Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Map Bending for Effective Visualization
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Map Bending for Effective Visualization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Map Bending for Effective Visualization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Map Bending for Effective Visualization

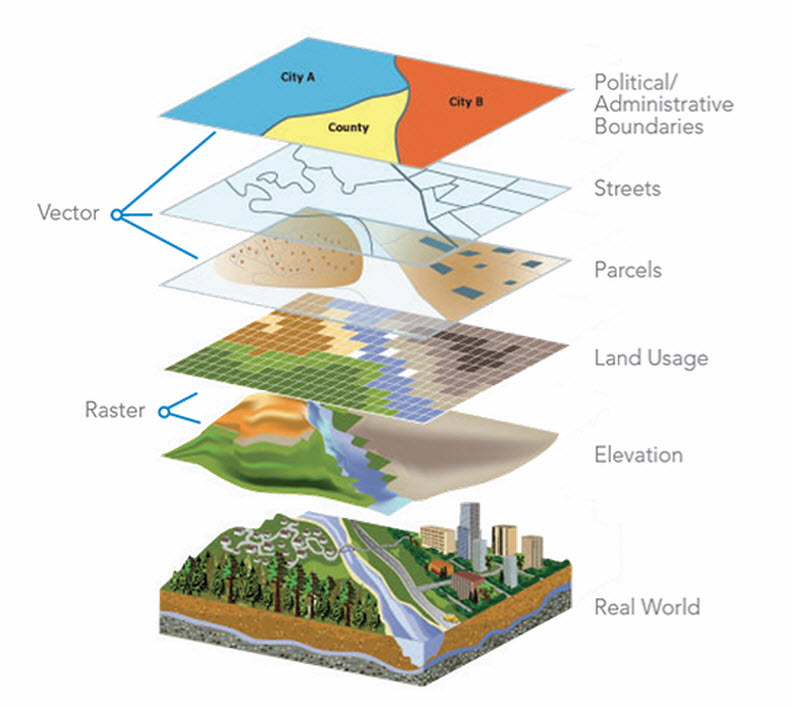
Maps are powerful tools that allow us to visualize and understand the world around us. However, the standard flat representation of a three-dimensional sphere can introduce distortions, particularly at larger scales. This is where the concept of "map bending" comes into play, offering a solution to accurately depict spatial relationships and enhance the understanding of geographic data.
The Challenge of Flattening the Globe:
The Earth is a sphere, but most maps are presented on flat surfaces. This process of transforming a spherical surface onto a plane inevitably introduces distortions. The Mercator projection, a widely used map projection, is a prime example. While it accurately portrays directions and shapes near the equator, it significantly exaggerates the size of landmasses towards the poles. This can lead to misinterpretations of distances, areas, and proportions.
Map Bending: A Solution to Distortion:
Map bending, also known as map warping or map deformation, is a technique that addresses the inherent distortions of flat maps. By strategically manipulating the shape and size of map elements, it aims to create a more accurate and visually compelling representation of spatial data. This manipulation can be achieved through various methods, including:
- Geometric transformations: These involve applying mathematical functions to alter the coordinates of points on the map, stretching or shrinking specific areas to compensate for distortions.
- Cartographic projections: Different map projections are designed to minimize specific types of distortions. Choosing the appropriate projection for the intended purpose can significantly improve the accuracy of the map.
- Data-driven techniques: These methods utilize data about the geographic features to guide the bending process. For example, population density or elevation data can be used to influence the stretching or shrinking of specific areas.
Benefits of Map Bending:
Map bending offers several advantages over traditional flat maps:
- Improved Accuracy: By reducing distortions, map bending provides a more accurate representation of distances, areas, and shapes, enhancing the reliability of spatial analysis.
- Enhanced Visual Clarity: The ability to manipulate map elements allows for a more visually appealing and intuitive presentation of geographic data, facilitating easier comprehension and interpretation.
- Customized Visualization: Map bending techniques can be tailored to specific needs and objectives, allowing for the creation of maps that emphasize particular aspects of the data, such as population distribution, environmental trends, or infrastructure networks.
- Interactive Exploration: Map bending can be integrated into interactive platforms, enabling users to explore and manipulate the map in real-time, gaining deeper insights into the data.
Applications of Map Bending:
Map bending finds applications in a wide range of fields:
- Cartography and Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Map bending is a crucial tool for cartographers and GIS professionals, enabling them to create accurate and visually appealing maps for diverse purposes, including navigation, urban planning, and environmental monitoring.
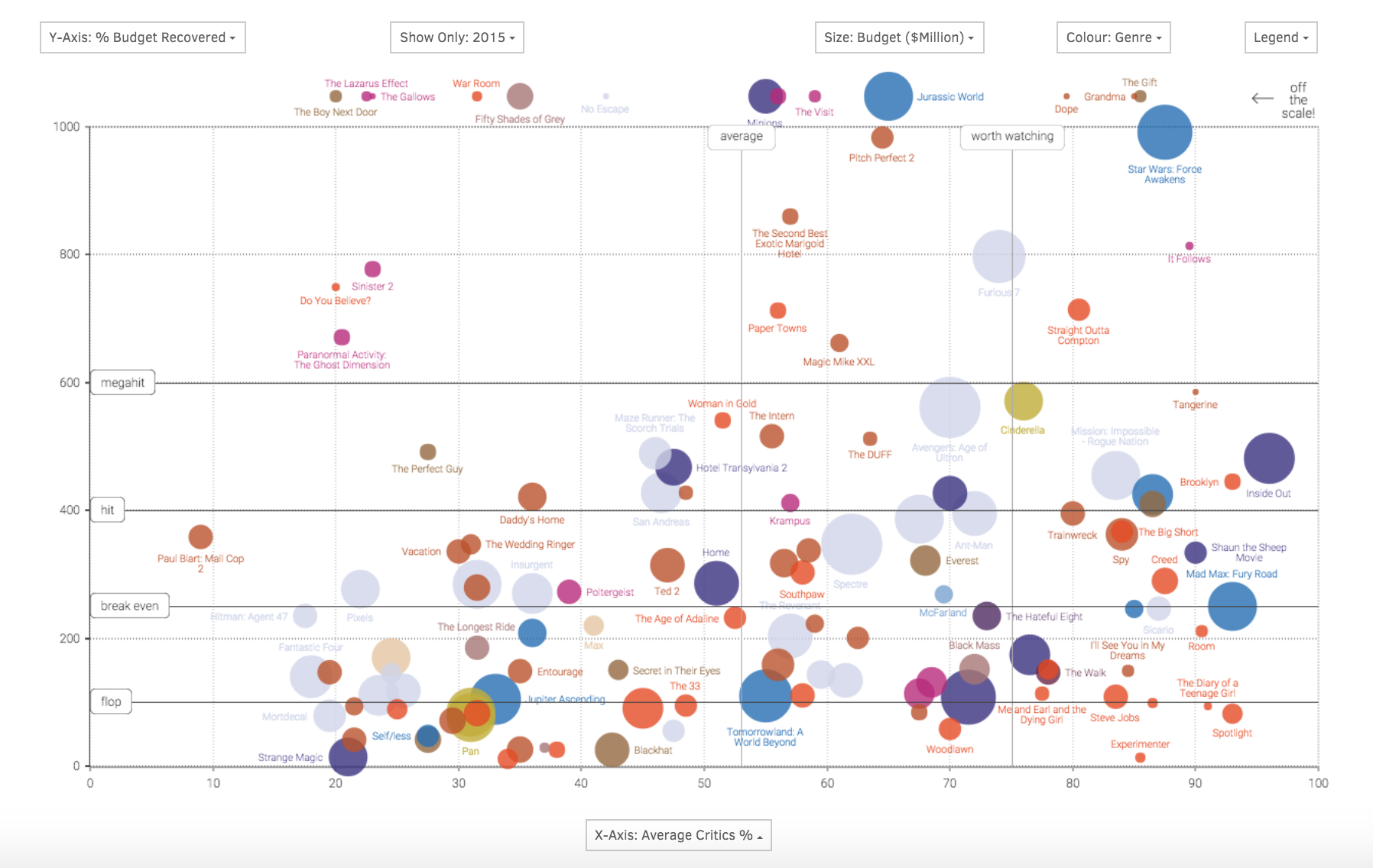
- Data Visualization: By providing a more accurate and visually engaging representation of data, map bending enhances the communication of spatial information, making it more accessible and impactful for audiences.
- Education and Research: Map bending can be used in educational settings to teach students about spatial relationships and geographic concepts, while researchers can utilize it to analyze and visualize complex spatial patterns.
- Design and Architecture: Map bending techniques can be applied in architectural and design projects to create visually compelling and functional representations of urban spaces and landscapes.
FAQs on Map Bending:
1. Is map bending a new technique?
Map bending is not a new concept. Cartographers have been exploring methods to minimize distortions in maps for centuries. However, recent advancements in computer technology and data analysis have significantly expanded the capabilities and applications of map bending.
2. How does map bending affect the accuracy of the data?
While map bending aims to reduce distortions, it’s important to note that it can introduce some degree of inaccuracy. The extent of this inaccuracy depends on the specific bending method used and the data being visualized. It’s crucial to choose the appropriate bending technique and to understand the potential limitations of the resulting map.
3. What are the limitations of map bending?
Map bending techniques are not a universal solution for all mapping challenges. They can be complex to implement, requiring specialized software and expertise. Additionally, the effectiveness of map bending depends on the quality and type of data used, and it may not be suitable for all types of maps.
4. How can I learn more about map bending?
There are numerous resources available to learn more about map bending, including online tutorials, academic publications, and specialized software documentation. Engaging with online communities and attending workshops can also provide valuable insights into the latest advancements and applications of map bending.
Tips for Using Map Bending Effectively:
- Define the purpose: Clearly identify the goals of the map and the specific information you want to convey. This will guide the choice of bending techniques and the overall design of the map.
- Choose the right projection: Select a map projection that minimizes distortions for the specific area and purpose of the map.
- Utilize data-driven techniques: Incorporate relevant data, such as population density or elevation, to inform the bending process and create a more accurate and visually compelling representation.
- Consider the target audience: Design the map with the intended audience in mind, ensuring it is visually appealing, easy to understand, and conveys the desired information effectively.
- Experiment and iterate: Explore different bending techniques and map designs to find the most effective and visually engaging solution for your specific needs.
Conclusion:
Map bending is a powerful tool that addresses the inherent limitations of flat maps, providing a more accurate and visually appealing representation of spatial data. By understanding the principles and applications of map bending, users can create informative and engaging maps that enhance the understanding of geographic information and support decision-making across diverse fields. As technology continues to evolve, map bending techniques are likely to become even more sophisticated, offering even greater possibilities for visualizing and interpreting the world around us.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Map Bending for Effective Visualization. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!