Unveiling the Power of Perception Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Perception Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Perception Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Perception Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
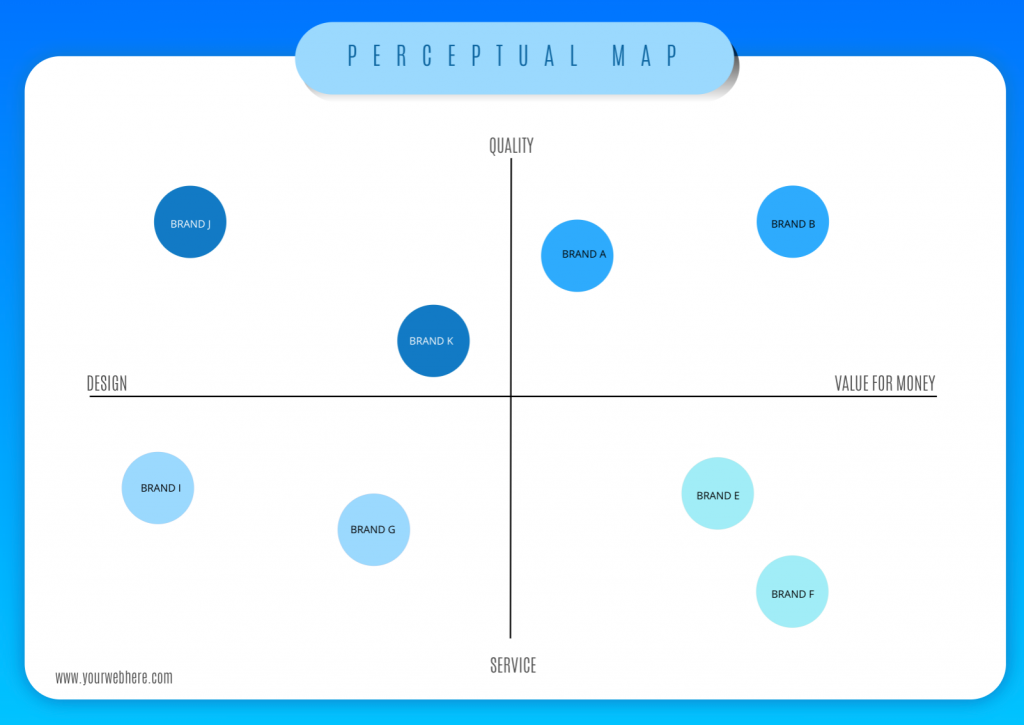
Perception maps, also known as perceptual maps, are powerful visual tools used in marketing and strategic analysis. They offer a clear and concise representation of how consumers perceive different brands, products, or services within a specific market. By plotting these perceptions on a two-dimensional graph, these maps provide valuable insights into competitive positioning, customer preferences, and potential market opportunities.
Understanding the Mechanics: Deconstructing the Perception Map
At its core, a perception map is a visual representation of consumer perceptions. It relies on two key elements:
- Attributes: These are the defining characteristics that consumers use to evaluate products or brands. They can be tangible factors like price, quality, or features, or intangible factors such as brand image, reliability, or customer service.
- Perceptions: These represent how consumers perceive different brands or products on these chosen attributes. These perceptions are typically gathered through market research, surveys, and customer interviews.
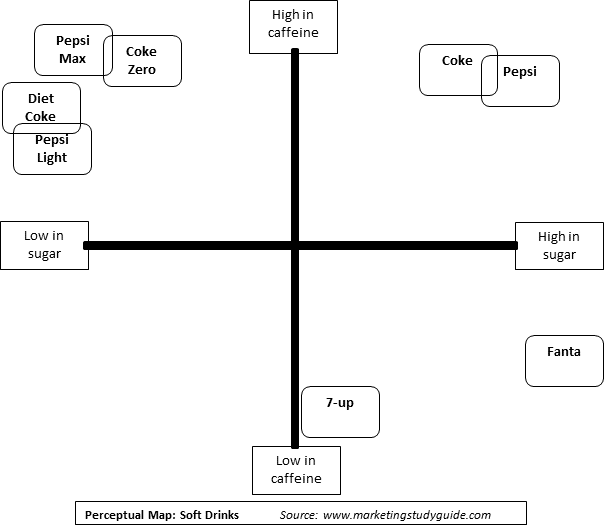
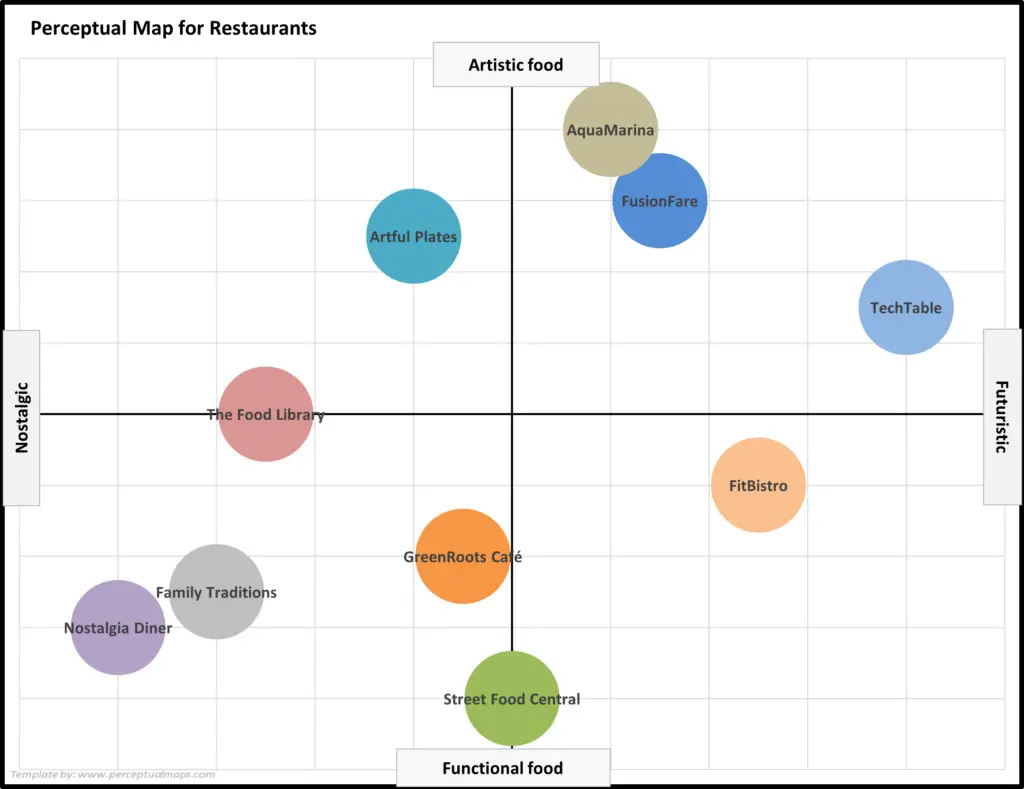
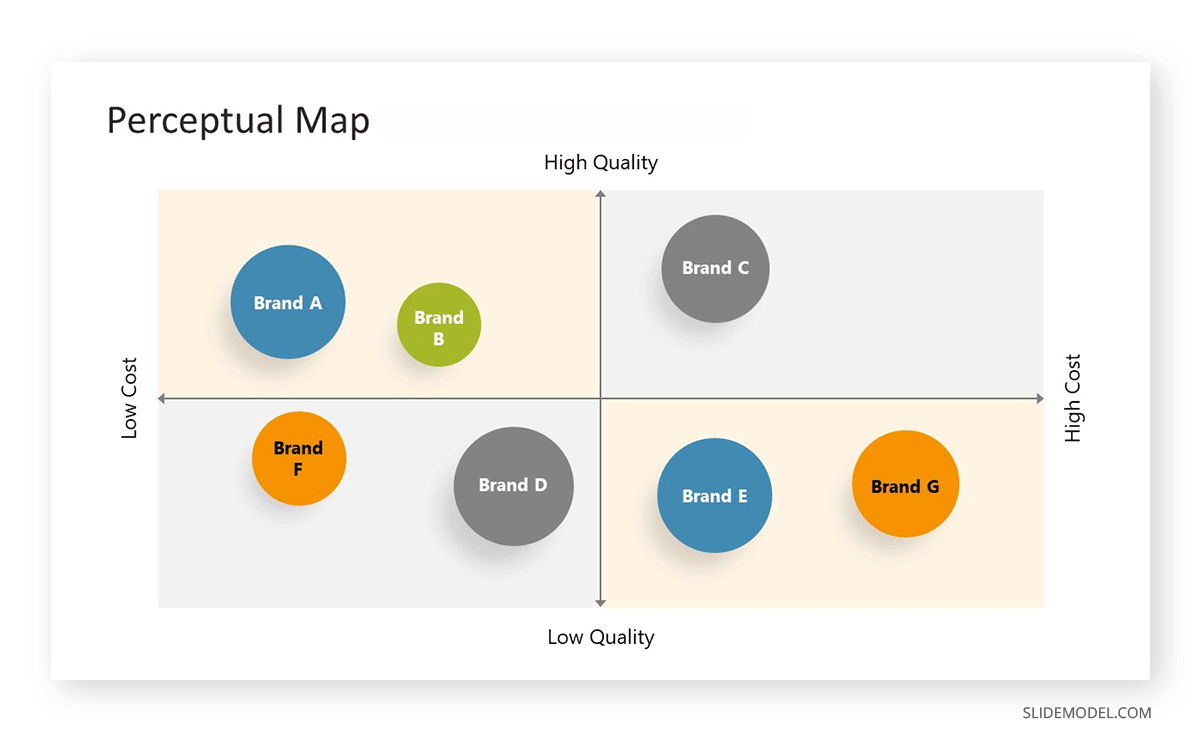
The map itself is constructed by plotting different brands or products on a two-dimensional graph. Each axis of the graph represents a specific attribute, allowing for a visual comparison of how different offerings are perceived across these dimensions.
Benefits of Utilizing Perception Maps: Navigating the Competitive Landscape
Perception maps offer a wealth of benefits, making them invaluable tools for strategic decision-making:
- Competitive Analysis: They provide a clear visual representation of the competitive landscape, highlighting how different brands are positioned relative to each other. This information can be used to identify potential competitive threats, opportunities for differentiation, and gaps in the market.
- Customer Understanding: By analyzing consumer perceptions, businesses gain insights into what customers value most, their preferred brand attributes, and their overall purchasing behavior. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective marketing strategies and product positioning.
- Product Development: Perception maps can guide product development efforts by highlighting areas where existing products are lacking or where there is an opportunity to create a unique offering.
- Marketing Strategy: By understanding consumer perceptions and competitive positioning, businesses can develop more targeted and effective marketing campaigns. This includes tailoring messaging, choosing appropriate channels, and optimizing pricing strategies.
- Brand Management: Perception maps can be used to monitor brand perception over time and identify potential threats or opportunities. This allows businesses to proactively adjust their branding strategies to maintain a strong and positive brand image.
Crafting Effective Perception Maps: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a robust and informative perception map requires a structured approach:
- Define the Target Market: Clearly identify the specific customer segment that the map will focus on. This ensures relevant attributes and perceptions are considered.
- Select Relevant Attributes: Choose two or three key attributes that are important to consumers in the target market and effectively differentiate between brands or products.
- Gather Perception Data: Conduct market research to gather data on how consumers perceive different brands or products on the selected attributes. This can be achieved through surveys, interviews, focus groups, or existing market data.
- Plot the Data: Use a two-dimensional graph to plot each brand or product based on their perceived position on the chosen attributes.
- Analyze and Interpret: Examine the map to identify key insights, including competitive positioning, customer preferences, and potential opportunities.
- Iterate and Refine: Regularly update the map based on new market data and changing consumer preferences. This ensures the map remains relevant and informative.
Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Concerns
Q1: What types of data can be used to create a perception map?
A: A variety of data sources can be used, including:
- Customer surveys: Gather direct feedback on brand perceptions.
- Market research reports: Access industry-specific data on consumer preferences and brand positioning.
- Competitor analysis: Analyze publicly available information on competitor offerings and marketing strategies.
- Social media monitoring: Track online conversations and sentiment related to brands and products.
Q2: How many attributes should be included in a perception map?
A: While two or three attributes are typically used, the number depends on the complexity of the market and the research objectives. Too many attributes can make the map cluttered and difficult to interpret, while too few may not capture the full picture.
Q3: How can I ensure the accuracy of my perception map?
A: To ensure accuracy:
- Use a representative sample: Select a sample size that accurately reflects the target market.
- Employ reliable data collection methods: Use validated survey instruments and rigorous data analysis techniques.
- Validate findings: Cross-check results with other data sources and conduct follow-up research to confirm initial findings.
Q4: How can I use a perception map to make strategic decisions?
A: Perception maps can inform decisions regarding:
- Product development: Identify gaps in the market or opportunities for innovation.
- Marketing strategy: Target specific customer segments and tailor messaging accordingly.
- Pricing strategies: Position products competitively based on perceived value.
- Brand management: Monitor brand perception and adjust branding strategies as needed.
Tips for Creating Effective Perception Maps:
- Keep it simple: Use clear and concise language and avoid using too many attributes.
- Use visuals effectively: Utilize colors, shapes, and sizes to highlight key insights and make the map visually appealing.
- Provide context: Include relevant information about the target market, the industry, and the competitive landscape.
- Regularly update: Monitor changes in consumer perceptions and update the map accordingly to ensure its relevance.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visual Insights
Perception maps are powerful tools for understanding consumer perceptions and navigating the competitive landscape. By providing a clear and concise representation of how different brands or products are perceived, these maps offer valuable insights for strategic decision-making across marketing, product development, and brand management. By leveraging this visual approach, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their target market, optimize their offerings, and achieve sustainable competitive advantage.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Perception Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!