Navigating the Pandemic: A State-by-State Guide to COVID-19 Data
Related Articles: Navigating the Pandemic: A State-by-State Guide to COVID-19 Data
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Pandemic: A State-by-State Guide to COVID-19 Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Pandemic: A State-by-State Guide to COVID-19 Data
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/22029739/Covid_epidemics_states_map.png)
The COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped our world, impacting every aspect of life from healthcare and education to the economy and social interactions. In the face of this global challenge, understanding the spread of the virus at a granular level is crucial. This is where state-by-state maps, displaying real-time data on COVID-19 cases, become invaluable tools for individuals, policymakers, and public health officials.
Understanding the Data Landscape
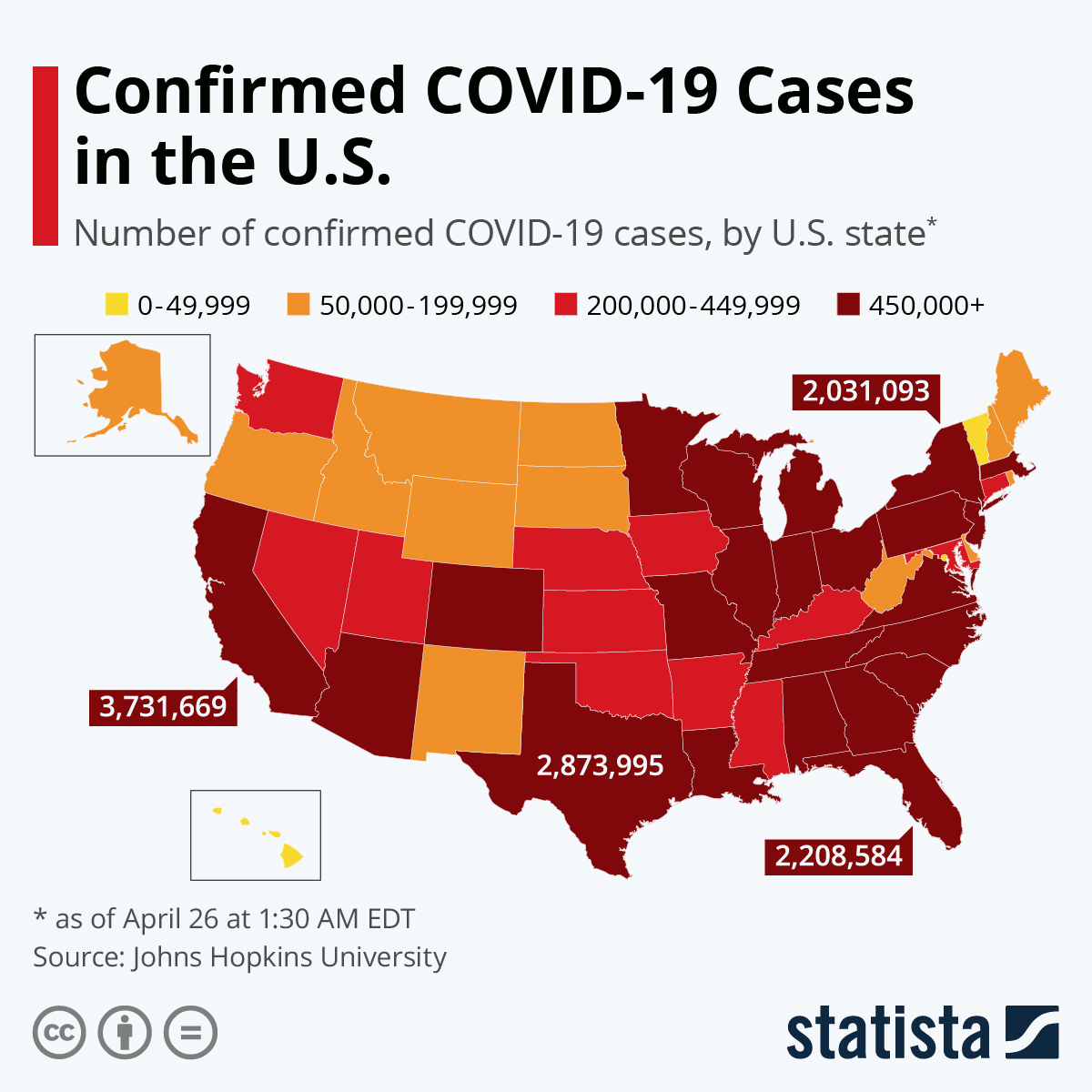
State-by-state COVID-19 maps provide a visual representation of the pandemic’s geographical spread. These maps typically showcase data points such as:
- Case Counts: The total number of confirmed COVID-19 cases in each state, often color-coded to indicate severity levels.
- Hospitalizations: The number of individuals hospitalized with COVID-19, reflecting the strain on healthcare systems.
- Deaths: The total number of COVID-19-related deaths reported in each state, highlighting the human cost of the pandemic.
- Vaccination Rates: The percentage of the population in each state that has been fully vaccinated against COVID-19, providing insights into community immunity.
- Testing Rates: The number of COVID-19 tests conducted per capita in each state, indicating the extent of testing efforts.
The Significance of State-Level Insights
Beyond providing a general overview of the pandemic’s trajectory, state-by-state maps offer critical insights for various stakeholders:
- Individuals: These maps empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and safety. By understanding the prevalence of COVID-19 in their state and local communities, individuals can take necessary precautions, such as mask-wearing, social distancing, and vaccination.
- Policymakers: State and local governments rely on this data to implement targeted public health measures. Maps help identify regions experiencing surges in cases, allowing authorities to allocate resources, enforce restrictions, and implement public awareness campaigns effectively.
- Healthcare Professionals: These maps provide essential information for healthcare providers, enabling them to understand the local burden of COVID-19 and anticipate potential surges in patient volume. This knowledge helps hospitals optimize resource allocation and prepare for increased demand.
- Researchers and Scientists: Researchers use state-level data to analyze the spread of the virus, identify risk factors, and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. This information helps inform the development of new treatments, vaccines, and public health strategies.
Navigating the Data: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the best source for accurate state-by-state COVID-19 data?
A: Reputable sources include the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the World Health Organization (WHO), and state-level health departments. These organizations collect and disseminate data directly from reporting institutions, ensuring accuracy and reliability.
Q: How often is the data on state-by-state maps updated?
A: Data updates vary depending on the source. Some sources update their maps daily, while others update them weekly or even monthly. It is essential to check the data source’s website for the most up-to-date information.
Q: Why might there be discrepancies between different data sources?
A: Discrepancies can arise due to differences in data collection methods, reporting delays, and variations in definitions used to classify cases. It is important to be aware of these potential discrepancies when comparing data from different sources.
Q: What are the limitations of state-by-state maps?
A: While valuable, state-by-state maps have limitations. They do not always capture the nuances of local transmission patterns, especially in densely populated areas with diverse demographics. Additionally, data reporting can be inconsistent across states, leading to potential inaccuracies.
Tips for Effective Data Interpretation
- Focus on trends: Analyze changes in case counts, hospitalizations, and deaths over time to identify potential surges and trends.
- Consider local context: Factor in local demographics, population density, and healthcare infrastructure when interpreting data.
- Compare across states: Use state-by-state maps to compare trends and identify areas with significantly higher or lower rates of COVID-19 activity.
- Stay informed: Regularly check updates from reputable sources to remain informed about the latest developments.
Conclusion
State-by-state COVID-19 maps provide a powerful tool for navigating the pandemic. They offer a visual representation of the virus’s spread, enabling individuals, policymakers, and healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions. While these maps have limitations, they remain a valuable resource for understanding the pandemic’s impact and guiding public health efforts. By leveraging the insights provided by these maps, we can better manage the pandemic and protect public health.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Pandemic: A State-by-State Guide to COVID-19 Data. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!