Tracking Twisters: A History of Tornado Maps and Their Impact
Related Articles: Tracking Twisters: A History of Tornado Maps and Their Impact
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Tracking Twisters: A History of Tornado Maps and Their Impact. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Tracking Twisters: A History of Tornado Maps and Their Impact

Tornadoes, nature’s furious whirlwinds, have long held a place of both fear and fascination in human history. Understanding their unpredictable nature and erratic paths has been a constant pursuit, leading to the development of a vital tool: the tornado map.
From early, rudimentary attempts to chart these destructive storms to sophisticated, data-driven visualizations, the history of tornado maps reflects a growing understanding of these meteorological phenomena and a commitment to protecting lives and property.
Early Beginnings: Recognizing the Threat
The earliest attempts at tornado mapping were primarily anecdotal, relying on eyewitness accounts and historical records. For centuries, communities affected by tornadoes would document the event, noting the date, location, and severity of the damage. These accounts, though often fragmented and subjective, provided valuable insights into the frequency and patterns of tornadoes.
The Dawn of Scientific Mapping: The Birth of the Fujita Scale
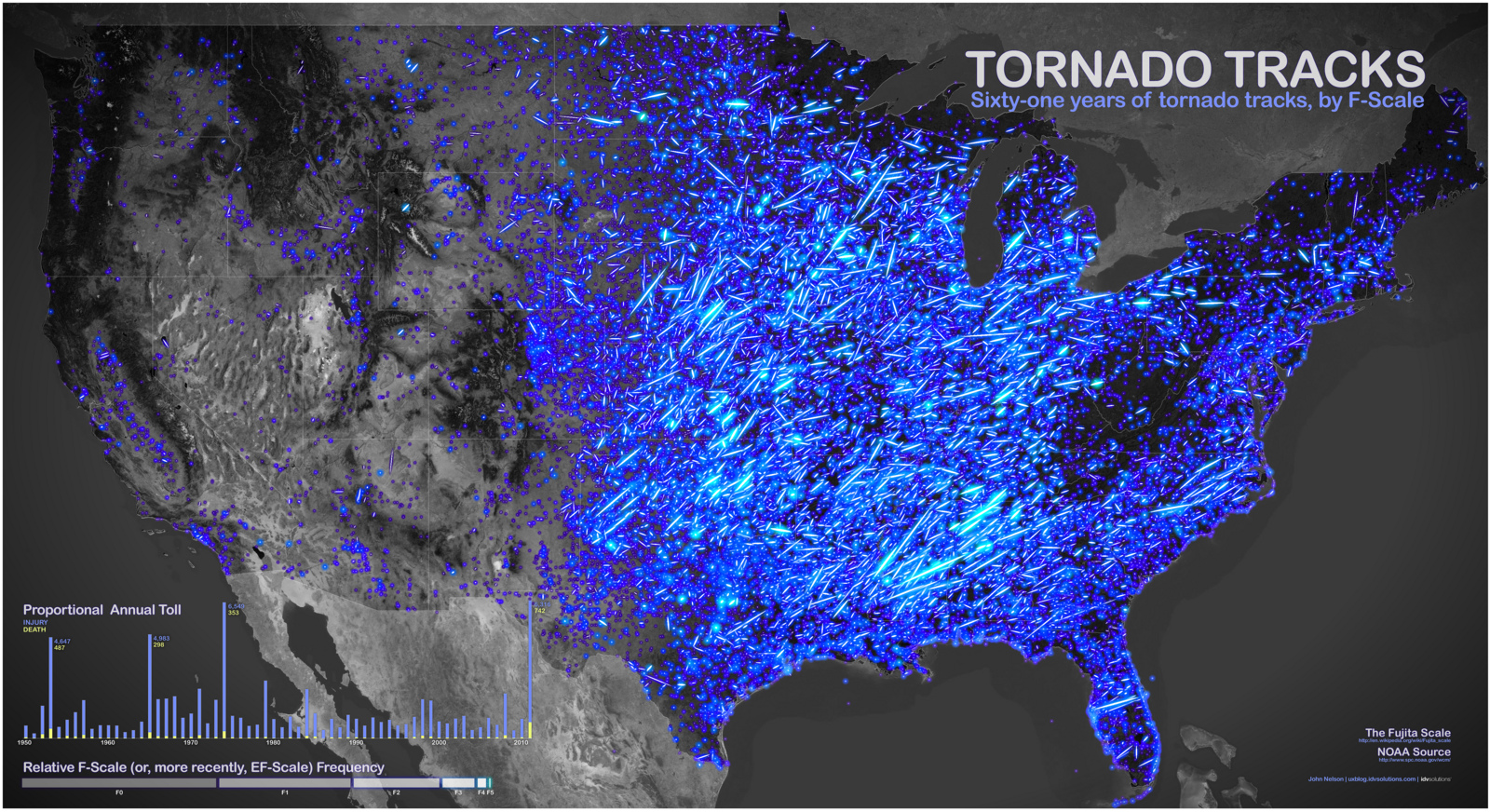
The 20th century witnessed a significant shift in tornado mapping. Scientific advancements in meteorology and the development of new technologies, such as weather radar, allowed for more accurate and detailed observations. In 1971, a pivotal development occurred: the introduction of the Fujita Scale by Dr. Tetsuya Theodore Fujita. This scale, measuring tornado intensity based on wind speed and damage, revolutionized tornado mapping by providing a standardized system for quantifying the destructive power of these storms.
The Era of Data and Visualization: Mapping the Unseen
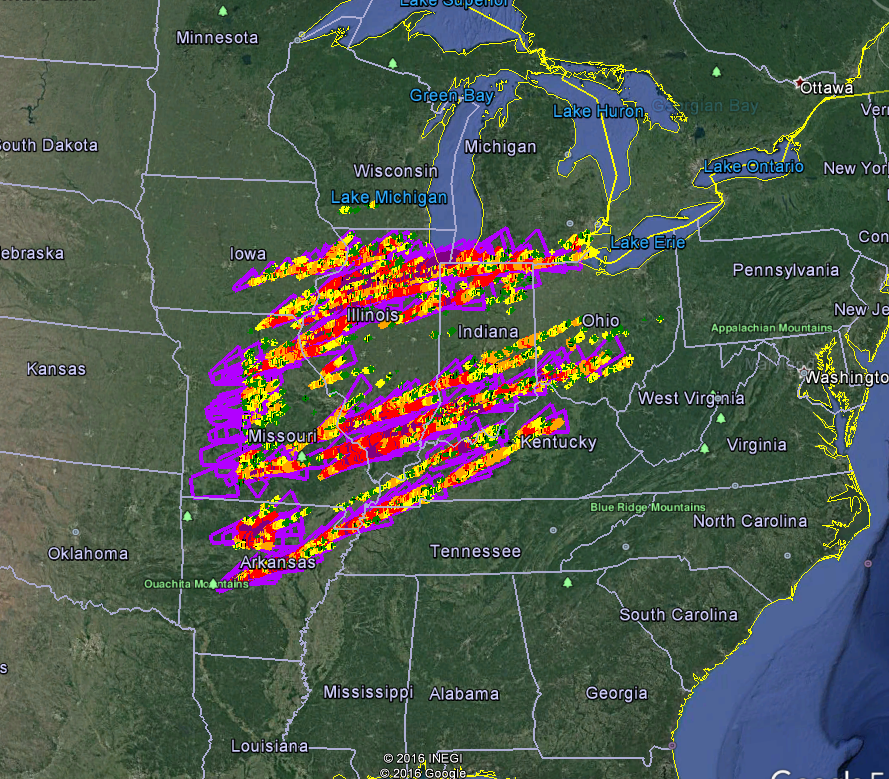
The advent of computers and advanced data processing techniques in the latter half of the 20th century ushered in a new era of tornado mapping. Weather data collected from radar, satellites, and ground-based sensors could now be analyzed and visualized in real-time, creating detailed maps that tracked the formation, movement, and intensity of tornadoes.
These maps, often presented as animated sequences, offered a dynamic view of the storm’s evolution, allowing meteorologists and emergency responders to predict its path and issue timely warnings.
Modern Mapping: Advanced Technology and Public Awareness
Today, tornado maps have become integral to weather forecasting and public safety. Sophisticated weather models, powered by supercomputers, simulate atmospheric conditions with unprecedented accuracy, enabling the prediction of tornado formation and movement with remarkable precision.
These maps, readily accessible to the public through various media platforms, play a crucial role in raising awareness about impending threats and encouraging timely action.
The Benefits of Tornado Mapping
The evolution of tornado maps has yielded numerous benefits:
- Improved Forecasting: Advanced mapping techniques allow for more accurate predictions of tornado occurrence, intensity, and path, giving communities valuable time to prepare and take shelter.
- Enhanced Public Safety: By disseminating timely warnings and providing clear visual representations of tornado threats, maps empower individuals and communities to make informed decisions, minimizing casualties and property damage.
- Scientific Research: Tornado maps provide valuable data for researchers studying these meteorological phenomena, helping them understand the factors that influence tornado formation and development. This knowledge contributes to the development of more effective warning systems and mitigation strategies.
- Historical Analysis: Detailed tornado maps, compiled over decades, offer a comprehensive historical record of tornado activity, revealing long-term trends and patterns. This information helps scientists assess the impact of climate change on tornado frequency and intensity, guiding future preparedness efforts.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Tornado Maps
1. How are tornado maps created?
Tornado maps are generated using a combination of data sources, including:
- Weather Radar: Doppler radar detects the movement and intensity of precipitation, providing crucial information about the formation and development of tornadoes.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites provide wide-area views of weather patterns, including the presence of thunderstorms and other conditions conducive to tornado formation.
- Ground-Based Sensors: Surface weather stations measure temperature, wind speed, and other meteorological parameters, providing valuable context for interpreting radar and satellite data.
- Numerical Weather Models: Sophisticated computer models simulate atmospheric conditions, predicting the likelihood of tornado formation and their potential paths.
2. What information is included on a tornado map?
Tornado maps typically include:
- Tornado Location: The current or predicted location of the tornado.
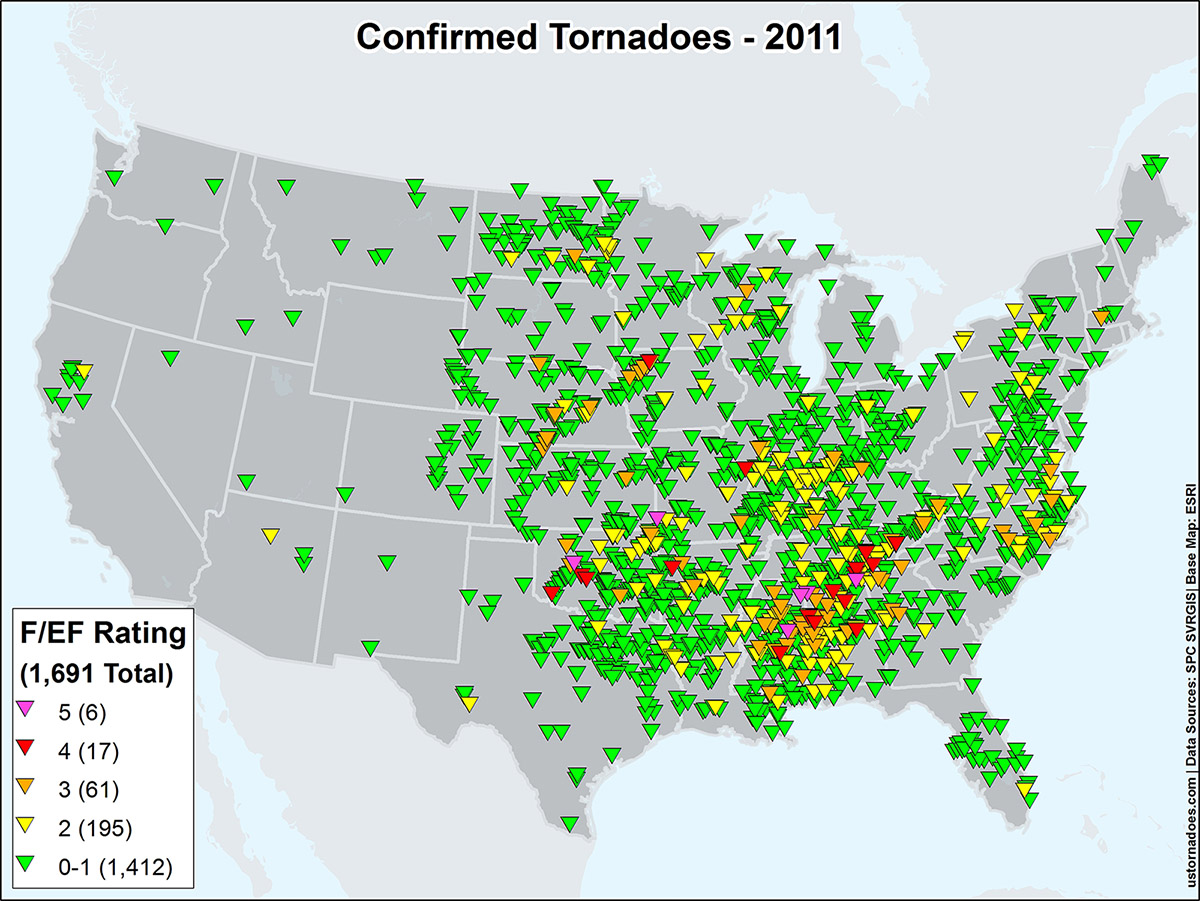
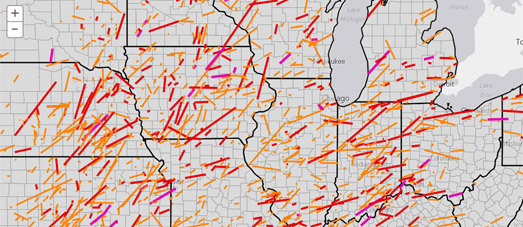
- Tornado Intensity: The estimated wind speed and damage potential, often indicated by the Fujita Scale or its successor, the Enhanced Fujita Scale.
- Tornado Movement: The direction and speed of the tornado’s movement.
- Warning Zones: Areas where a tornado is likely to occur or has been confirmed.
- Time Stamps: The time of observation or prediction.
3. How accurate are tornado maps?
Tornado mapping technology has significantly improved over the years, but predicting the exact path and behavior of a tornado remains a complex challenge.
While maps provide valuable insights into potential threats, they are not infallible. Factors like rapidly changing weather conditions and the unpredictable nature of tornadoes can influence their accuracy.
4. What should I do if a tornado is predicted in my area?
If a tornado warning is issued for your area, take the following steps:
- Seek Shelter Immediately: Find a sturdy structure, such as a basement or an interior room on the lowest floor, and stay away from windows.
- Stay Informed: Monitor local news and weather reports for updates on the tornado’s path and intensity.
- Be Prepared: Have a plan in place for how to respond to a tornado warning, including where to seek shelter and what emergency supplies to have on hand.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing Tornado Maps
- Know Your Local Warning Systems: Familiarize yourself with the warning systems used in your area, such as sirens, weather radios, and mobile phone alerts.
- Interpret Map Symbols: Understand the different symbols used on tornado maps, including those indicating tornado intensity, movement, and warning zones.
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports regularly, especially during periods of severe weather.
- Develop a Family Plan: Discuss tornado safety procedures with your family and ensure everyone knows where to go and what to do in case of a warning.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Innovation and Protection
The history of tornado maps is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of knowledge. From early, rudimentary attempts to chart these destructive storms to sophisticated, data-driven visualizations, the evolution of tornado maps reflects a growing understanding of these meteorological phenomena and a commitment to protecting lives and property.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more accurate and detailed tornado maps, further enhancing our ability to anticipate and mitigate the risks posed by these powerful forces of nature. The legacy of tornado mapping lies not only in its scientific advancements but also in its impact on public safety, empowering communities to face these storms with greater preparedness and resilience.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Tracking Twisters: A History of Tornado Maps and Their Impact. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!