The North Pole: A Point of Convergence on Earth’s Map
Related Articles: The North Pole: A Point of Convergence on Earth’s Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The North Pole: A Point of Convergence on Earth’s Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The North Pole: A Point of Convergence on Earth’s Map

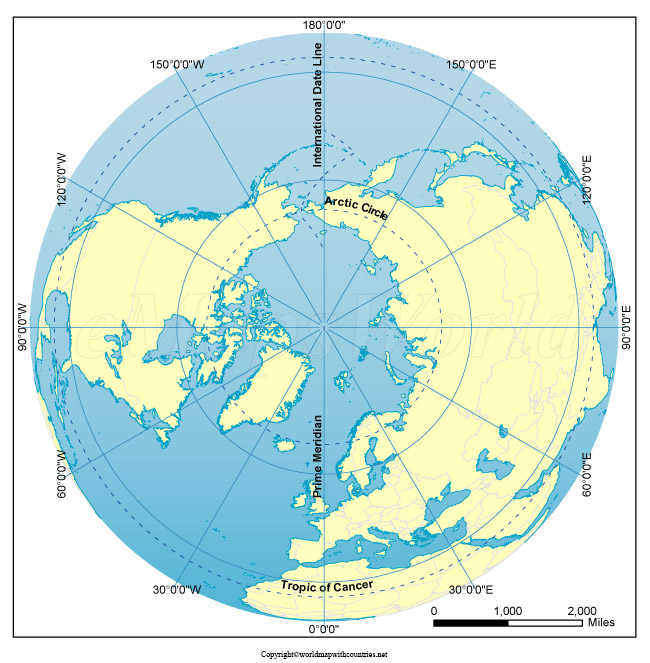
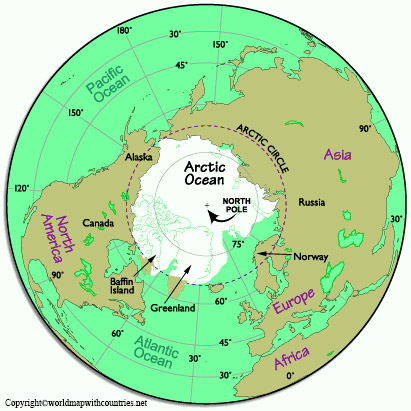
The North Pole, a point of immense geographical and symbolic significance, occupies a unique position on our planet. It is the northernmost point on Earth, where all lines of longitude converge. This singular location serves as a crucial reference point for navigation, timekeeping, and understanding Earth’s geography.
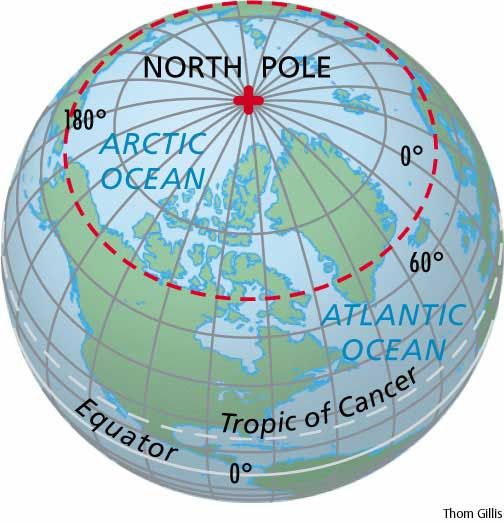
The North Pole on Maps: A Visual Representation of Earth’s Rotation
On a standard world map, the North Pole is typically depicted at the top, often marked with a star or a circle. This placement reflects the Earth’s rotation, with the North Pole serving as the axis around which the planet spins. This rotation is responsible for day and night, and the North Pole’s position on the map directly reflects this fundamental aspect of Earth’s motion.
Beyond the Map: The Reality of the North Pole
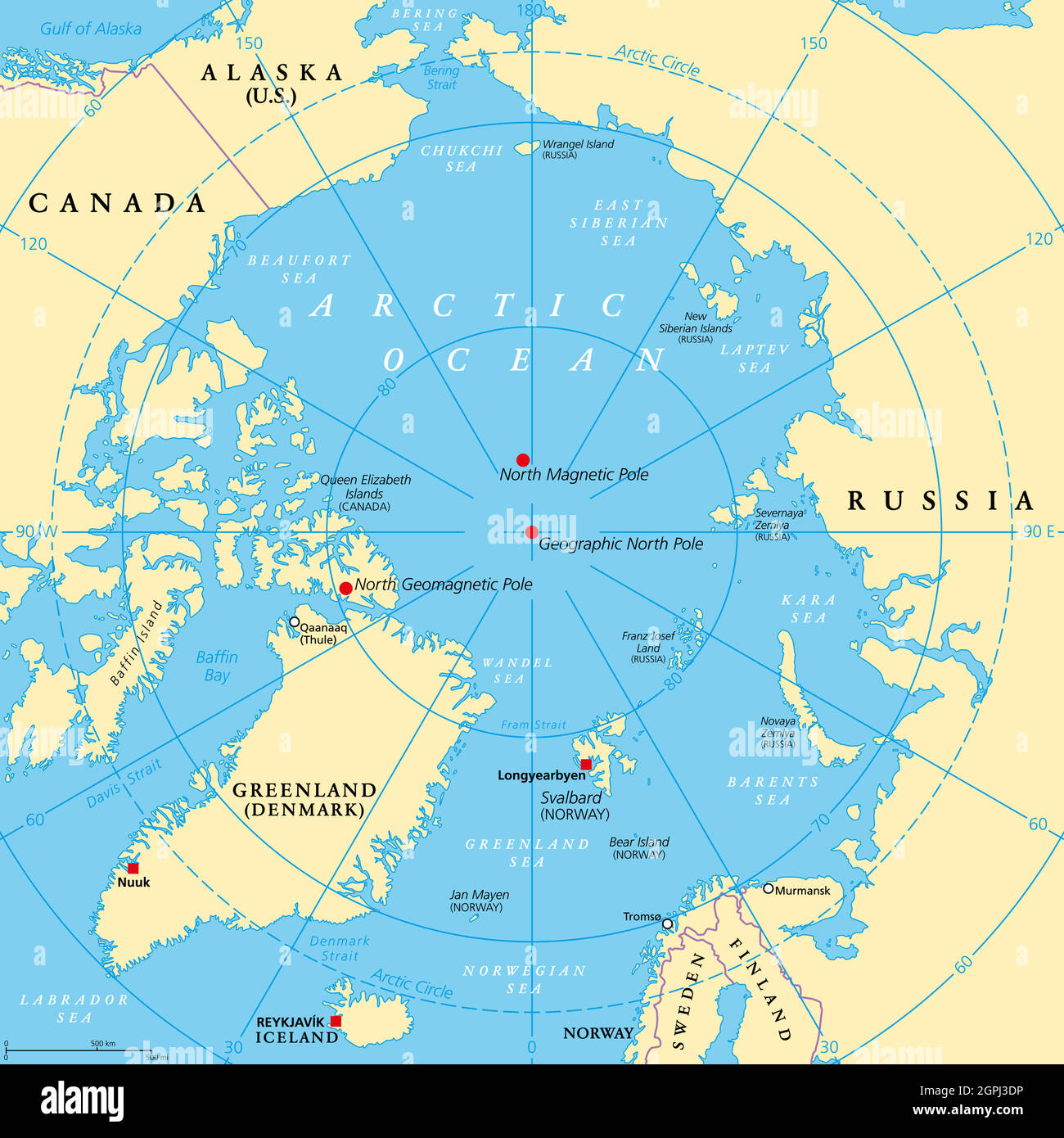
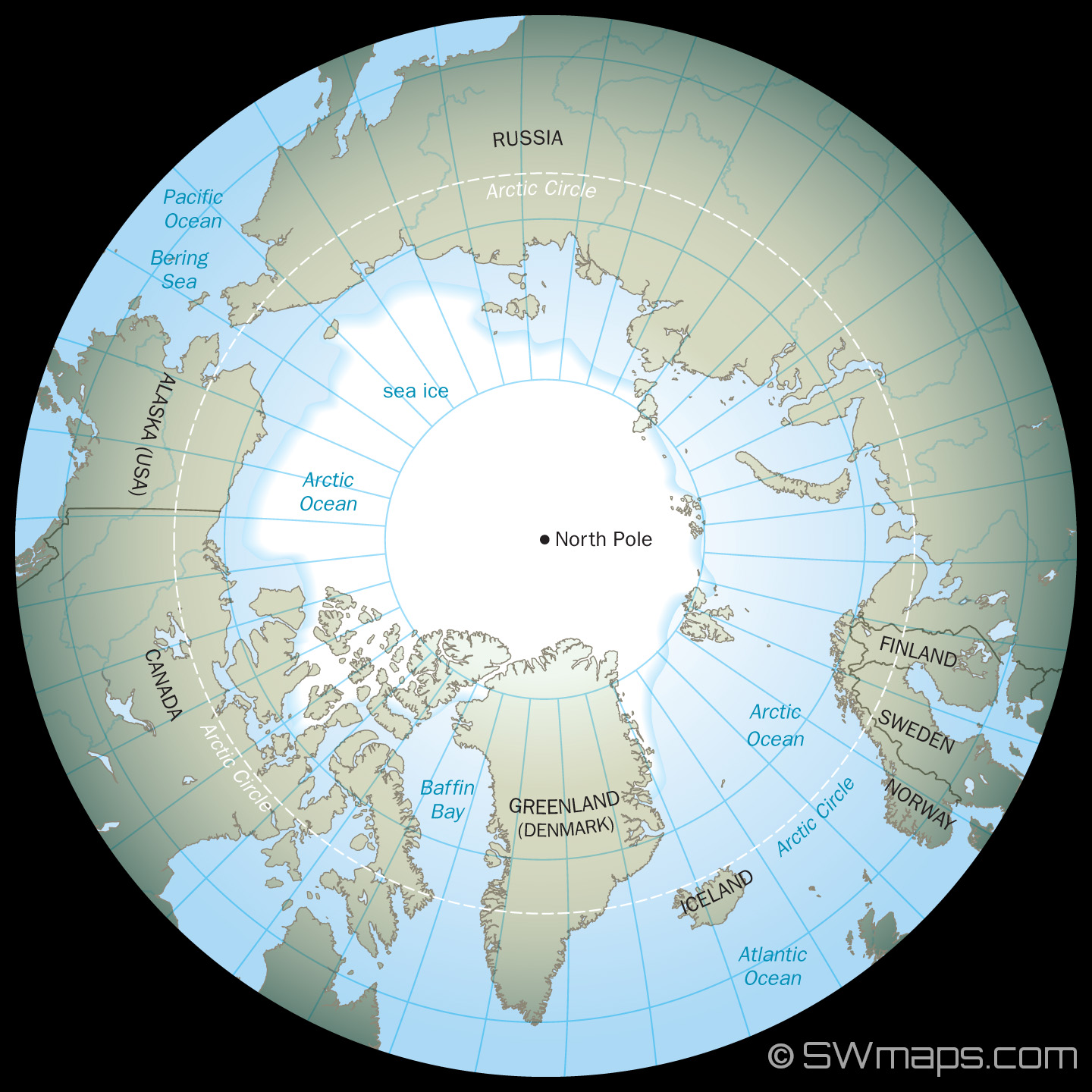
While maps provide a visual representation, the reality of the North Pole is quite different. It is not a fixed piece of land but rather a point in the Arctic Ocean, permanently covered by a thick layer of sea ice. This ice sheet fluctuates in size and thickness depending on the season, making the North Pole a dynamic and constantly changing environment.
Navigational Significance: A Guiding Star for Explorers
The North Pole has long held a prominent place in the history of exploration. Early seafarers used the North Star (Polaris) for navigation, as it remains relatively stationary in the night sky, pointing towards the North Pole. This celestial guide proved invaluable for explorers navigating vast oceans and charting unknown territories.
A Pivotal Point for Time Zones
The North Pole also plays a critical role in the global system of time zones. It is considered the starting point for the Prime Meridian, the zero-degree line of longitude that divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. This line, passing through Greenwich, England, establishes a universal time reference, allowing for standardized timekeeping across the globe.
Understanding Earth’s Magnetic Field: A Compass’s North
The Earth’s magnetic field, invisible but crucial for life, originates from the planet’s core. The North Pole is a point of magnetic convergence, attracting the north pole of a compass needle. While the geographic and magnetic North Poles are not exactly aligned, their proximity is crucial for understanding the Earth’s magnetic field and its influence on various phenomena.
The North Pole: A Focus of Scientific Research
Due to its unique position and challenging environment, the North Pole attracts scientists from various disciplines. Researchers study climate change, ice dynamics, ocean currents, and atmospheric conditions, utilizing the North Pole as a natural laboratory to understand Earth’s complex systems.
The North Pole: A Symbol of Exploration and Resilience
The North Pole holds a powerful symbolic significance, representing the ultimate point of northern exploration and the human spirit’s relentless pursuit of discovery. It also serves as a reminder of the fragility of our planet and the importance of environmental stewardship.
Frequently Asked Questions about the North Pole
Q: Is the North Pole a country?
A: No, the North Pole is not a country. It is a geographical point located in the Arctic Ocean, not belonging to any specific nation.
Q: Can you walk on the North Pole?
A: It is possible to walk on the North Pole, but only during certain times of the year when the sea ice is thick enough to support weight. However, due to the unpredictable nature of the ice and the extreme weather conditions, it is a highly dangerous and challenging endeavor.
Q: Why is the North Pole so cold?
A: The North Pole is extremely cold due to its location at the top of the Earth, where sunlight hits at a very oblique angle. This results in low solar energy reaching the surface, leading to freezing temperatures.
Q: What animals live near the North Pole?
A: The Arctic region surrounding the North Pole is home to a variety of animals adapted to the harsh environment, including polar bears, walruses, seals, arctic foxes, and various bird species.
Q: Is the North Pole getting smaller?
A: Yes, the sea ice surrounding the North Pole is shrinking due to climate change. This phenomenon is a significant concern, as it has far-reaching consequences for Arctic ecosystems and the global climate.
Tips for Understanding the North Pole
- Utilize online maps and interactive globes to visualize the North Pole’s location and its relationship to other parts of the world.
- Explore documentaries and educational resources about the Arctic region to gain insights into its unique environment, challenges, and the importance of conservation.
- Engage with scientific research and reports on climate change and its impact on the North Pole and the surrounding Arctic region.
- Consider visiting a planetarium or science museum to learn more about the Earth’s rotation, magnetic field, and the North Pole’s role in these phenomena.
Conclusion: The North Pole’s Enduring Significance
The North Pole, a point of convergence on Earth’s map, represents a confluence of geographical, navigational, scientific, and symbolic importance. Its unique location, dynamic environment, and enduring role in human exploration continue to fascinate and inspire, reminding us of the interconnectedness of our planet and the crucial need for environmental stewardship.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The North Pole: A Point of Convergence on Earth’s Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!