Decoding Arizona’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Legislative Districts
Related Articles: Decoding Arizona’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Legislative Districts
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Decoding Arizona’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Legislative Districts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Decoding Arizona’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Legislative Districts

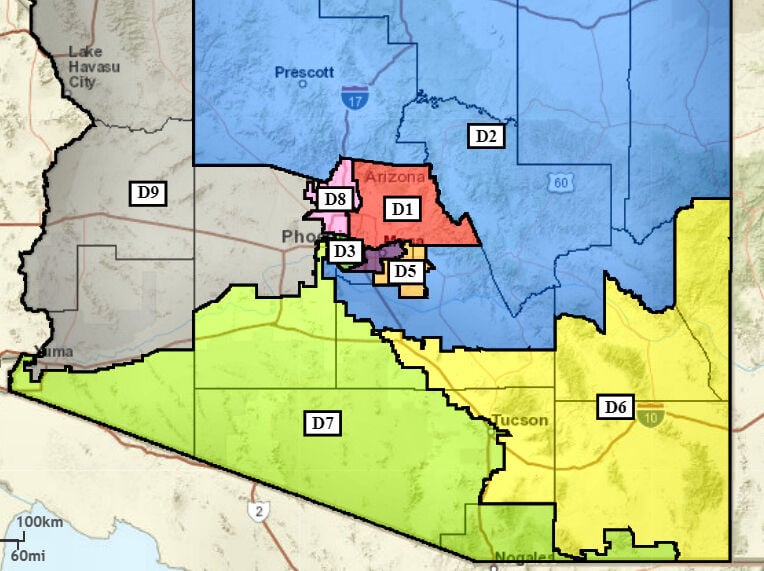
Arizona, a state known for its diverse geography and vibrant political landscape, is divided into distinct legislative districts, each representing a specific portion of the state’s population. These districts, drawn every ten years following the decennial census, serve as the foundation for the state’s political structure, influencing the representation of various communities and shaping the course of legislation. Understanding the Arizona district map is crucial for navigating the state’s political dynamics, engaging in informed civic participation, and comprehending the intricacies of policy-making.
Navigating the Map: A Closer Look at Arizona’s Legislative Districts
Arizona’s legislative districts are divided into two primary categories: Senate districts and House districts. Each Senate district encompasses a larger geographical area and is represented by one senator, while House districts are smaller and each elects one representative. The state is currently divided into 30 Senate districts and 60 House districts, ensuring representation for a diverse range of communities across the state.
Factors Shaping District Boundaries
The process of drawing district boundaries, known as redistricting, is a complex endeavor guided by several key principles. The primary goal is to ensure equal representation by dividing the state’s population as evenly as possible among each district. This principle, known as the "one person, one vote" doctrine, is enshrined in the Fourteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.
Beyond equal representation, redistricting efforts aim to create districts that are contiguous, meaning they form a single, unbroken area without gaps or overlaps. Additionally, districts should be compact, minimizing the distance between different parts of the district and facilitating communication between constituents and their representatives.
The Importance of Community Representation
The district map plays a critical role in ensuring that diverse communities have a voice in the legislative process. By drawing districts that reflect the demographics and interests of different groups, redistricting aims to promote fair representation and prevent the dilution of minority voting power. This principle, known as "minority representation," is essential for fostering a truly representative democracy.
The Impact of Redistricting on Arizona’s Political Landscape
The redrawing of district boundaries can have a significant impact on the political landscape of Arizona. By strategically manipulating district lines, politicians can influence the outcome of elections and the composition of the legislature. This practice, known as gerrymandering, can create districts that favor one party or group over another, potentially skewing the political balance and undermining the principle of fair representation.
Transparency and Accountability in Redistricting
To ensure fairness and transparency in the redistricting process, Arizona has implemented several measures. The state constitution requires that redistricting be conducted by an independent commission, the Independent Redistricting Commission (IRC), comprised of five members appointed by the governor and confirmed by the legislature. The IRC is responsible for drawing district boundaries based on objective criteria, including population, contiguity, and compactness.
Navigating the Political Landscape: Understanding the Arizona District Map
The Arizona district map is a valuable tool for understanding the state’s political dynamics and engaging in informed civic participation. By studying the map, individuals can identify their own legislative district, learn about the representatives who represent them, and track the progress of legislation that impacts their community.
FAQs about the Arizona District Map
1. How often are district boundaries redrawn?
District boundaries are redrawn every ten years following the decennial census, which is conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau.
2. Who is responsible for drawing district boundaries in Arizona?
The Independent Redistricting Commission (IRC) is responsible for drawing district boundaries in Arizona.
3. How can I find my legislative district?
You can find your legislative district by using the Arizona Legislature’s online district locator tool, which allows you to enter your address and find your corresponding Senate and House districts.
4. What are the key principles guiding redistricting in Arizona?
The key principles guiding redistricting in Arizona are equal representation, contiguity, compactness, and minority representation.
5. How can I participate in the redistricting process?
You can participate in the redistricting process by attending public hearings held by the IRC, submitting written testimony, and contacting your elected officials to express your views on the proposed district boundaries.
Tips for Navigating the Arizona District Map
- Use online resources: The Arizona Legislature’s website provides valuable information about district boundaries, representatives, and legislative activities.
- Engage with your representatives: Contact your senator and representative to share your views on important issues and stay informed about their legislative priorities.
- Attend public hearings: Public hearings on redistricting and other legislative matters provide opportunities to voice your concerns and engage in the democratic process.
- Stay informed about political developments: Follow news coverage of state politics to stay updated on key issues and legislative actions.
- Support organizations advocating for fair representation: Many organizations work to promote fair redistricting and ensure that all communities have a voice in the legislative process.
Conclusion
The Arizona district map is a vital tool for understanding the state’s political landscape and engaging in informed civic participation. By ensuring equal representation, promoting community representation, and fostering transparency in the redistricting process, Arizona strives to create a fair and equitable system of governance. Through understanding the map’s intricacies and engaging in the democratic process, individuals can play an active role in shaping the future of their communities and the state as a whole.


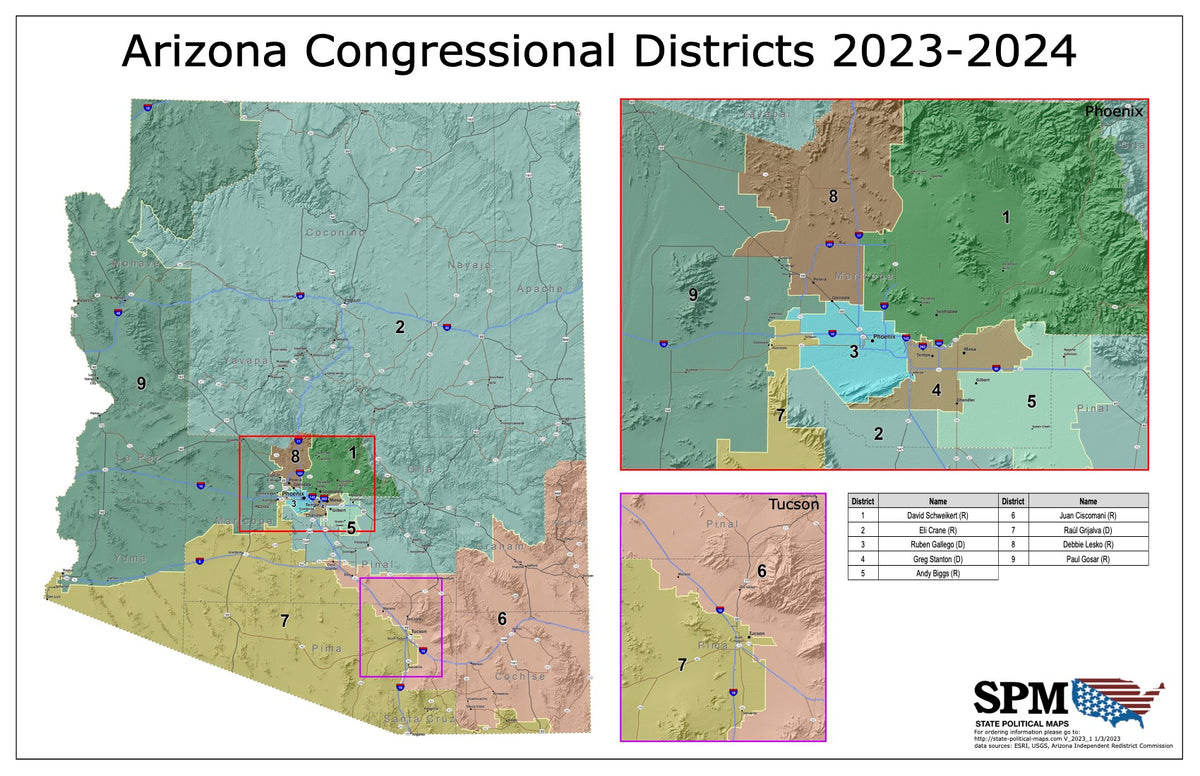
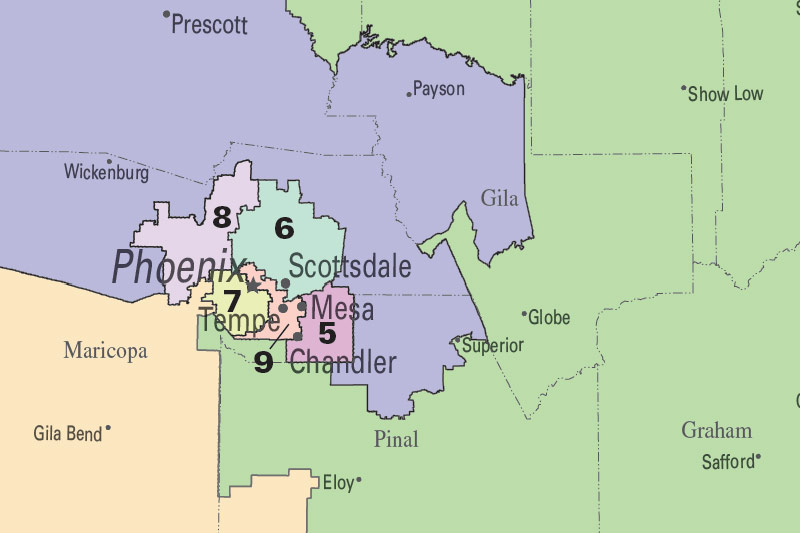
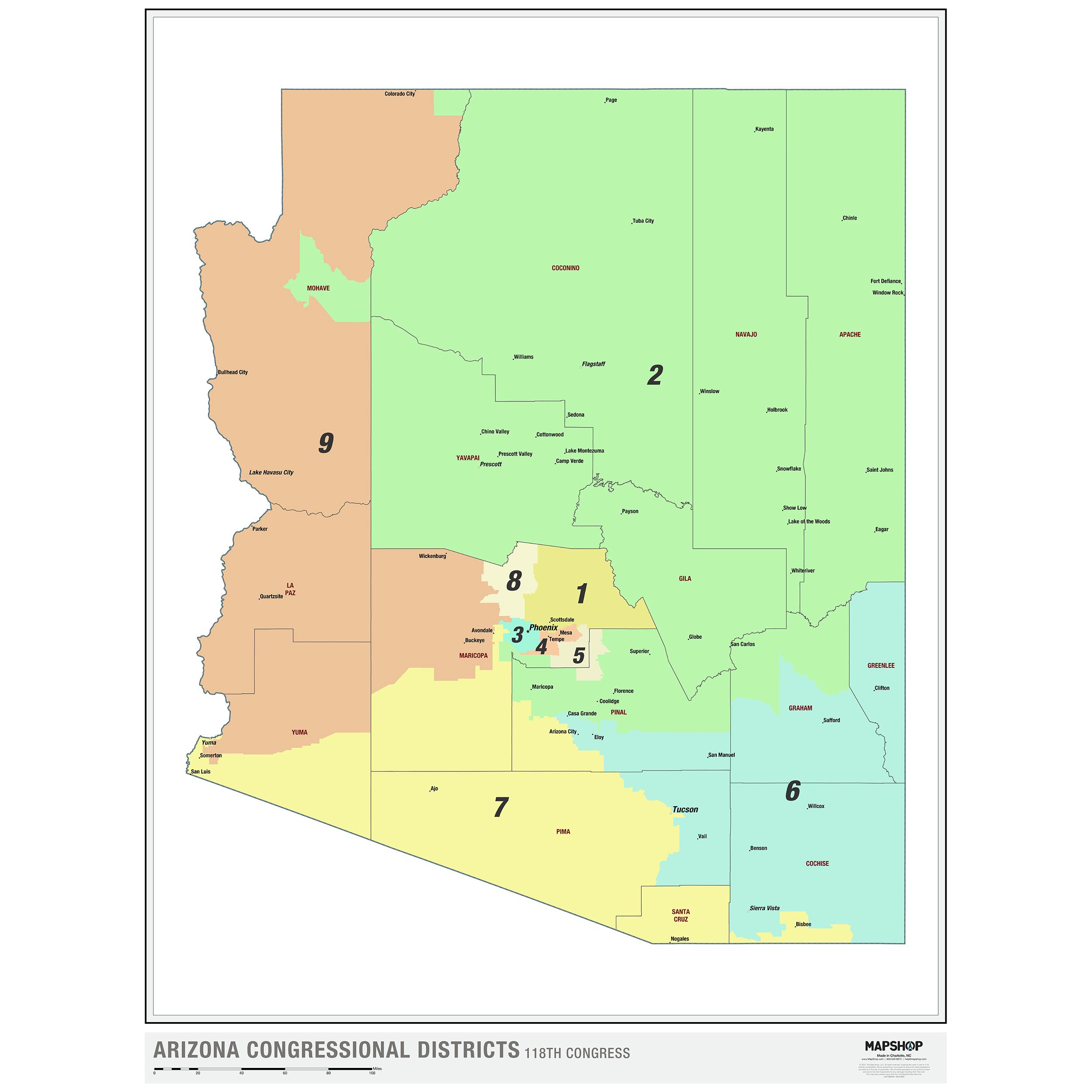
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Decoding Arizona’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Legislative Districts. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!