Unraveling the Past: A Journey Through World Ice Age Maps
Related Articles: Unraveling the Past: A Journey Through World Ice Age Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Past: A Journey Through World Ice Age Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Past: A Journey Through World Ice Age Maps
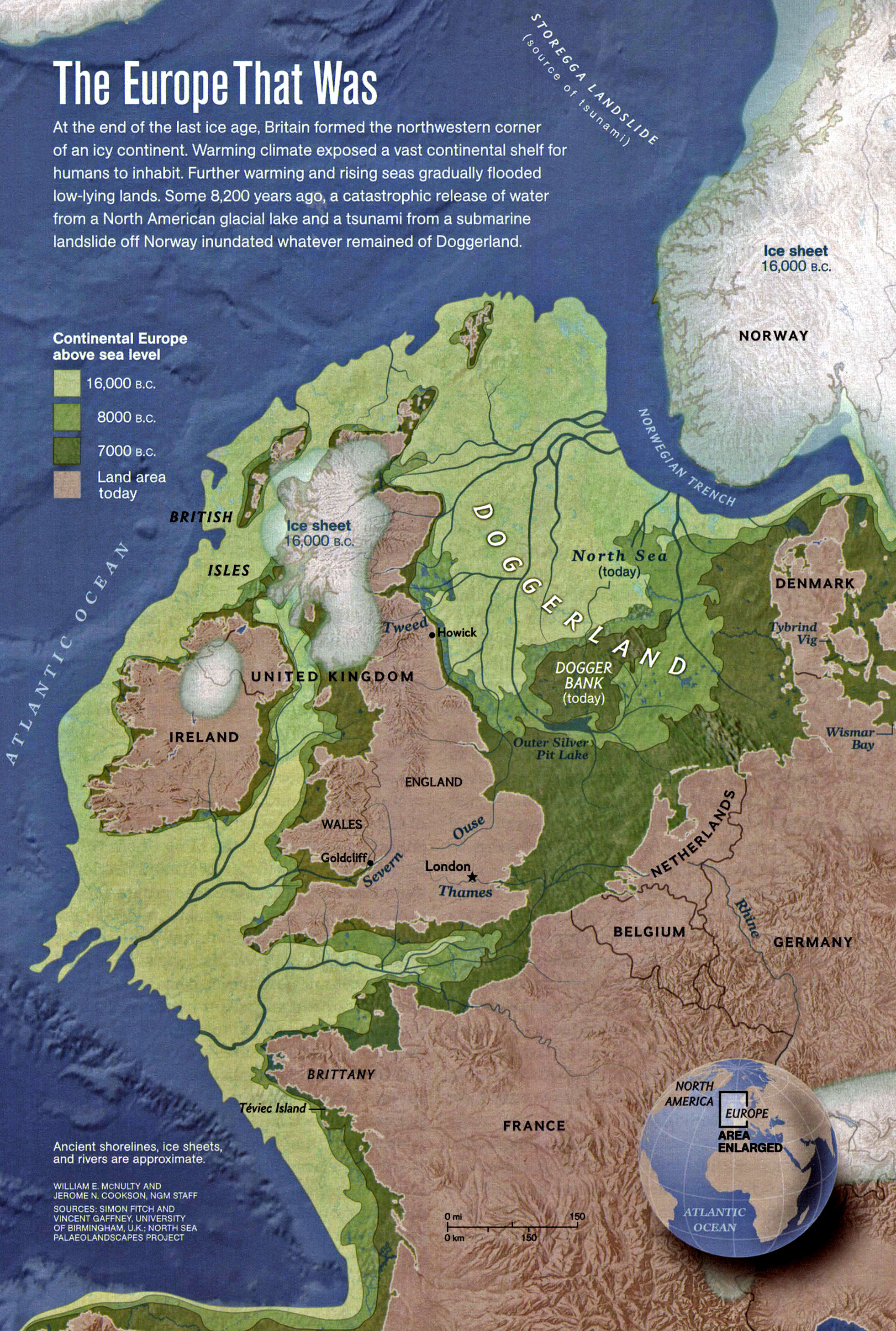
The Earth’s history is a tapestry woven with dramatic shifts in climate, marked by periods of intense cold known as ice ages. These glacial epochs, characterized by vast ice sheets blanketing continents and sea levels plummeting, have left an indelible imprint on the planet’s landscape, flora, and fauna. Understanding these ancient ice ages is crucial for comprehending the Earth’s dynamic climate system and its potential future trajectory.
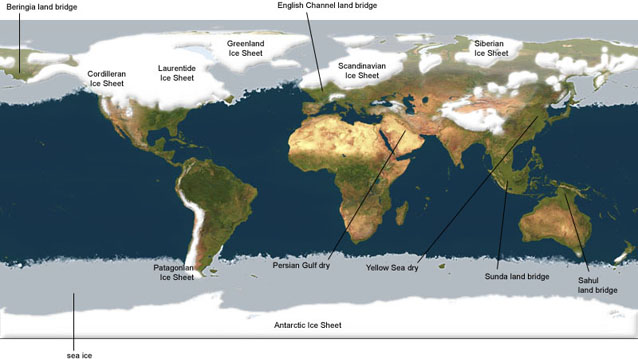
One of the key tools for studying ice ages is the world ice age map. This map, a culmination of geological data, paleoclimate research, and meticulous analysis, provides a visual representation of the extent and distribution of ice sheets during various glacial periods. It reveals the frozen landscapes of the past, showcasing the dramatic transformations the Earth has undergone.
Decoding the World Ice Age Map:
The world ice age map is not a static depiction but rather a series of maps representing different glacial periods, each with its unique characteristics. These maps are constructed through a multidisciplinary approach, integrating data from various sources:
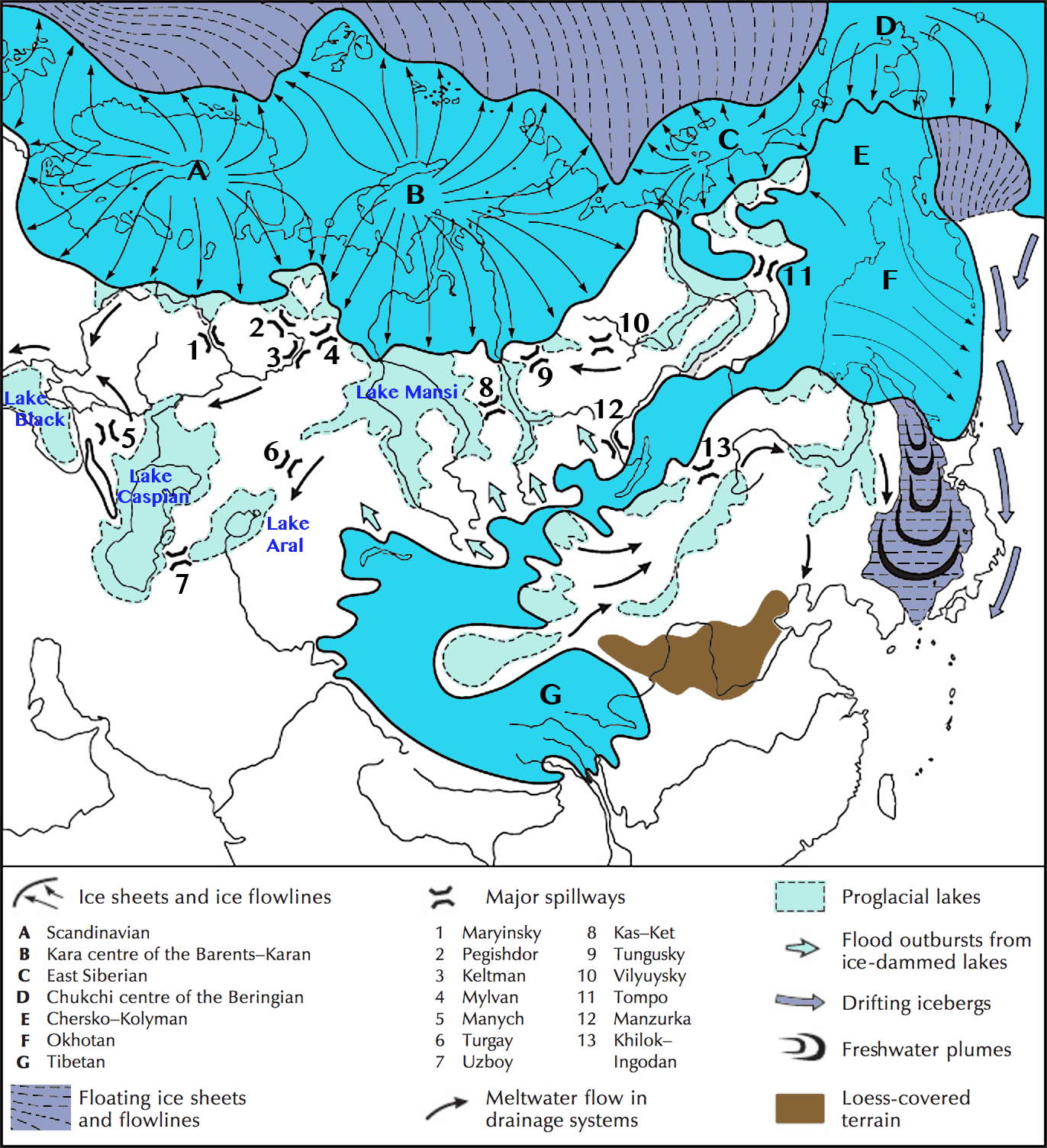
- Geomorphological Evidence: Glacial landforms, such as moraines, drumlins, and glacial valleys, provide tangible evidence of past ice sheet movements. Analyzing these features allows scientists to reconstruct the ice sheet’s extent and direction of flow.
- Sedimentary Records: Cores extracted from lakes, oceans, and glaciers contain layers of sediment that reveal the climate conditions at the time of their deposition. Studying the composition of these sediments, including the presence of glacial debris and pollen, provides insights into the timing and magnitude of glacial advances and retreats.
- Isotopic Analysis: The ratio of stable isotopes, such as oxygen-18 and oxygen-16, in ice cores and marine sediments offers a precise record of past temperatures. These isotopic signatures act as a proxy for understanding climate variations over time.
- Fossil Records: The distribution and types of fossils found in different geological layers reveal the presence or absence of certain species, indicating the climate conditions and the availability of habitats during particular periods.
By integrating these diverse data sources, scientists can create a comprehensive picture of the Earth’s ice age history. World ice age maps visually depict the spread of ice sheets across continents, highlighting the areas that were once covered in ice and the regions that remained ice-free. They also reveal the fluctuating boundaries of the ice sheets over time, showcasing the dynamic nature of glacial cycles.
The Significance of World Ice Age Maps:
The world ice age map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the Earth’s climate system and its implications for the present and future. Its significance lies in its ability to:
- Unravel the Dynamics of Climate Change: By analyzing the patterns of glacial advance and retreat, scientists gain insights into the factors that drive climate change, such as variations in solar radiation, atmospheric composition, and tectonic activity.
- Predict Future Climate Scenarios: Understanding past climate fluctuations allows scientists to develop models that can project future climate change scenarios, including potential sea level rise, changes in precipitation patterns, and the impact on ecosystems.
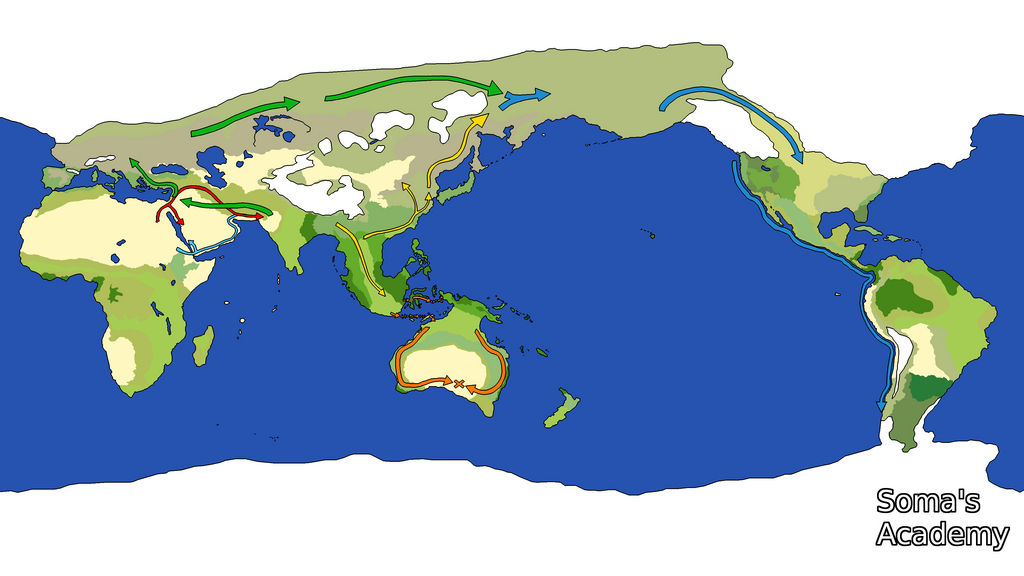
- Reveal the Impact of Ice Ages on Life: World ice age maps help us understand the profound impact of glacial cycles on the evolution of life on Earth. They reveal how species adapted to changing environments, migrated to new territories, and faced extinction.
- Guide Resource Management: Knowledge of past glacial activity is crucial for understanding the distribution of water resources, mineral deposits, and other natural resources. This information is essential for sustainable resource management.
- Inform Archaeological and Paleontological Research: By providing a framework for understanding past environments, world ice age maps guide archaeologists and paleontologists in their investigations of human and animal remains, providing context for their discoveries.
FAQs about World Ice Age Maps:
1. What are the different types of ice ages?
There are two main types of ice ages:
- Global Ice Ages: These are characterized by widespread glaciation across the globe, with ice sheets covering large portions of continents.
- Pleistocene Ice Age: This is the most recent ice age, which began around 2.6 million years ago and ended around 11,700 years ago.
2. How many ice ages have there been in Earth’s history?
Earth has experienced numerous ice ages throughout its history, with the most recent one being the Pleistocene Ice Age. The exact number of ice ages is still under debate, but scientists estimate that there have been at least five major ice ages in the past 500 million years.
3. How do we know about past ice ages?
We learn about past ice ages through a combination of geological evidence, sedimentary records, isotopic analysis, and fossil records. These sources provide a multi-dimensional view of the Earth’s climate history.
4. What is the difference between a glacial period and an interglacial period?
A glacial period is a time of extensive glaciation, with ice sheets expanding and covering large areas of land. An interglacial period is a warmer period between two glacial periods, characterized by a retreat of ice sheets and a rise in global temperatures.
5. How do world ice age maps help us understand climate change?
World ice age maps provide a historical perspective on climate change, allowing us to see how the Earth’s climate has fluctuated over long periods. By studying the patterns of glacial advance and retreat, we can gain insights into the factors that drive climate change and predict potential future scenarios.
Tips for Understanding World Ice Age Maps:
- Pay attention to the time scale: World ice age maps often depict different glacial periods, so it is essential to understand the time frame represented on each map.
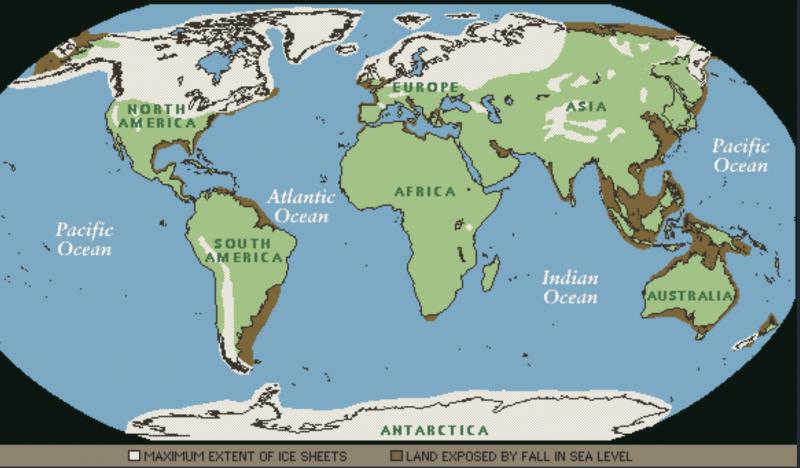
- Focus on the extent of ice sheets: The maps highlight the areas covered by ice sheets, providing a visual representation of the extent of glaciation during different periods.
- Consider the impact on sea level: Ice sheets hold vast amounts of water, and their melting or expansion directly impacts global sea levels. World ice age maps can help us understand how sea levels have fluctuated over time.
- Recognize the limitations: World ice age maps are based on the best available data, but they are still subject to limitations and ongoing research.
Conclusion:
World ice age maps are essential tools for understanding the Earth’s dynamic climate history. They provide a visual representation of the extent and distribution of ice sheets during various glacial periods, revealing the dramatic transformations the Earth has undergone. By analyzing these maps, scientists gain valuable insights into the factors that drive climate change, the impact of glacial cycles on life, and the potential for future climate scenarios. As we continue to explore the Earth’s past, world ice age maps will remain crucial for unraveling the mysteries of our planet’s climate system and its influence on life.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Past: A Journey Through World Ice Age Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!