The Indian Railway Network: A Vital Lifeline Across a Vast Landscape
Related Articles: The Indian Railway Network: A Vital Lifeline Across a Vast Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Indian Railway Network: A Vital Lifeline Across a Vast Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Indian Railway Network: A Vital Lifeline Across a Vast Landscape
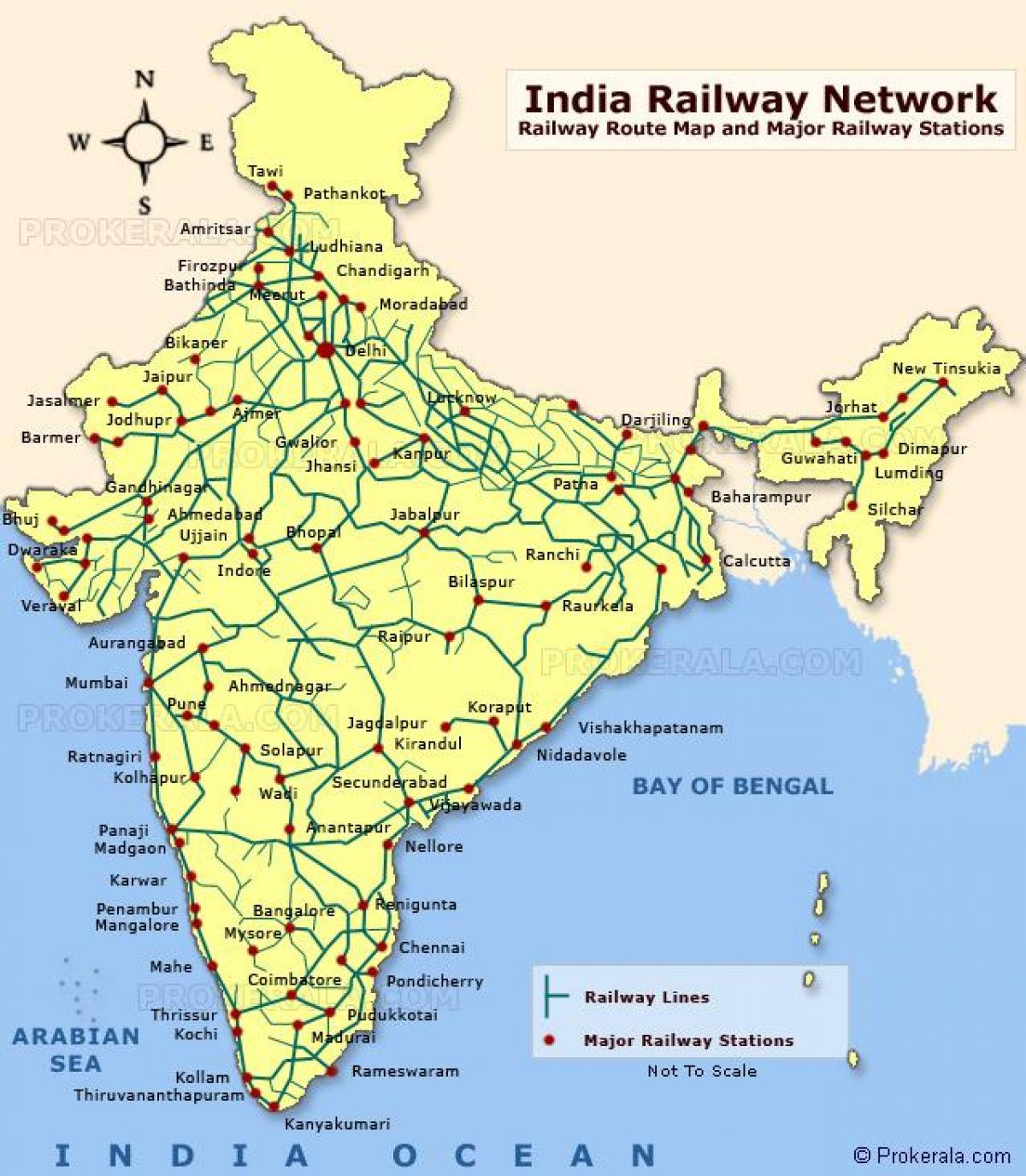
The Indian railway network is a colossal undertaking, spanning over 67,000 kilometers and connecting every corner of the country. This vast network, the fourth largest in the world, is more than just a mode of transport; it is a lifeline for millions of Indians, facilitating trade, tourism, and societal progress. Understanding the intricate tapestry of this network, its history, and its future is crucial for grasping the pulse of India’s economic and social landscape.
A Historical Perspective:
The seeds of the Indian railway network were sown in the mid-19th century under British rule. The first train journey took place in 1853, carrying passengers a mere 21 miles from Bombay to Thane. This marked the beginning of a transformative era, as railway lines progressively extended across the subcontinent, connecting cities, ports, and agricultural hubs. The network’s growth was fueled by the need to transport raw materials, facilitate trade, and bolster military movements.
The Modern Network:
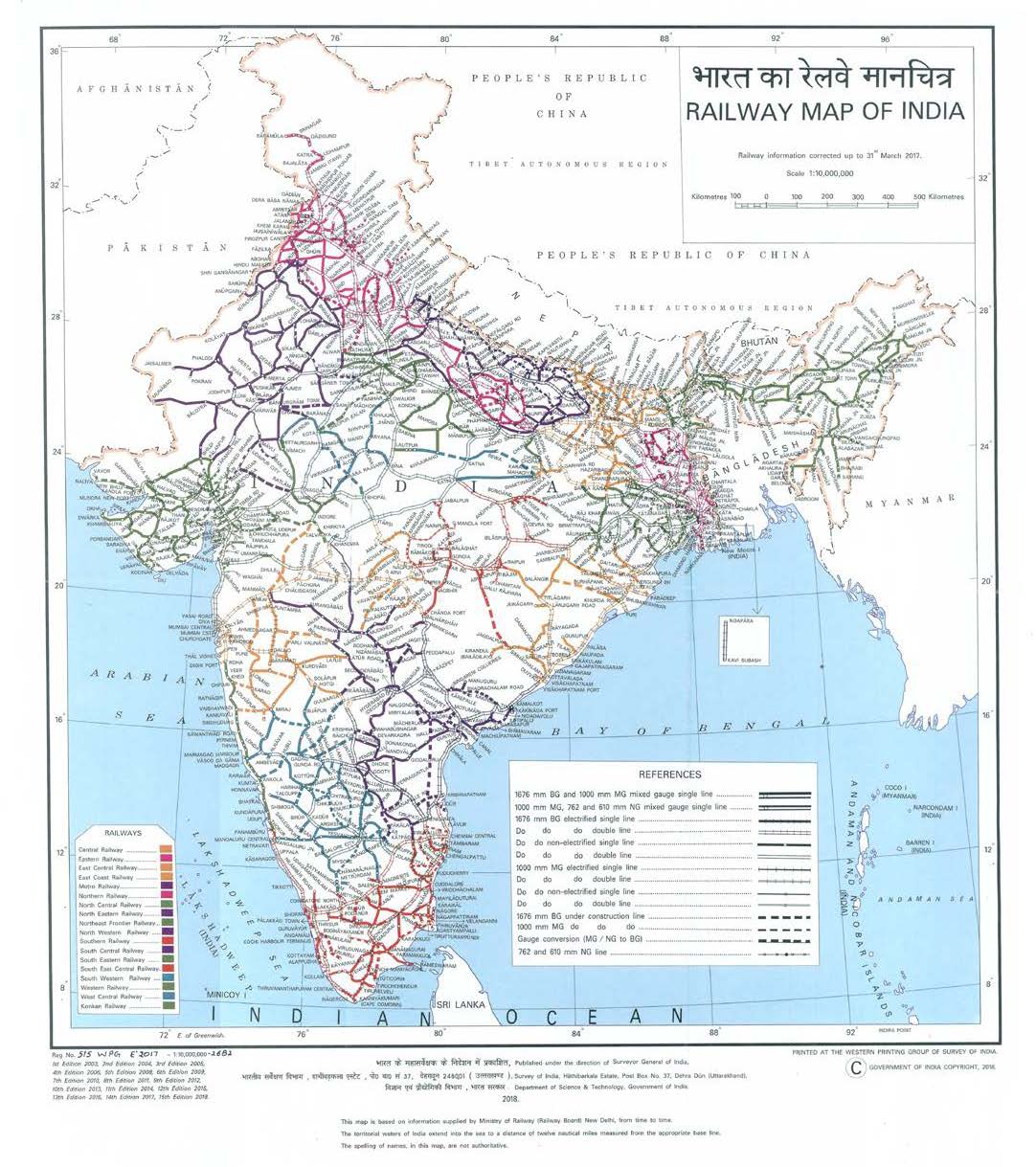
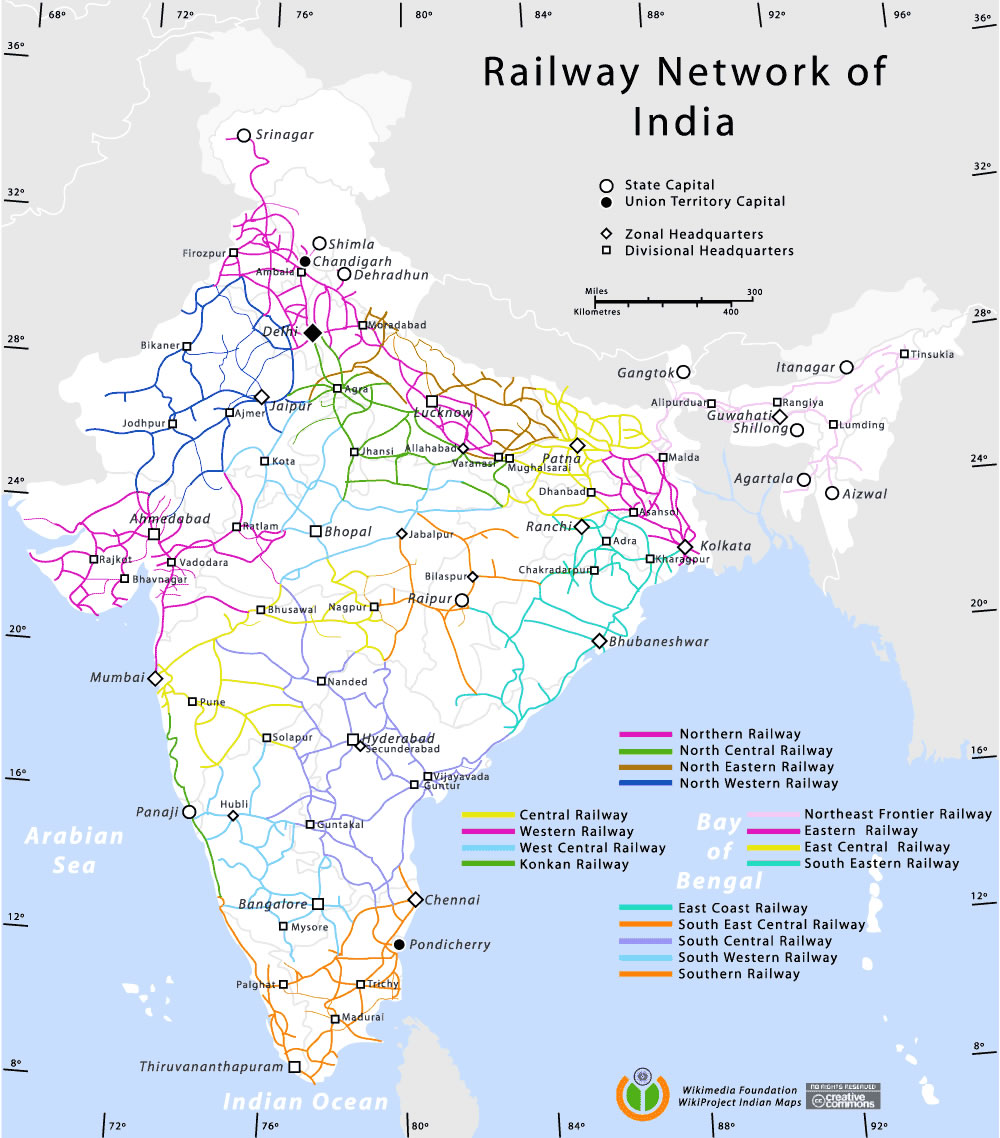
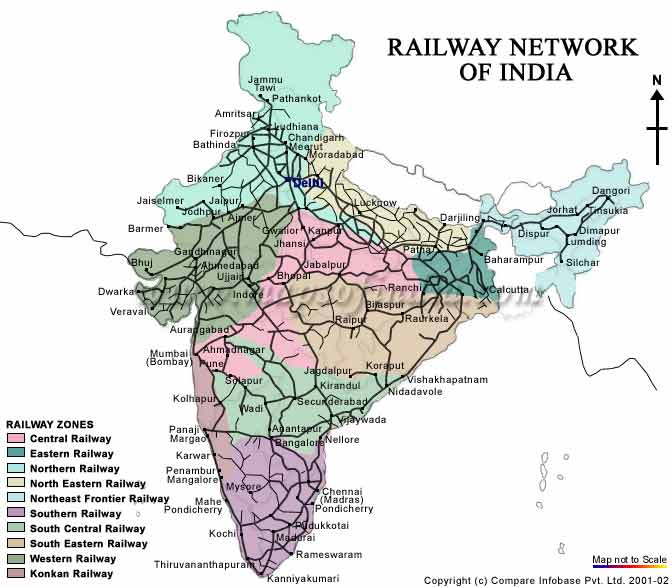
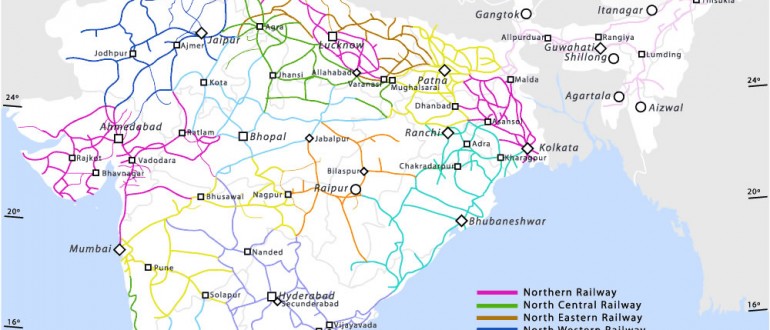
Today, the Indian Railways is a state-owned enterprise, operating under the Ministry of Railways. It comprises 17 railway zones, each responsible for managing a specific geographical region. The network features a diverse range of tracks, including broad gauge (1.676 meters), meter gauge (1 meter), and narrow gauge (0.762 meters). The majority of the network is broad gauge, offering high-speed capacity for freight and passenger trains.
The Importance of the Indian Railway Network:
The Indian Railways plays a pivotal role in the country’s economy and social fabric. It is the largest employer in the country, providing livelihoods for millions. The network is a critical artery for transporting goods, connecting agricultural regions to markets, and facilitating industrial growth. It is the backbone of the nation’s logistics and supply chains, enabling the movement of essential commodities like food grains, fertilizers, and raw materials.
Beyond economic benefits, the Indian Railways has a profound social impact. It connects remote areas to urban centers, fostering cultural exchange and promoting social inclusion. It provides affordable transportation for millions of people, enabling them to access healthcare, education, and employment opportunities. The network also serves as a lifeline during natural disasters, providing essential relief supplies and evacuating affected populations.
Exploring the Railway Map:
The Indian railway map is a testament to the network’s sprawling reach and intricate connections. It reveals a complex web of lines crisscrossing the country, linking major cities, industrial centers, and pilgrimage sites. Understanding the map requires an appreciation for the geographical diversity of India, encompassing vast plains, towering mountains, and dense forests.
Key Features of the Railway Map:
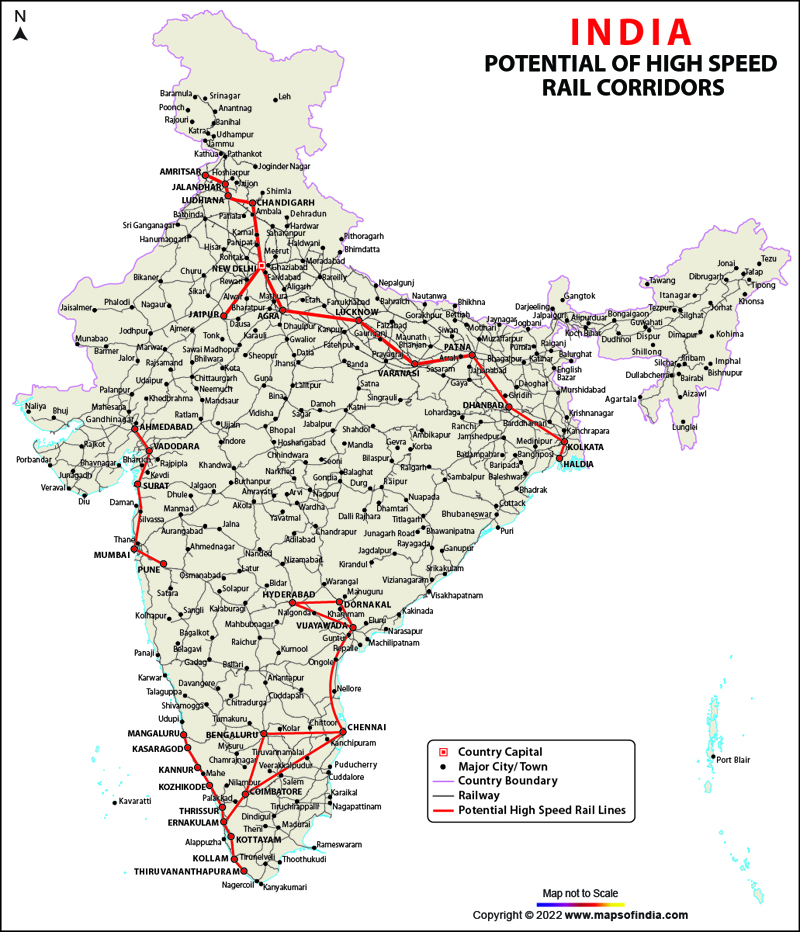
- Major Lines: The map highlights major trunk lines, like the Howrah-Delhi Main Line, the Mumbai-Chennai Main Line, and the Golden Quadrilateral, which connects the major cities of Delhi, Kolkata, Mumbai, and Chennai.
- Branch Lines: Branch lines extend from the main lines, connecting smaller cities, towns, and rural areas.
- Mountain Lines: The map showcases the remarkable engineering feats of the Indian Railways, with lines traversing challenging terrains like the Himalayas, the Western Ghats, and the Eastern Ghats.
- Coastal Lines: The network extends along the coastlines, connecting major ports and facilitating trade.
- Regional Variations: The map reveals the varying densities of the railway network across different regions. For example, the northern plains have a denser network compared to the mountainous regions.
Navigating the Map:
Using the railway map effectively requires understanding its key elements:
- Stations: The map indicates major railway stations, which serve as hubs for passenger and freight traffic.
- Track Types: The map differentiates between broad gauge, meter gauge, and narrow gauge tracks, providing information about the capacity and speed of trains.
- Train Routes: The map depicts train routes, showing the paths taken by various trains.
- Distance and Time: The map may include distance and estimated travel time between stations.
FAQs about the Indian Railway Network:
1. What is the total length of the Indian railway network?
The Indian railway network is approximately 67,000 kilometers long.
2. How many railway zones are there in India?
There are 17 railway zones in India.
3. What are the major train routes in India?
Some of the major train routes in India include the Howrah-Delhi Main Line, the Mumbai-Chennai Main Line, and the Golden Quadrilateral.
4. What is the difference between broad gauge, meter gauge, and narrow gauge tracks?
Broad gauge tracks have a width of 1.676 meters, meter gauge tracks have a width of 1 meter, and narrow gauge tracks have a width of 0.762 meters.
5. What are some of the challenges faced by the Indian Railways?
The Indian Railways faces challenges such as overcrowding, infrastructure bottlenecks, and safety concerns.
6. What are the future plans for the Indian Railways?
The Indian Railways aims to modernize its infrastructure, introduce high-speed rail lines, and improve safety and efficiency.
Tips for Understanding the Railway Map:
- Use a detailed map: Choose a map that provides a comprehensive overview of the network, including station names, track types, and train routes.
- Focus on specific regions: If you are interested in a particular region, zoom in on the map to explore the local railway network.
- Study train routes: Identify the routes taken by trains to understand the connections between cities and towns.
- Consider different travel options: The map can help you compare different train routes and choose the most suitable option for your journey.
- Stay updated: The Indian railway network is constantly evolving, so make sure to refer to updated maps and resources.
Conclusion:
The Indian railway network is a testament to the country’s ambition, resilience, and its commitment to progress. It is a vital infrastructure that connects people, businesses, and communities, playing a crucial role in the nation’s economic growth and social development. Understanding the railway map is essential for appreciating the complexity and significance of this vast network, its historical legacy, and its potential for shaping the future of India. As the network continues to evolve, it will remain a powerful symbol of the nation’s aspirations for a connected and prosperous future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Indian Railway Network: A Vital Lifeline Across a Vast Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!