The Language of Color: Deciphering the European Map
Related Articles: The Language of Color: Deciphering the European Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Language of Color: Deciphering the European Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Language of Color: Deciphering the European Map

The European map, a tapestry woven with vibrant hues, is more than just a visual representation of the continent’s geography. Each color holds a distinct meaning, conveying vital information about the region’s diverse political, cultural, and economic landscapes. Understanding these nuances allows for a deeper comprehension of Europe’s complex history, present realities, and future potential.
Unveiling the Political Spectrum
Political maps of Europe often utilize a spectrum of colors to depict the continent’s diverse political systems and affiliations.
- Red: Frequently associated with leftist or socialist ideologies, red often represents countries with strong social welfare programs, robust labor unions, and a focus on social justice.
- Blue: Often associated with right-wing or conservative ideologies, blue frequently signifies countries with a strong emphasis on free markets, individual liberty, and traditional values.
- Green: Frequently representing environmentalist or agrarian movements, green often indicates countries with a strong focus on sustainable development, environmental protection, and agricultural policies.
- Yellow: Often associated with liberal or centrist ideologies, yellow frequently symbolizes countries with a balanced approach to economic and social policies, promoting both individual freedom and social responsibility.
These colors, however, are not rigid markers of political ideologies. Political landscapes are complex and fluid, with many countries exhibiting a mix of ideologies within their political systems. Additionally, the specific meaning of each color can vary depending on the context and the cartographer’s intentions.
Highlighting Cultural Tapestry
Color plays a crucial role in depicting Europe’s rich cultural diversity.
- Shades of Brown: Often employed to represent regions with a strong agricultural tradition, brown signifies areas known for their fertile lands, pastoral landscapes, and rural communities.
- Vibrant Yellows and Oranges: Frequently used to represent regions with Mediterranean climates, these colors symbolize areas known for their sunny skies, warm temperatures, and vibrant cultures.
- Deep Blues and Greens: Often employed to represent mountainous regions, these colors highlight areas characterized by rugged landscapes, diverse flora and fauna, and a strong sense of place.
- Rich Purples and Reds: Frequently used to represent regions with a long history of winemaking, these colors symbolize areas renowned for their vineyards, wineries, and culinary traditions.
These colors, however, are not exhaustive representations of European culture. Every region boasts a unique cultural heritage, shaped by its history, language, traditions, and art.
Navigating Economic Landscapes
Color is also instrumental in showcasing Europe’s economic realities.
- Darker Shades of Green: Often employed to represent regions with high agricultural output, these colors highlight areas with fertile lands, efficient farming practices, and significant contributions to the agricultural sector.
- Bright Blues and Greens: Frequently used to represent regions with high industrial output, these colors signify areas with strong manufacturing sectors, advanced technology, and significant contributions to the economy.
- Gold and Silver: Often used to represent regions with high financial activity, these colors highlight areas with major financial institutions, thriving stock markets, and significant contributions to the global economy.
However, these colors do not fully capture the complexities of Europe’s economic landscape. Each region faces unique challenges and opportunities, influenced by factors like infrastructure, education, and innovation.
Understanding the Importance of Color
The use of color on maps of Europe is not merely decorative. It serves as a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s diverse landscapes, political systems, cultural identities, and economic realities. By decoding these color-coded messages, individuals gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and nuances that define Europe.
FAQs by Color in Map of Europe
1. What does the color red signify on a political map of Europe?
Red often represents countries with strong leftist or socialist ideologies, emphasizing social welfare programs, robust labor unions, and a focus on social justice. However, the specific meaning can vary depending on the context and the cartographer’s intentions.
2. What does the color green signify on a cultural map of Europe?
Green often represents regions with a strong agricultural tradition, signifying areas known for their fertile lands, pastoral landscapes, and rural communities. It can also represent areas with a strong emphasis on environmentalism and sustainable development.
3. What does the color blue signify on an economic map of Europe?
Blue often represents regions with high industrial output, signifying areas with strong manufacturing sectors, advanced technology, and significant contributions to the economy. However, the specific meaning can vary depending on the context and the cartographer’s intentions.
4. What does the color yellow signify on a political map of Europe?
Yellow often represents countries with liberal or centrist ideologies, symbolizing a balanced approach to economic and social policies, promoting both individual freedom and social responsibility.
5. What does the color brown signify on a cultural map of Europe?
Brown often represents regions with a strong agricultural tradition, signifying areas known for their fertile lands, pastoral landscapes, and rural communities.
Tips by Color in Map of Europe
- Focus on the context: When interpreting color on a map, consider the map’s purpose, the specific colors used, and the cartographer’s intentions.
- Look for patterns and trends: Observe how colors are clustered and distributed across the map to identify regional trends and variations.
- Consider the historical context: Understanding the historical events and influences that shaped the region can provide valuable insights into the meaning of colors on the map.
- Don’t rely solely on color: While color is a valuable tool, it’s important to consult other sources of information and consider diverse perspectives to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region.
Conclusion by Color in Map of Europe
The use of color on maps of Europe is a powerful tool for communication and understanding. By carefully interpreting the colors employed, individuals can gain valuable insights into the continent’s political, cultural, and economic landscapes. This knowledge fosters a deeper appreciation for Europe’s diverse realities and the complexities that shape its present and future.




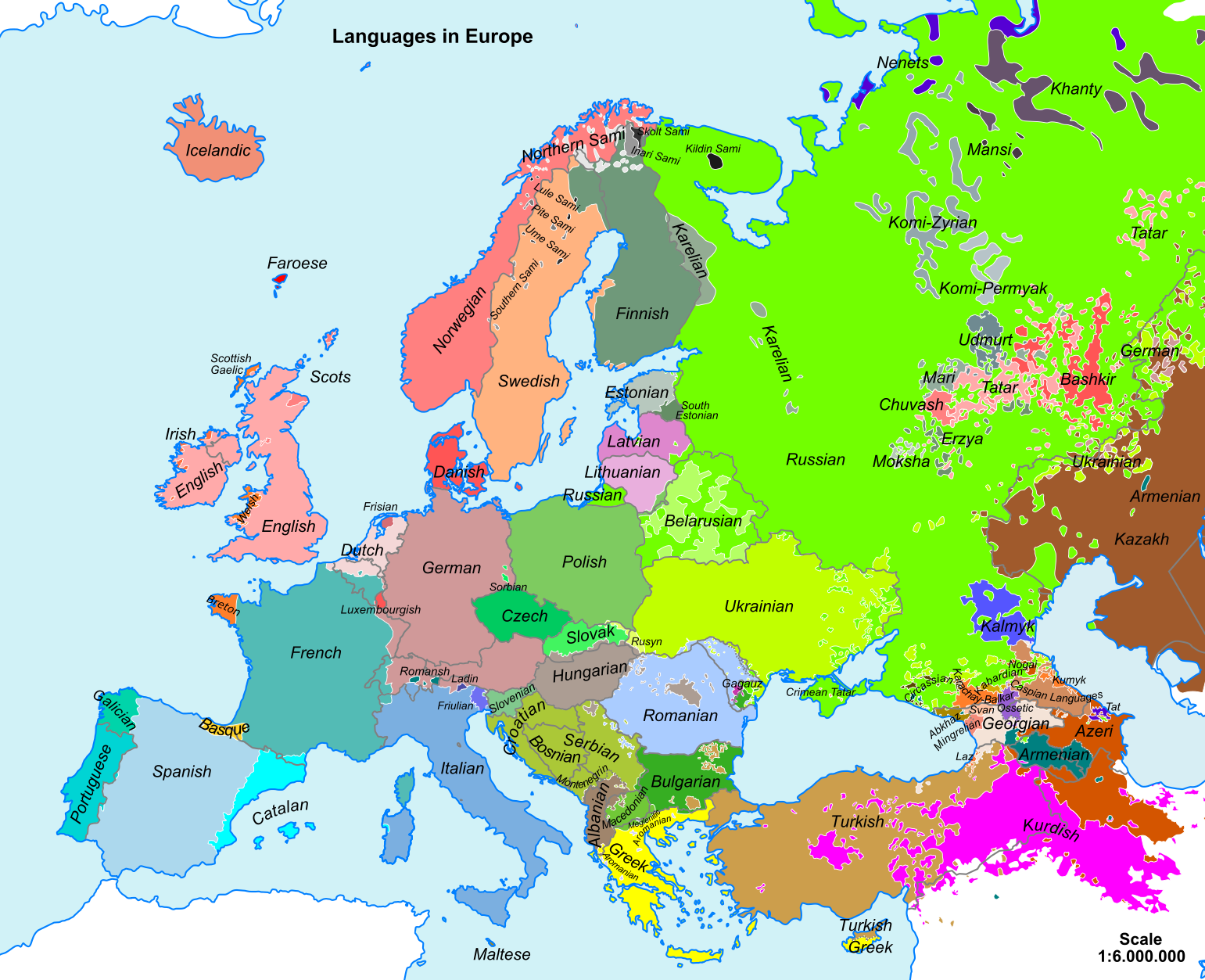
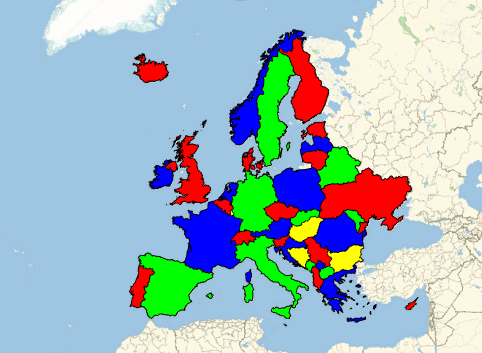
![Language families of Europe [1837x1655] : r/MapPorn](https://i.redd.it/47oz3xlfjsuz.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Language of Color: Deciphering the European Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!