Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions of Japan
Related Articles: Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions of Japan
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions of Japan. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions of Japan
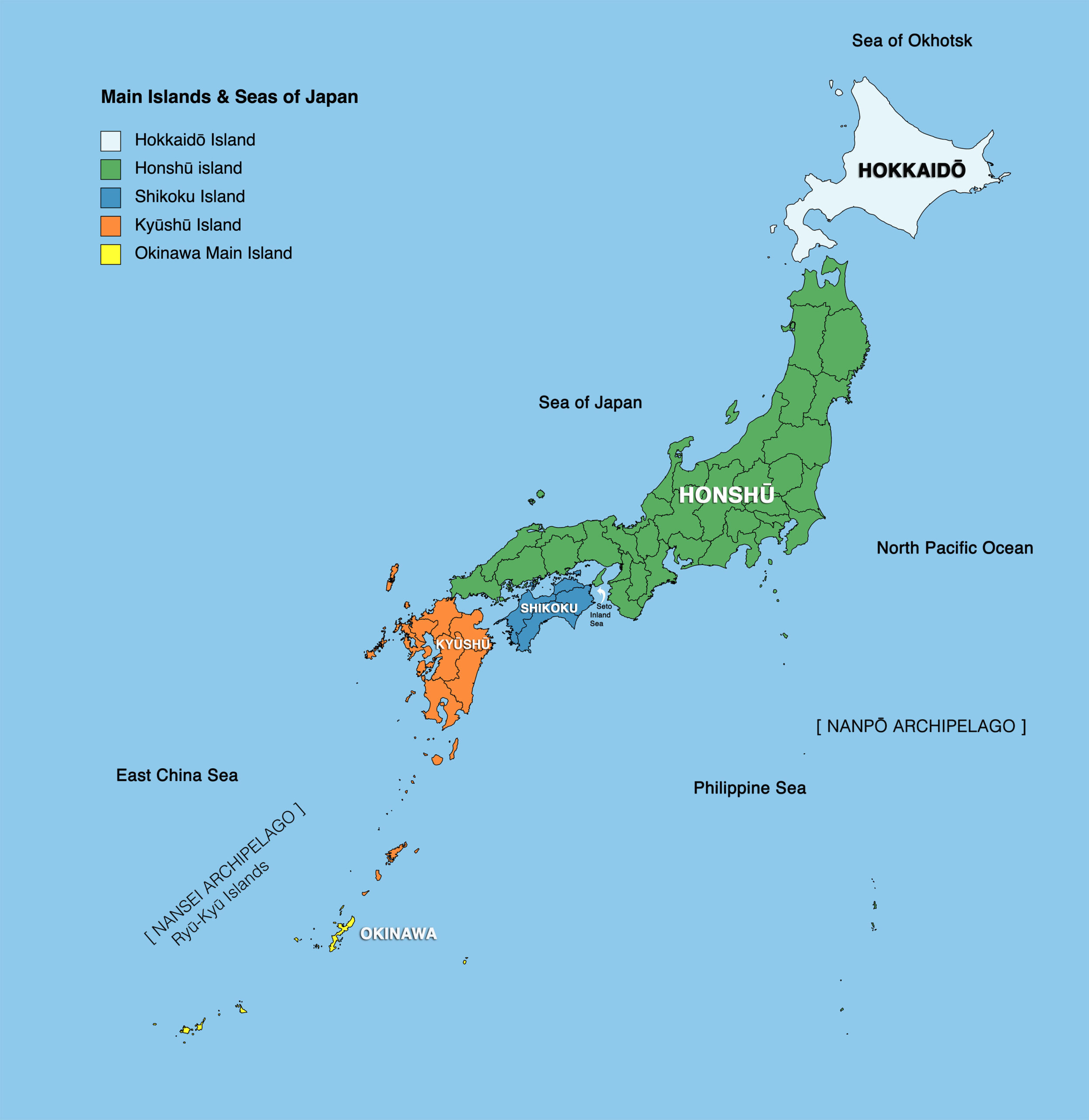
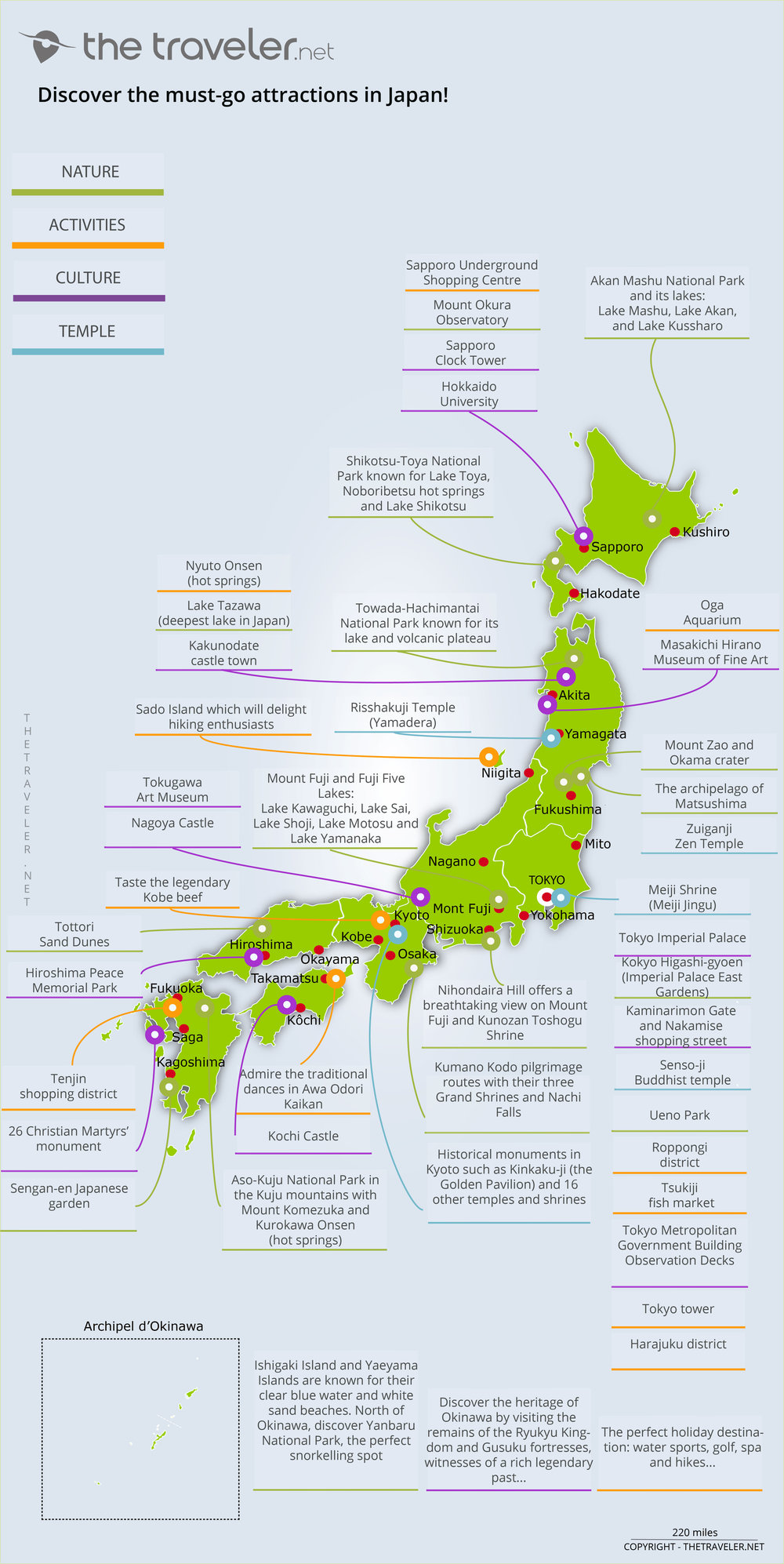
Japan, an island nation rising from the Pacific Ocean, boasts a rich tapestry of culture, history, and natural beauty. Understanding the country’s diverse regions is crucial for appreciating its unique character. This article delves into the geographical and cultural nuances of Japan, providing a detailed overview of its eight major regions, each offering a distinct experience for the discerning traveler.
A Geographic Overview:
Japan’s archipelago, comprised of four main islands (Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu) and thousands of smaller islands, stretches over 3,000 kilometers from north to south. This vast expanse, shaped by volcanic activity and tectonic shifts, gives rise to a diverse landscape. From the snow-capped peaks of the Japanese Alps to the serene beauty of the Inland Sea, Japan offers a spectrum of natural wonders.
Delving into the Regions:
1. Hokkaido: The northernmost island, Hokkaido, is known for its vast wilderness, pristine lakes, and volcanic landscapes. Sapporo, the capital city, is renowned for its annual Snow Festival, while the Shiretoko Peninsula is a UNESCO World Heritage site with abundant wildlife. Hokkaido’s agricultural bounty, particularly its dairy products and seafood, is a key part of its identity.
2. Tohoku: This region, located on the northeastern coast of Honshu, is known for its rugged mountains, hot springs, and ancient temples. Sendai, the largest city, is a cultural hub, while the scenic Matsushima Bay with its picturesque islands is a popular tourist destination. Tohoku is also home to the famous "Tsugaru Shamisen" traditional music, and its coastline is a haven for seafood lovers.
3. Kanto: The most populous region in Japan, Kanto encompasses Tokyo, the capital city, and its surrounding areas. Tokyo’s vibrant energy and modern infrastructure are a stark contrast to the serene beauty of Mount Fuji, a dormant volcano and Japan’s highest peak. The region is also home to Kamakura, known for its numerous Zen Buddhist temples, and Hakone, a picturesque mountain resort area.
4. Chubu: Located in the heart of Honshu, Chubu encompasses the Japanese Alps, a mountain range renowned for its breathtaking scenery and hiking trails. The region is also home to the historic city of Kyoto, the former imperial capital, and Nagoya, known for its impressive Nagoya Castle. Chubu is a hub for traditional crafts, with Takayama being famous for its woodcarving and Hida beef.
5. Kansai: This region, located in the western part of Honshu, is home to Osaka, Japan’s second-largest city, known for its bustling atmosphere and street food culture. Kyoto, with its serene temples and gardens, is also part of Kansai, along with Nara, famous for its friendly deer roaming freely in the city. Kansai is a cultural melting pot, with a strong tradition of performing arts like Kabuki and Bunraku puppet theater.
6. Chugoku: Situated in the southwestern part of Honshu, Chugoku is known for its stunning coastal scenery, including the Seto Inland Sea, with its numerous islands and picturesque harbors. Hiroshima, the city known for its historical significance and the Peace Memorial Park, is a key part of Chugoku. The region is also home to the Izumo Taisha Shrine, one of Japan’s oldest and most important Shinto shrines.
7. Shikoku: The smallest of the four main islands, Shikoku, is known for its spiritual significance and scenic beauty. The island is home to the Shikoku Pilgrimage, a 1,200-kilometer route connecting 88 temples, offering a spiritual journey for pilgrims. Shikoku also boasts stunning natural landscapes, including the Oboke Gorge and the Iya Valley, known for its unique vine bridges.
8. Kyushu: The southernmost main island, Kyushu, is a vibrant region with a distinct culture. Fukuoka, the largest city, is known for its bustling nightlife and delicious ramen. The island is also home to Kumamoto Castle, one of Japan’s most impressive feudal castles, and the volcanic island of Sakurajima, offering breathtaking views of active volcanic activity. Kyushu’s volcanic soils are ideal for growing a variety of fruits, including the famous Miyazaki mango.
Understanding the Importance:
Understanding the regions of Japan is crucial for a deeper appreciation of its cultural diversity, historical significance, and natural beauty. Each region has its unique character, offering a distinct experience for visitors. By exploring these regions, one can gain a comprehensive understanding of Japan’s multifaceted identity.
FAQs:
Q: What is the best time to visit Japan?
A: The best time to visit Japan depends on personal preferences. Spring (March-May) offers cherry blossoms, while autumn (September-November) showcases vibrant foliage. Summer (June-August) is hot and humid, while winter (December-February) brings snow and cold temperatures.
Q: How many regions are there in Japan?
A: Japan is traditionally divided into eight major regions: Hokkaido, Tohoku, Kanto, Chubu, Kansai, Chugoku, Shikoku, and Kyushu.
Q: What are the major cities in each region?
A:
- Hokkaido: Sapporo
- Tohoku: Sendai
- Kanto: Tokyo, Yokohama
- Chubu: Nagoya, Kyoto
- Kansai: Osaka, Kyoto
- Chugoku: Hiroshima
- Shikoku: Matsuyama
- Kyushu: Fukuoka
Q: What are some popular tourist attractions in each region?
A:
- Hokkaido: Shiretoko Peninsula, Sapporo Snow Festival
- Tohoku: Matsushima Bay, Zao Fox Village
- Kanto: Mount Fuji, Tokyo Disneyland, Kamakura
- Chubu: Japanese Alps, Takayama, Shirakawa-go
- Kansai: Fushimi Inari Shrine, Osaka Castle, Nara Park
- Chugoku: Hiroshima Peace Memorial Park, Miyajima Island
- Shikoku: Shikoku Pilgrimage, Oboke Gorge
- Kyushu: Kumamoto Castle, Sakurajima Volcano, Beppu Hot Springs
Tips for Traveling through Japan:
- Plan ahead: Japan’s transportation system is efficient, but booking tickets in advance is recommended, especially for popular attractions.
- Learn basic Japanese: While English is spoken in tourist areas, knowing basic Japanese phrases will enhance your experience and interactions with locals.
- Respect Japanese customs: Bowing, taking off shoes before entering homes and temples, and avoiding loud conversations in public are common courtesies.
- Embrace the local cuisine: Japan is a culinary paradise, with diverse regional specialties. Try local dishes, from ramen in Fukuoka to sushi in Tokyo.
- Explore beyond the major cities: Each region has hidden gems and unique experiences waiting to be discovered.
Conclusion:
The regions of Japan offer a diverse and captivating journey through the country’s rich history, culture, and natural beauty. From the rugged mountains of Hokkaido to the bustling streets of Osaka, each region presents a unique and unforgettable experience. By understanding the distinct character of each region, travelers can embark on a deeper and more meaningful exploration of Japan’s multifaceted identity.
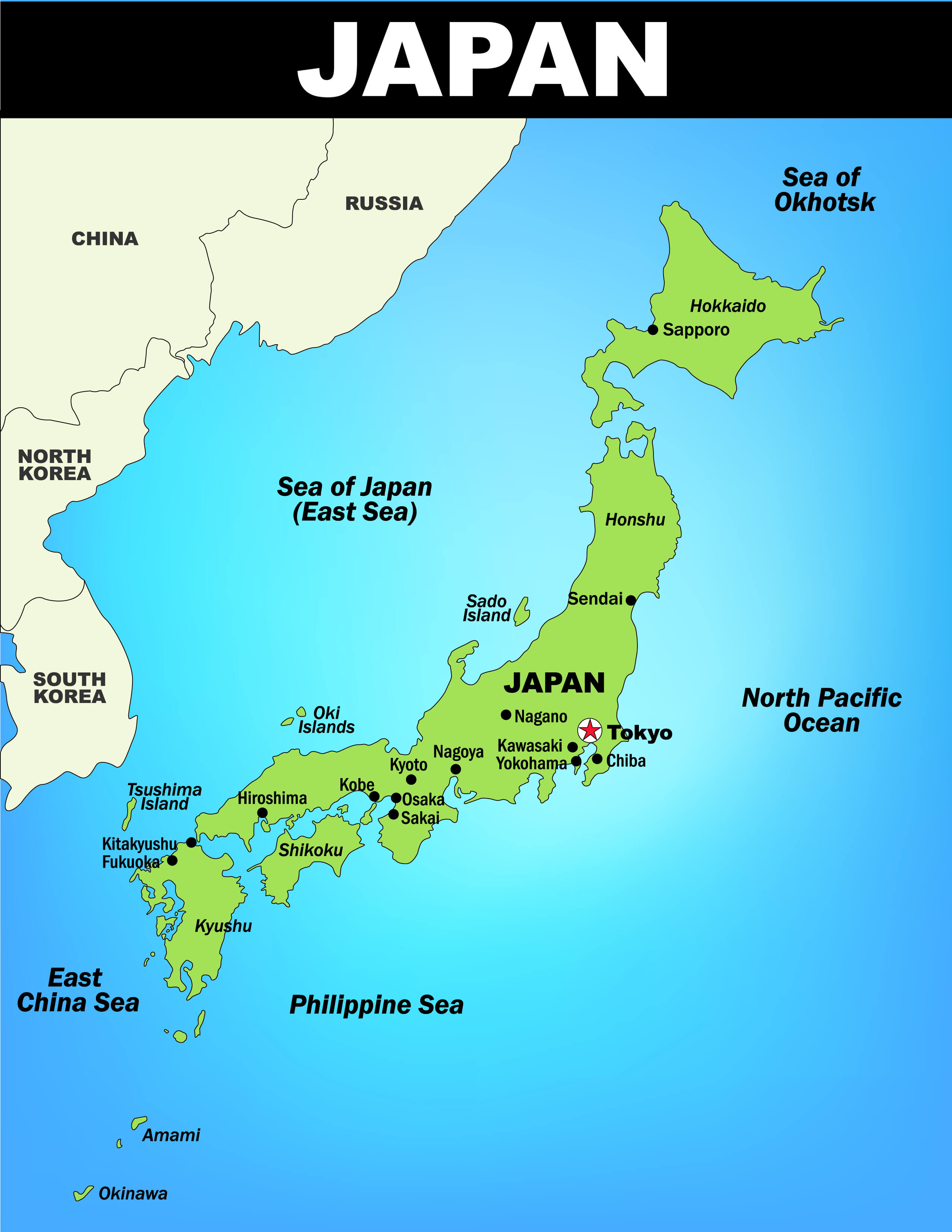

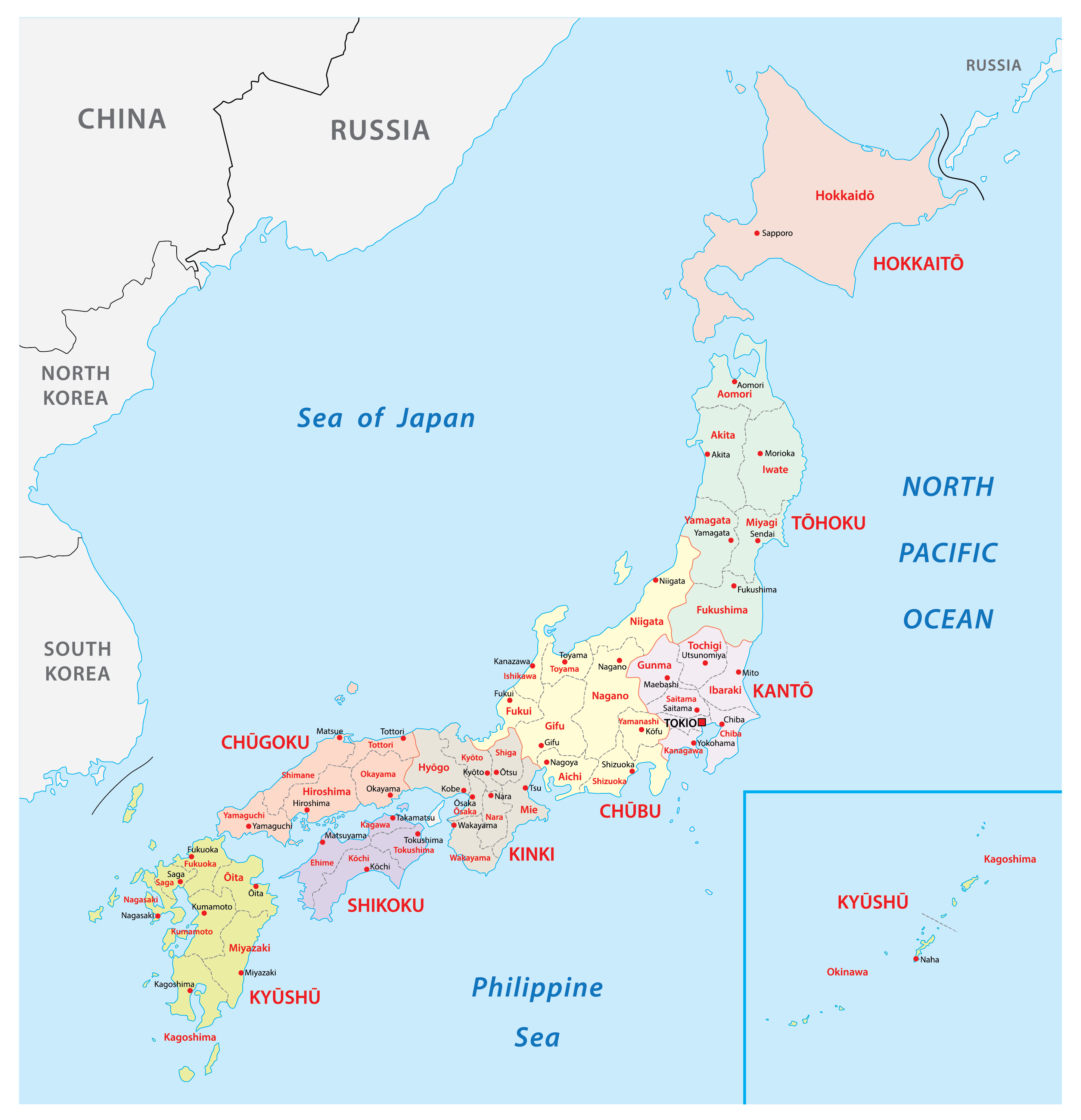


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions of Japan. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!