Navigating the Waters: Understanding the North Carolina Flood Zone Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Waters: Understanding the North Carolina Flood Zone Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Waters: Understanding the North Carolina Flood Zone Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Waters: Understanding the North Carolina Flood Zone Map
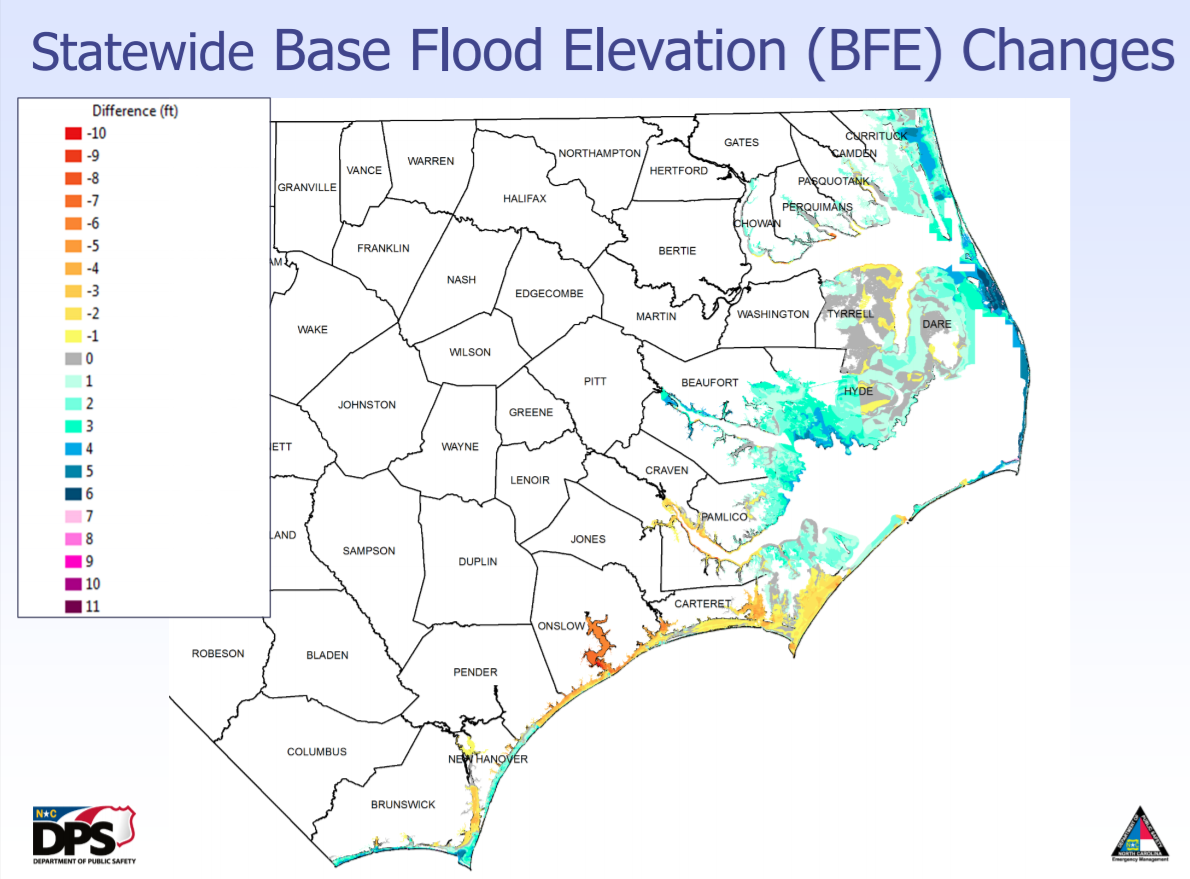
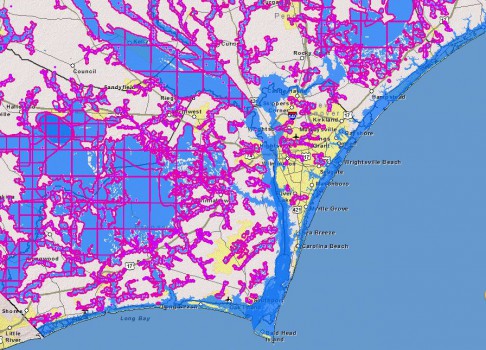
North Carolina, with its diverse landscapes, from the rugged mountains to the sprawling coastal plains, is susceptible to flooding. The state’s proximity to the Atlantic Ocean, its extensive river systems, and its vulnerability to hurricanes and other weather events make understanding flood risk crucial for residents, businesses, and communities alike. The North Carolina Flood Zone Map, a vital tool developed by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), provides a comprehensive overview of flood hazards across the state, serving as a cornerstone for informed decision-making and mitigation efforts.
Decoding the Map: Flood Zones and Their Implications
The North Carolina Flood Zone Map, often referred to as the Flood Insurance Rate Map (FIRM), categorizes areas based on their likelihood of experiencing flooding. These flood zones are designated using a standardized system of letters and numbers:
- Special Flood Hazard Areas (SFHAs): These are the areas with the highest risk of flooding, typically classified as Zone A or Zone AE. Zone A represents areas with a 1% annual chance of flooding (a 100-year flood), while Zone AE indicates areas with a 1% chance of flooding and a defined base flood elevation (BFE).
- Areas of Minimal Flood Hazard (AML): These areas have a lower risk of flooding compared to SFHAs, typically classified as Zone X. However, it’s important to note that even areas designated as AML can still experience flooding.
- Other Zones: The map also includes other zones, such as Zones B, C, and D, which represent areas with varying degrees of flood risk.
Understanding the flood zone designation for a property is crucial for several reasons:
- Flood Insurance Requirements: Properties located within SFHAs are typically required to obtain flood insurance if they have a federally backed mortgage. Flood insurance policies can provide financial protection against flood damage, mitigating potential financial hardship.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Building codes and regulations often differ depending on the flood zone designation. Properties in SFHAs may require specific construction standards, such as elevated foundations, to minimize flood damage.
- Community Planning and Development: The flood zone map provides critical data for local governments and planners in developing strategies for flood mitigation, infrastructure development, and land use planning.
Beyond the Map: Understanding Flood Risk Dynamics
While the flood zone map offers a valuable snapshot of flood risk, it’s important to recognize that flood hazards are dynamic and influenced by various factors:
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels, increased precipitation, and more frequent extreme weather events due to climate change can exacerbate flood risks, potentially leading to changes in flood zone designations over time.
- Land Use Changes: Urban development, deforestation, and other land use modifications can alter drainage patterns and increase flood susceptibility in previously unaffected areas.
- River and Coastal Dynamics: Changes in river flow, coastal erosion, and storm surge patterns can significantly impact flood risk, even in areas not currently designated as SFHAs.
Accessing and Utilizing the Flood Zone Map
The North Carolina Flood Zone Map can be accessed through various resources:
- FEMA’s Flood Map Service Center: This online portal provides access to the most up-to-date flood zone maps, allowing users to search by address, location, or map number.
- North Carolina Department of Insurance: The state’s insurance department offers resources and guidance on flood insurance and flood risk, including information about the flood zone map.
- Local Government Agencies: Many local governments maintain their own flood zone maps and provide additional information on local flood risks and mitigation strategies.
FAQs about the North Carolina Flood Zone Map
Q: What if my property is not located within a designated flood zone?
A: While properties outside of SFHAs may have a lower risk of flooding, it’s important to note that they are not immune. Flood risks can be influenced by various factors, including proximity to rivers, streams, and coastal areas, and can vary over time. It’s advisable to consult local authorities and consider flood insurance even for properties outside of designated flood zones.
Q: How often are the flood zone maps updated?
A: FEMA regularly updates flood zone maps based on new data, changes in flood risk, and other factors. The frequency of updates varies depending on the specific area and the nature of the changes.
Q: What happens if my property is reclassified to a higher flood zone?
A: If your property is reclassified to a higher flood zone, you may be required to purchase flood insurance if you have a federally backed mortgage. Additionally, you may need to comply with stricter building codes and regulations for future renovations or construction projects.
Q: Can I appeal a flood zone designation?
A: Yes, property owners can appeal a flood zone designation if they believe it is inaccurate or unfair. The appeal process involves providing evidence and documentation to support the claim.
Tips for Navigating the North Carolina Flood Zone Map
- Consult with a qualified professional: Seek guidance from a licensed surveyor, engineer, or other qualified professional to accurately interpret the flood zone map and assess your property’s specific flood risk.
- Research flood history: Explore historical flood data for your area to gain a better understanding of past flood events and potential future risks.
- Consider flood mitigation measures: Implement flood mitigation strategies, such as elevating structures, installing flood barriers, or improving drainage, to reduce flood damage and minimize risks.
- Stay informed about updates: Regularly check for updates to the flood zone map and stay informed about changes in flood risk.
Conclusion
The North Carolina Flood Zone Map is an indispensable tool for understanding and mitigating flood risk in the state. By providing a clear picture of flood hazards, the map empowers residents, businesses, and communities to make informed decisions regarding flood insurance, building codes, and land use planning. As climate change continues to influence weather patterns and flood risks, the map will remain a vital resource for navigating the challenges posed by a changing environment. By understanding the information provided by the map and taking proactive steps to mitigate flood risks, North Carolina can build a more resilient future for its communities and its natural resources.

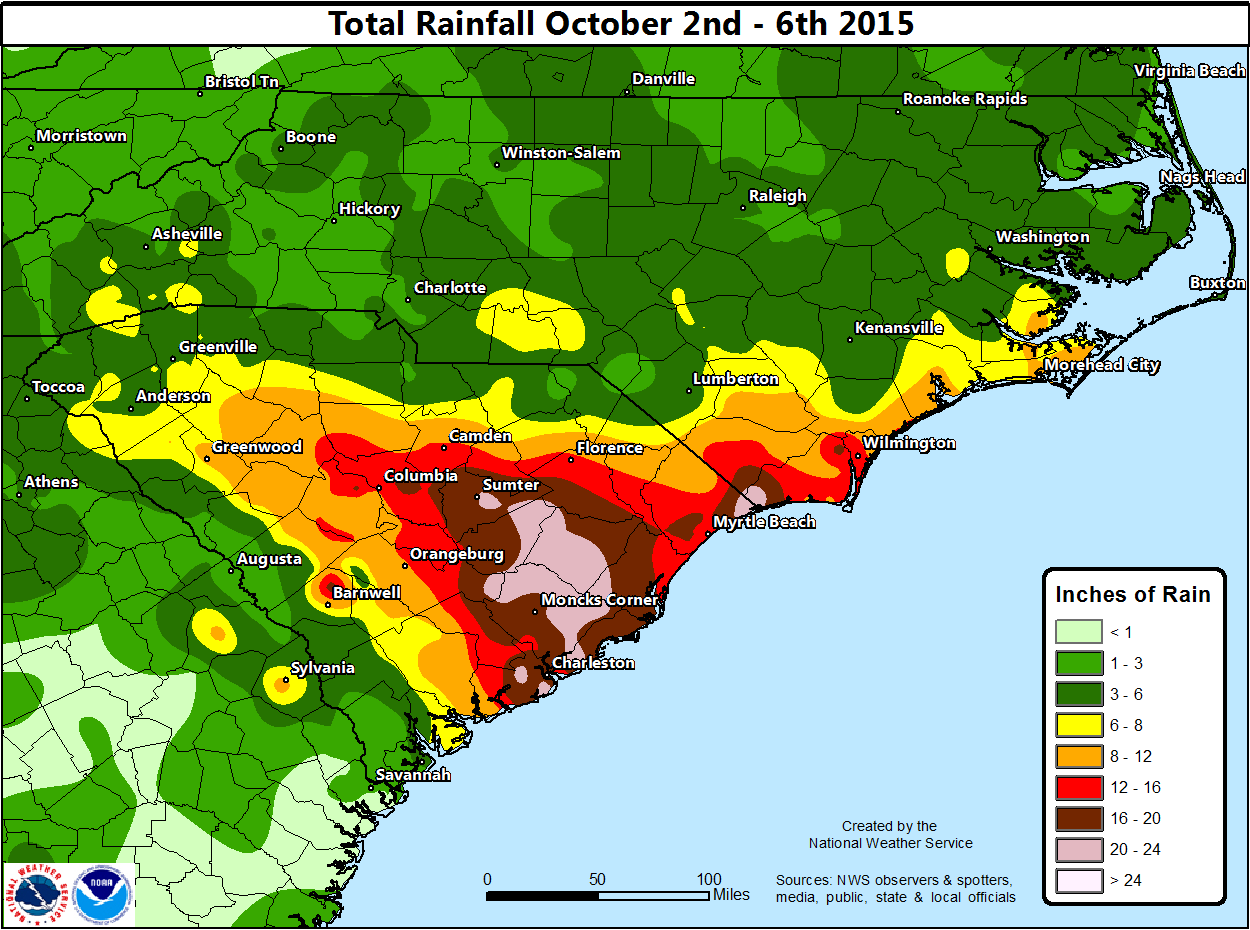
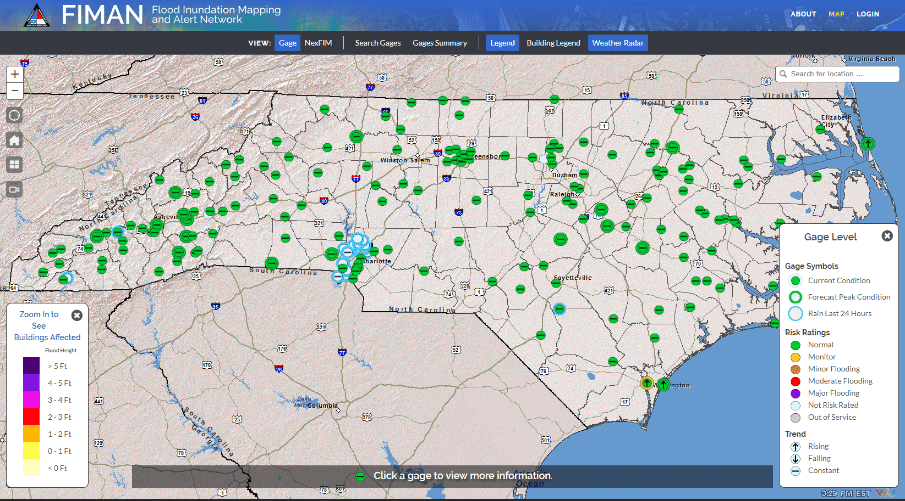

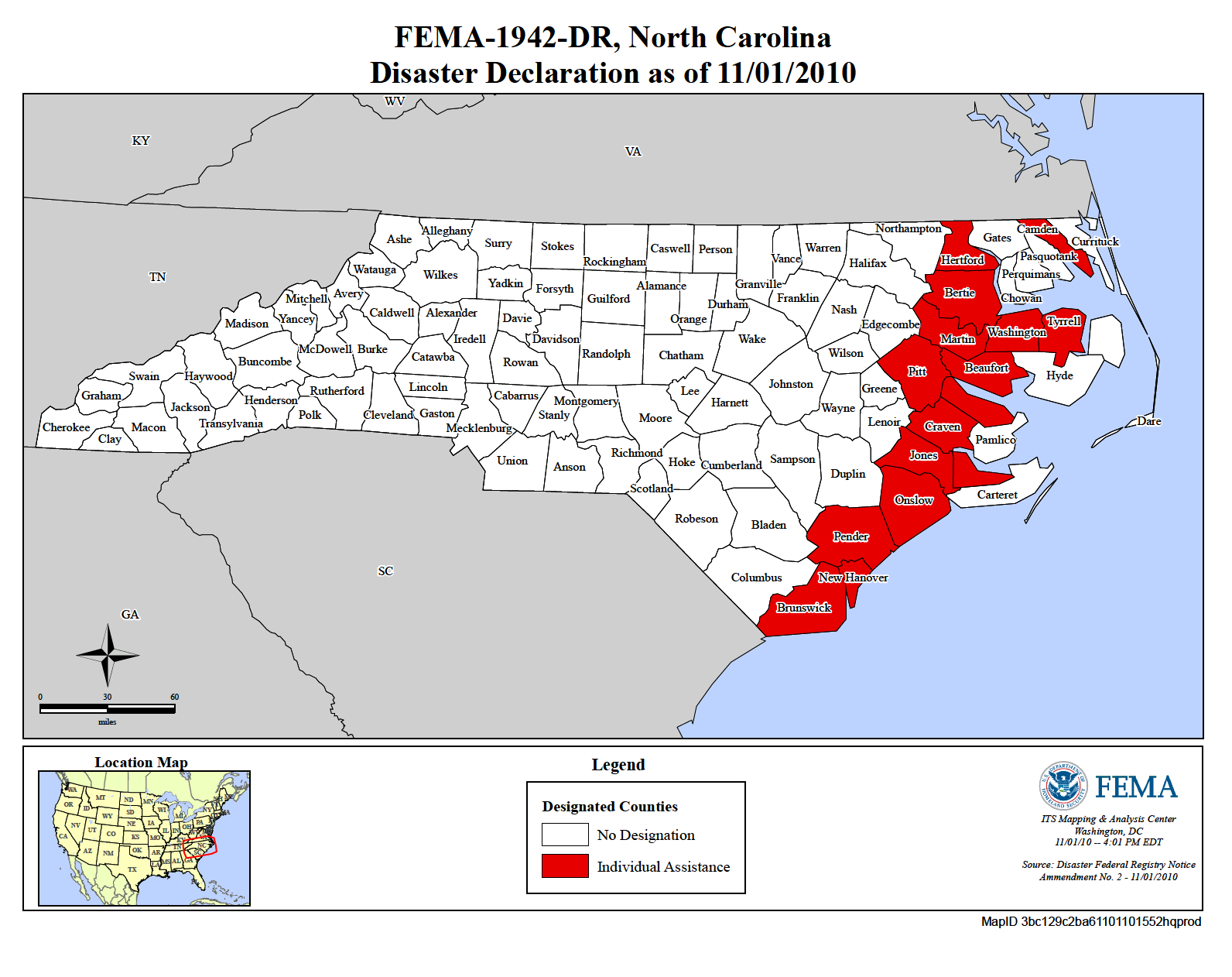

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Waters: Understanding the North Carolina Flood Zone Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!