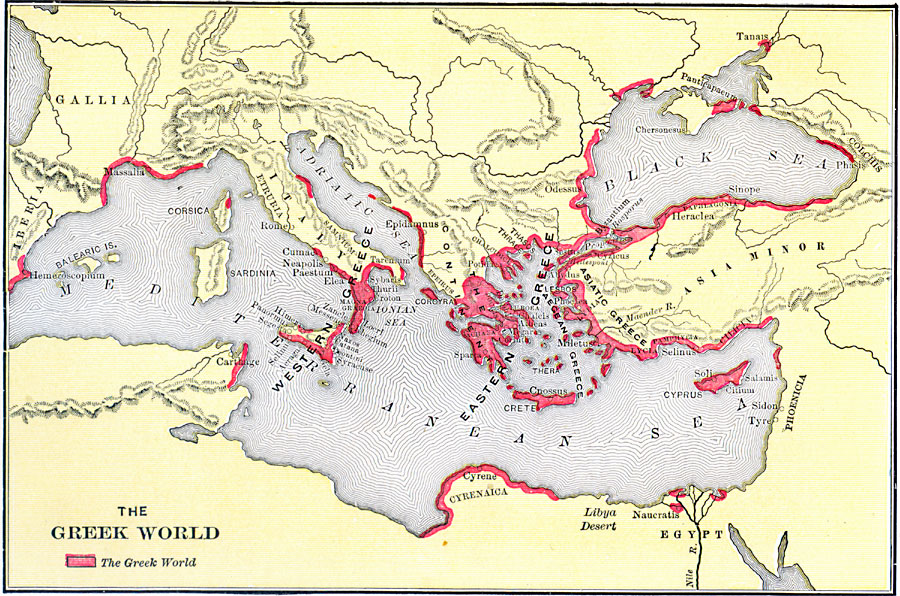
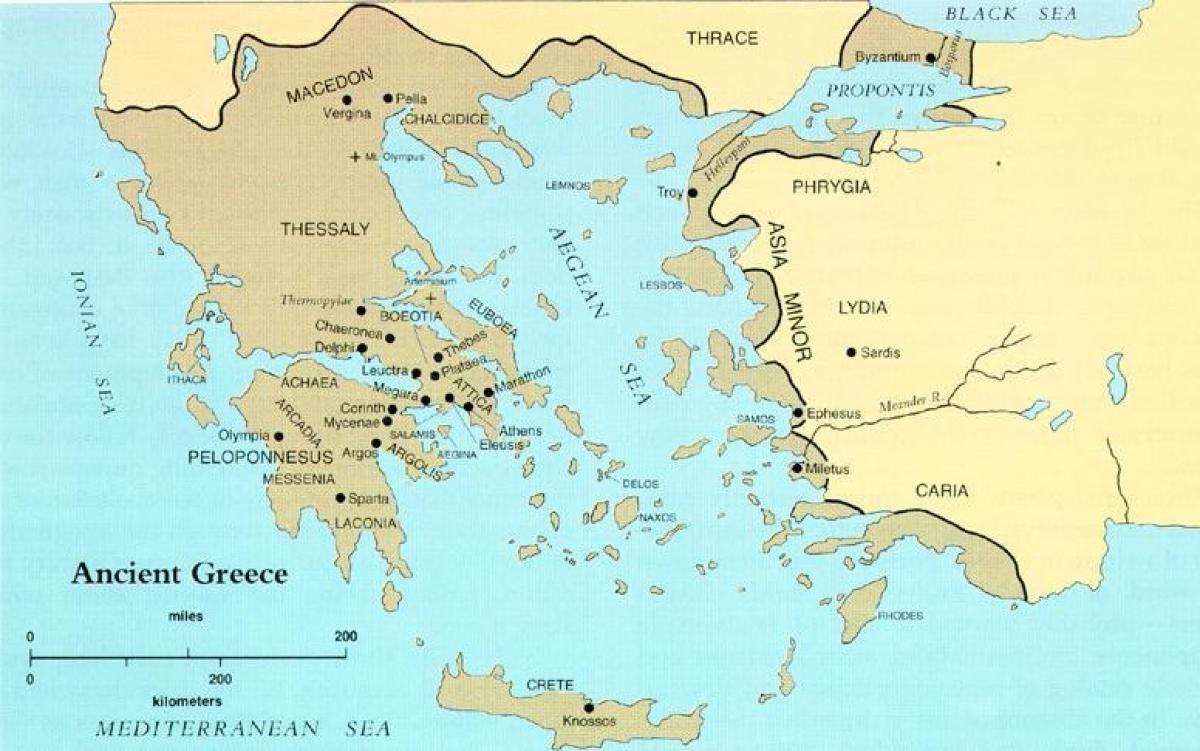
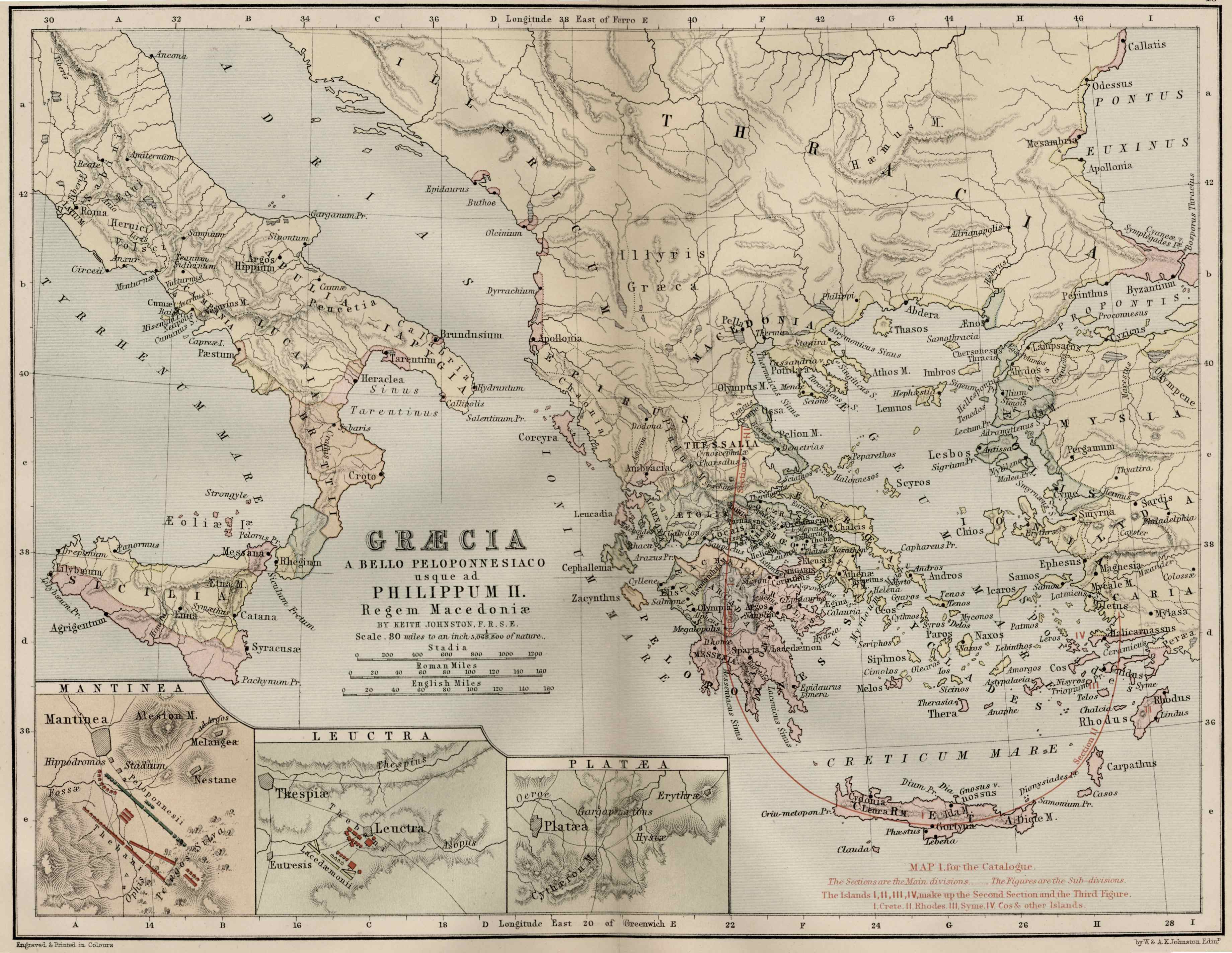
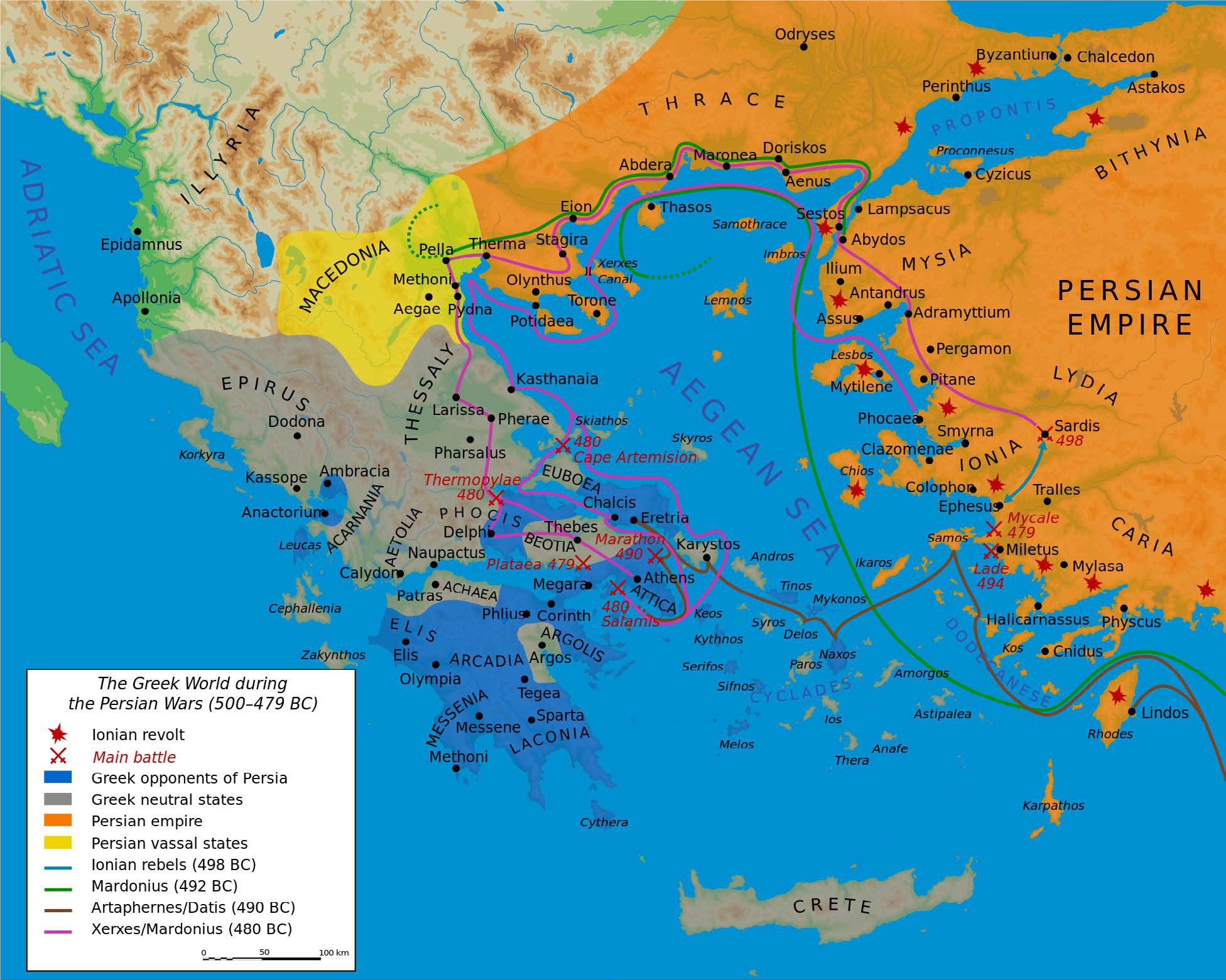
The study of ancient Greece and Rome is enriched by the presence of maps, which serve as invaluable tools for understanding the geographical, political, and cultural landscape of these civilizations. Examining these maps allows us to visualize the physical environment that shaped the lives of ancient peoples, trace the expansion of empires, and gain insight into the complex interactions between different regions.
Understanding the Importance of Maps in Ancient Greece and Rome:
Maps were not merely static representations of the world but dynamic tools used for a variety of purposes. In ancient Greece, maps were employed for:
- Navigation: Sailors relied on maps to navigate the Aegean Sea, charting courses to trade routes and exploring new territories.
- Military Strategy: Generals used maps to plan campaigns, understanding terrain and positioning their forces strategically.
- Land Management: Maps were used to divide land, assess resources, and manage agricultural production.
- Education: Maps were used in schools to teach geography and history, fostering an understanding of the world beyond their immediate surroundings.
Similarly, in ancient Rome, maps played a crucial role in:
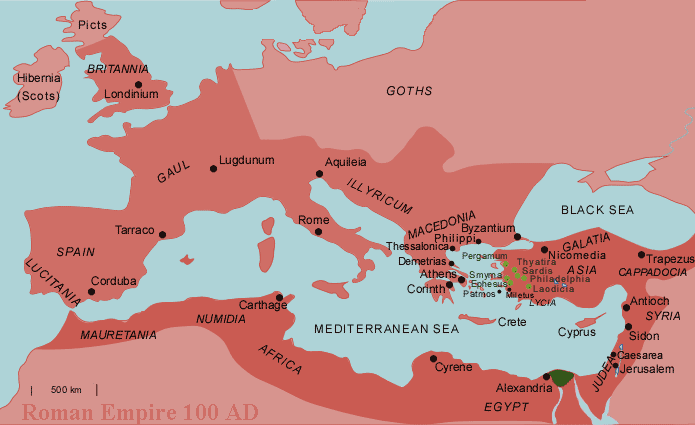
- Empire Building: Maps were essential for managing the vast Roman Empire, allowing administrators to track resources, manage infrastructure, and maintain control over distant provinces.
- Military Campaigns: Roman generals used maps to plan campaigns, assess enemy positions, and deploy troops effectively.
- Urban Planning: Maps were used to design and manage cities, ensuring efficient distribution of resources and effective infrastructure.
- Public Works: Maps were crucial for planning and constructing roads, aqueducts, and other public works projects.
Types of Maps Used in Ancient Greece and Rome:
Ancient maps were created using a variety of materials and techniques, ranging from simple sketches on clay tablets to elaborate mosaics. Some of the most common types include:
- Papyri: These maps, written on papyrus scrolls, were often used for navigation and military purposes. The famous Peutinger Table, a late Roman map depicting the Roman road network, is an example of a papyrus map.
- Mosaics: Intricate mosaics, often found in Roman villas and public spaces, depicted geographical features and provided detailed representations of cities and regions.
- Relief Maps: These three-dimensional models, carved in stone or wood, provided a more realistic representation of terrain and were used for educational and decorative purposes.
- Tables: These maps, often engraved on stone or bronze, were used for practical purposes like surveying and land management.
Key Features of Greek and Roman Maps:
While ancient maps lacked the accuracy and detail of modern cartography, they offered a unique perspective on the world of their time. Key features of Greek and Roman maps include:
- Focus on the Known World: Maps primarily focused on the areas known to the Greeks and Romans, with limited knowledge of regions beyond their immediate sphere of influence.
- Emphasis on Practicality: Maps were designed for practical purposes, prioritizing information relevant to navigation, military strategy, or land management.
- Symbolic Representations: Maps often used symbols to represent geographical features, cities, and other important landmarks.
- Limited Scale and Perspective: Maps lacked the precision of modern cartography, with varying scales and often lacking accurate representation of distances and proportions.
Examining Notable Examples:
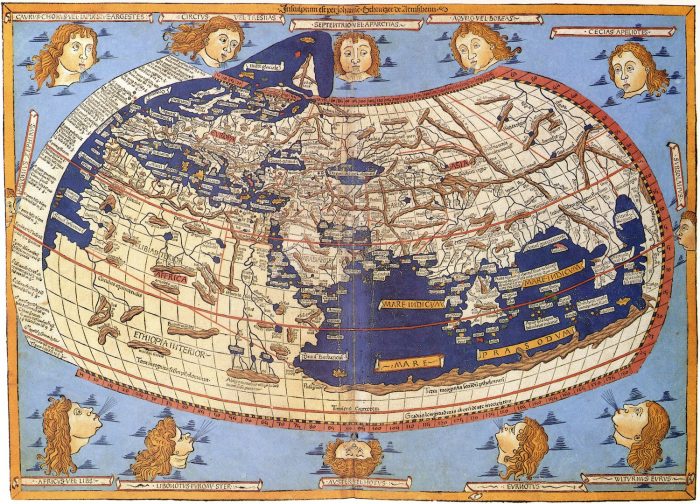
- The Anaximander Map: This map, attributed to the Greek philosopher Anaximander, is considered one of the earliest surviving representations of the world. It depicted the Earth as a flat disk surrounded by a vast ocean.
- The Peutinger Table: This late Roman map, discovered in the 16th century, is a valuable source of information about the Roman road network. It depicts the entire Roman Empire, stretching from Britain to the Middle East.
- The Tabula Peutingeriana: This map, also known as the Peutinger Table, is a 13th-century copy of a 4th-century Roman map showing the road network of the Roman Empire. It is a significant source for understanding the Roman road system and its importance in connecting the empire.
- The Ravenna Cosmography: This 7th-century map, created in Ravenna, Italy, is a unique representation of the world based on ancient Greek and Roman sources. It depicts the world as a circular disk surrounded by the ocean, with Jerusalem at its center.
FAQs Regarding Greek and Roman Maps:
Q: How accurate were ancient Greek and Roman maps?
A: Ancient maps were not as accurate as modern maps. They lacked the precision of modern cartography and often used symbolic representations instead of accurate measurements. However, they provided valuable insights into the geographical knowledge of their time.
Q: What were the limitations of ancient maps?
A: Ancient maps were limited by the available technology and knowledge of the time. They often lacked accurate scales, distances, and geographical features. They also relied on anecdotal accounts and limited exploration, leading to inaccuracies and incomplete representations of the world.
Q: What can we learn from ancient maps?
A: Ancient maps offer a unique window into the world of their time. They reveal the geographical knowledge of ancient peoples, their understanding of the world, and their priorities in representing it. They also provide valuable information about the political, economic, and cultural landscapes of ancient Greece and Rome.
Tips for Understanding Greek and Roman Maps:
- Consider the context: Ancient maps were created for specific purposes and reflect the knowledge and priorities of their time.
- Focus on key features: Pay attention to the geographical features, cities, and other landmarks depicted on the map.
- Compare with modern maps: Comparing ancient maps with modern maps can help you understand the limitations and inaccuracies of ancient cartography.
- Look for symbolism: Ancient maps often used symbols to represent different features and locations.
- Remember the limitations: Ancient maps lacked the precision of modern maps and were often influenced by bias and incomplete information.
Conclusion:
Greek and Roman maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding the ancient world. They provide insights into the geographical, political, and cultural landscapes of these civilizations, revealing their knowledge, priorities, and perspectives. Examining these maps allows us to appreciate the ingenuity and limitations of ancient cartography, enriching our understanding of the past and its impact on the present. By exploring these maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of ancient history and the enduring legacy of these civilizations.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Ancient World: A Comprehensive Look at Greek and Roman Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!