us aquifers map
Related Articles: us aquifers map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to us aquifers map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Vital Network: A Deep Dive into the U.S. Aquifer Map
![USGS Map of US Aquifers [OS] [1440 x 1076] : r/MapPorn](https://pubs.usgs.gov/ha/ha730/ch_a/gif/A004_us.gif)
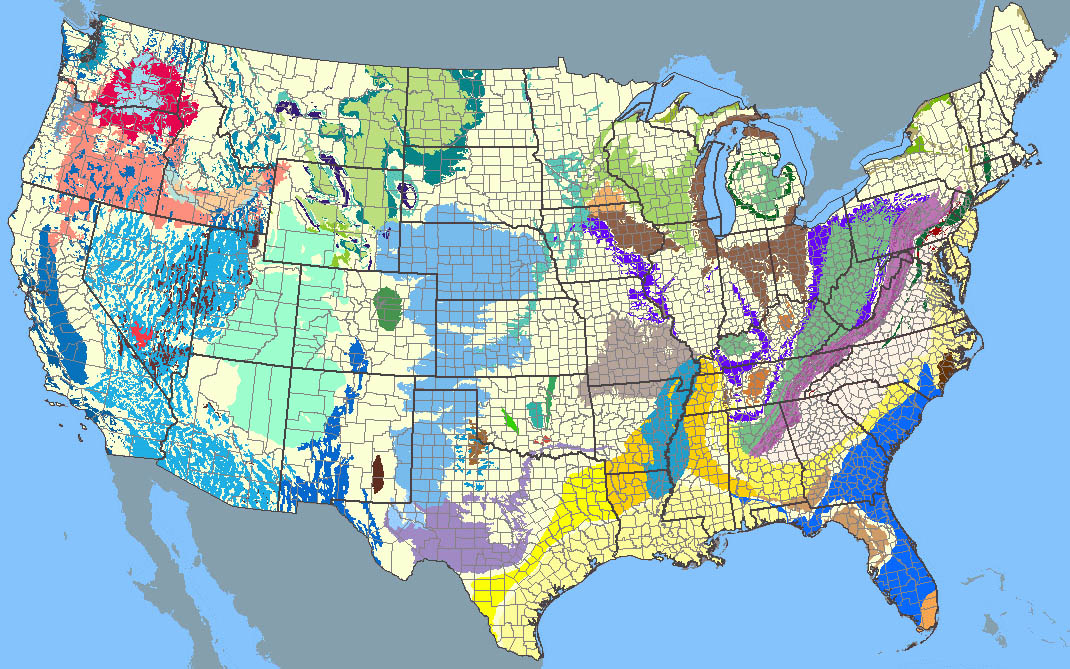
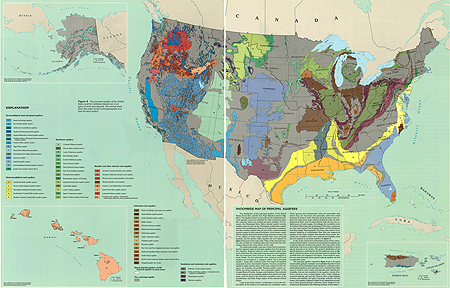
The United States boasts a vast and complex network of underground water sources, known as aquifers. These geological formations act as natural reservoirs, storing and transmitting water through porous rock and soil. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of these aquifers is paramount for sustainable water management, particularly in a nation facing increasing water stress. The U.S. Aquifer Map, a comprehensive visual representation of these underground water sources, serves as a crucial tool for policymakers, researchers, and the public alike.
Delving into the Depths: Aquifer Basics
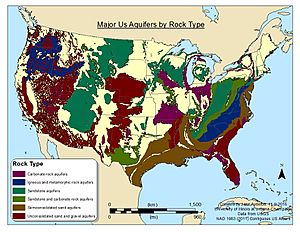
Aquifers are essentially underground layers of rock, sand, or gravel that hold groundwater. They are classified based on their geological structure and the ability of water to flow through them.
- Unconfined aquifers: These are directly connected to the surface, allowing for relatively easy recharge from precipitation.
- Confined aquifers: These are sandwiched between layers of impermeable rock, limiting recharge and often containing water under pressure.
The U.S. Aquifer Map, developed and maintained by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), provides a detailed overview of the nation’s aquifers, highlighting their geographical distribution, geological characteristics, and water quality. This map is not merely a static representation; it is a dynamic tool that incorporates ongoing research, data updates, and evolving scientific understanding.
The Importance of the U.S. Aquifer Map
The U.S. Aquifer Map serves as a vital resource for a multitude of purposes:
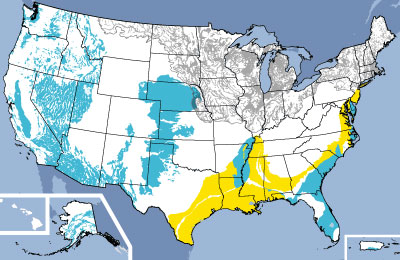
- Water Resource Management: The map assists in identifying areas with abundant groundwater resources, enabling efficient water allocation and planning for future water needs. It also helps pinpoint areas facing water scarcity, allowing for targeted conservation efforts and the development of alternative water sources.
- Agricultural Sustainability: Agriculture heavily relies on groundwater, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions. The map aids in understanding the availability and quality of groundwater for irrigation, supporting sustainable agricultural practices and ensuring food security.
- Urban Planning and Development: As urban areas expand, the demand for water increases. The map helps inform urban planning decisions, ensuring access to adequate water supplies and minimizing the environmental impact of development.
- Environmental Protection: Groundwater contamination poses a significant threat to human health and the environment. The map assists in identifying areas vulnerable to contamination, enabling the development of effective monitoring and remediation strategies.
- Disaster Preparedness: Aquifers play a crucial role in disaster response, providing emergency water supplies during droughts, floods, and other natural disasters. The map aids in identifying potential water sources for disaster relief efforts.
- Scientific Research: The map serves as a foundation for ongoing research on groundwater resources, facilitating a deeper understanding of aquifer dynamics, water quality, and the impact of climate change on groundwater availability.
Navigating the U.S. Aquifer Map: A Closer Look
The U.S. Aquifer Map is a complex and comprehensive tool, offering a wealth of information. It encompasses various layers and datasets, each providing valuable insights into the nation’s groundwater resources.
- Aquifer Boundaries: The map clearly delineates the boundaries of major aquifers across the U.S., providing a visual representation of their geographical extent.
- Aquifer Characteristics: The map includes information on aquifer types, geological formations, and the depth of the water table, offering insights into the physical characteristics of each aquifer.
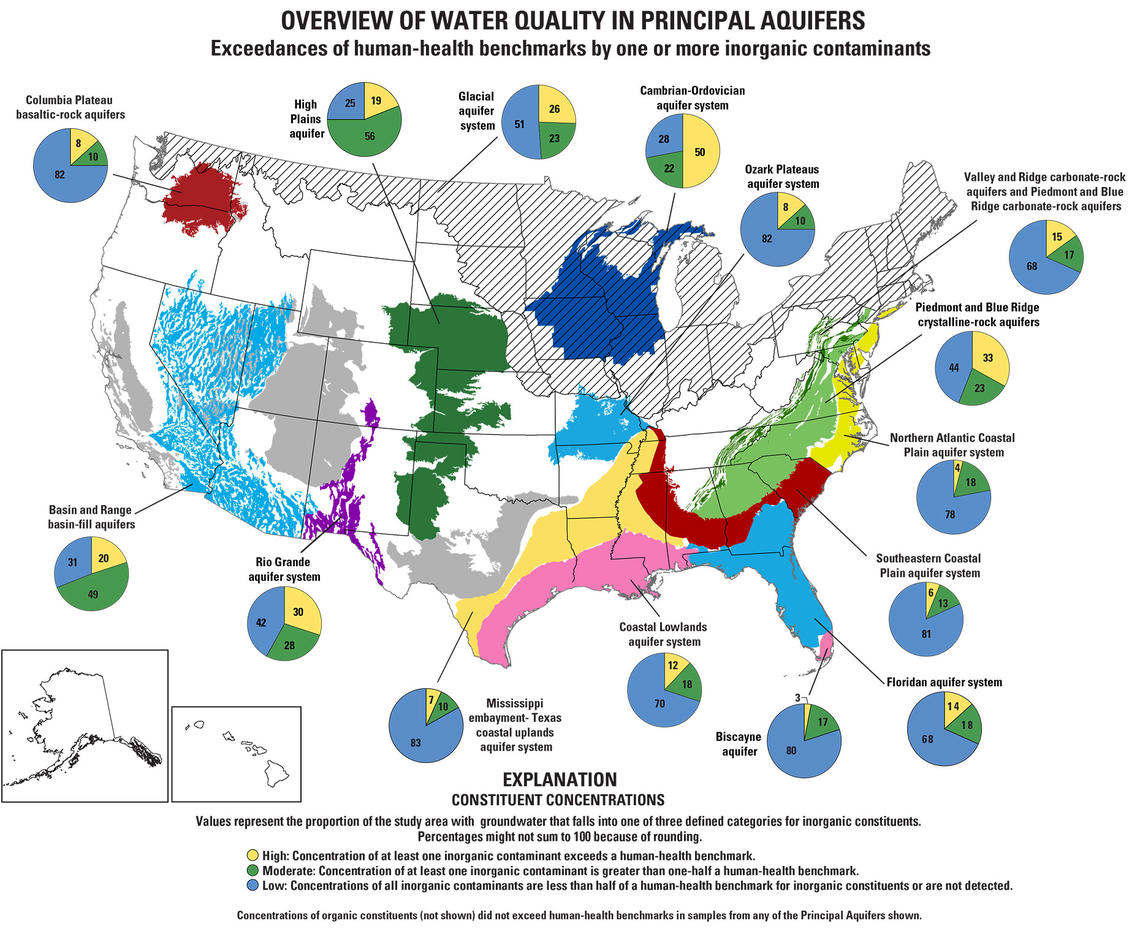
- Water Quality Data: The map integrates data on groundwater quality, including parameters like dissolved solids, contaminants, and pH levels, providing valuable information on the suitability of groundwater for various uses.
- Recharge and Discharge Areas: The map highlights areas where groundwater is replenished through precipitation and areas where it is naturally discharged, providing a holistic understanding of aquifer dynamics.
- Water Use Data: The map incorporates information on groundwater withdrawal for various purposes, such as irrigation, industrial use, and municipal supply, offering a comprehensive view of water demand across the nation.
- Vulnerability Assessment: The map integrates data on potential threats to groundwater quality, including contamination sources and the impact of climate change, enabling informed decision-making for water resource management.
FAQs Regarding the U.S. Aquifer Map
1. What is the purpose of the U.S. Aquifer Map?
The U.S. Aquifer Map provides a comprehensive overview of the nation’s groundwater resources, aiding in sustainable water management, environmental protection, and scientific research.
2. Who uses the U.S. Aquifer Map?
The map is utilized by a wide range of stakeholders, including policymakers, water resource managers, researchers, agricultural producers, urban planners, and the general public.
3. How is the U.S. Aquifer Map updated?
The map is continuously updated with new data, research findings, and evolving scientific understanding, ensuring its relevance and accuracy.
4. Can I access the U.S. Aquifer Map online?
Yes, the U.S. Aquifer Map is available online through the USGS website, providing easy access to its data and functionalities.
5. How does the U.S. Aquifer Map contribute to water conservation?
The map helps identify areas facing water scarcity, enabling targeted conservation efforts and the development of alternative water sources, promoting sustainable water use.
Tips for Utilizing the U.S. Aquifer Map
- Understand the Map’s Scope: Familiarize yourself with the map’s layers, datasets, and functionalities to extract relevant information.
- Utilize Available Tools: Explore the map’s interactive features, including zoom capabilities, data overlays, and data download options.
- Consult with Experts: Seek guidance from hydrogeologists, water resource managers, or other experts to interpret the map’s data and its implications.
- Consider Local Conditions: Remember that the map provides a regional overview, and local conditions can influence groundwater availability and quality.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of updates and changes to the map, ensuring you have access to the most current information.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for a Sustainable Future
The U.S. Aquifer Map stands as a testament to the importance of understanding and managing our nation’s precious groundwater resources. It provides a crucial foundation for informed decision-making, enabling us to navigate the challenges of water scarcity, pollution, and climate change. By leveraging the insights provided by this map, we can ensure a sustainable future for our communities and the environment. As we continue to invest in research, data collection, and technological advancements, the U.S. Aquifer Map will continue to evolve, becoming an even more powerful tool for safeguarding our nation’s water resources for generations to come.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into us aquifers map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!