A Shifting Panorama: Europe’s Map Through the First World Conflict
Associated Articles: A Shifting Panorama: Europe’s Map Through the First World Conflict
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to A Shifting Panorama: Europe’s Map Through the First World Conflict. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
A Shifting Panorama: Europe’s Map Through the First World Conflict

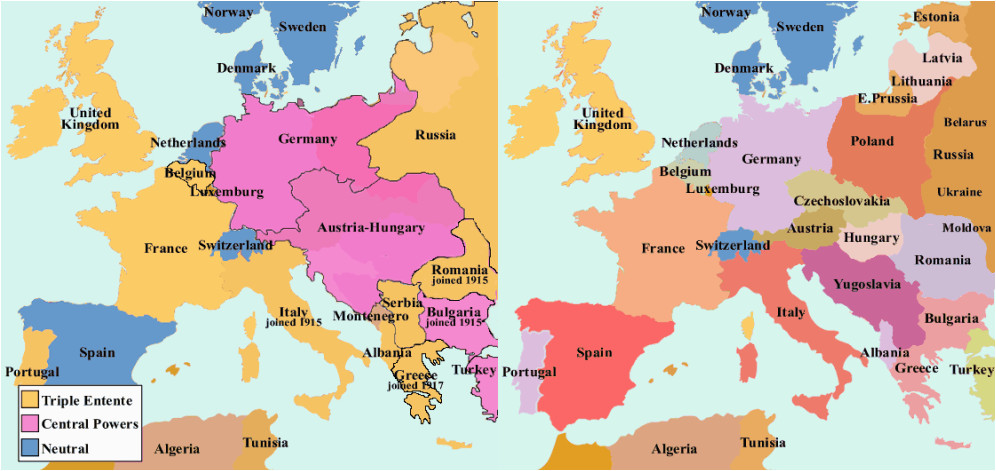
The First World Conflict (1914-1918) irrevocably altered the political map of Europe. Greater than only a battle of empires, it was a crucible that solid new nations, dissolved previous ones, and redrew the boundaries of the continent in ways in which proceed to resonate as we speak. Understanding the evolution of the European map throughout this era requires analyzing not solely the preliminary alignments but additionally the gradual shifts in energy and territory all through the warfare’s 4 brutal years.
The Pre-Conflict Panorama: A Continent of Empires and Tensions
Earlier than the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand ignited the powder keg of Europe, the continent was a posh tapestry of empires, kingdoms, and smaller states. The foremost gamers included:
- The German Empire: A comparatively younger however quickly industrializing energy, Germany’s ambitions and army power posed a big problem to the prevailing order. Its alliance with Austria-Hungary shaped the Central Powers.
- Austria-Hungary: An enormous, multi-ethnic empire teetering getting ready to collapse, Austria-Hungary’s inside tensions and its management over Slavic populations within the Balkans had been key components resulting in the warfare.
- Russia: The most important empire in Europe, Russia’s autocratic Tsarist regime held sway over an unlimited territory and a various inhabitants, however its industrial and army capabilities lagged behind these of the Western powers. It allied with France and Nice Britain, forming the Allied Powers.
- France: Recovering from its defeat within the Franco-Prussian Conflict, France sought to reclaim misplaced territory (Alsace-Lorraine) and avenge its previous humiliations. Its alliance with Russia and later Nice Britain was essential to countering German expansionism.
- Nice Britain: A worldwide empire with a robust navy, Nice Britain initially adopted a coverage of cautious neutrality however finally joined the warfare to stop German dominance of Europe.
- The Ottoman Empire: A declining however nonetheless vital energy, the Ottoman Empire allied with the Central Powers, bringing huge territories within the Center East and the Balkans into the battle.
- Italy: Initially impartial, Italy finally joined the Allied Powers in 1915, pushed by irredentist claims on Austrian territory.
- The Balkan States: A patchwork of impartial and semi-independent states, the Balkans had been a powder keg of ethnic tensions and competing nice energy pursuits. Serbia, specifically, performed a vital position in igniting the warfare.
This pre-war map, characterised by a steadiness of energy that was more and more unstable, could be dramatically reshaped by the warfare’s end result.
The Conflict’s Influence on the Map: Shifting Fronts and Territorial Features
The preliminary levels of the warfare noticed a comparatively static Western Entrance, with trench warfare dominating the panorama. Nevertheless, the Jap Entrance was much more fluid, with vital territorial positive factors and losses for each side. Russia initially made advances into German territory, however its army was in the end outmatched and suffered devastating defeats. The collapse of the Russian Empire in 1917 led to the withdrawal of Russian forces from the Jap Entrance, liberating up vital German assets to be deployed elsewhere.
The Ottoman Empire, regardless of its preliminary successes, suffered vital territorial losses as Allied forces superior into the Center East. The Arab Revolt, fueled by British guarantees of independence, additional weakened the Ottoman Empire’s management over its Arab provinces.
Italy’s entry into the warfare led to combating on the Italian Entrance, primarily within the mountainous areas of the Alps. Whereas Italy made some territorial positive factors, the combating was brutal and expensive.
The Treaty of Versailles and its Aftermath: A New European Order
The Treaty of Versailles, signed in 1919, marked the formal finish of the warfare and considerably redrew the map of Europe. The treaty imposed harsh penalties on Germany, together with territorial losses, demilitarization, and crippling reparations. Alsace-Lorraine was returned to France, and vital territories within the east had been ceded to newly created or expanded states.
The treaty additionally led to the creation of a number of new nations:
- Poland: Restored to independence after centuries of partition, Poland gained vital territory from Germany, Russia, and Austria-Hungary.
- Czechoslovakia: Fashioned from components of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, Czechoslovakia emerged as a brand new impartial nation.
- Yugoslavia: A kingdom shaped from varied Slavic territories, Yugoslavia aimed to unite South Slavic peoples beneath a single banner. Nevertheless, its multi-ethnic composition sowed the seeds of future conflicts.
- Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania: These Baltic states gained independence from Russia following the Bolshevik Revolution.
The Ottoman Empire was largely dismantled, with its territories partitioned amongst varied Allied powers. The creation of the League of Nations, meant to stop future conflicts, was a big try to determine a brand new worldwide order.
Lengthy-Time period Penalties: Seeds of Future Conflicts
The Treaty of Versailles, whereas aiming to create a steady peace, in the end sowed the seeds of future conflicts. The cruel phrases imposed on Germany fueled resentment and contributed to the rise of extremist ideologies, in the end resulting in the Second World Conflict. The redrawing of borders typically didn’t account for ethnic and nationwide identities, resulting in ongoing tensions and conflicts in varied areas of Europe.
The map of Europe after World Conflict I used to be a patchwork of newly created states, a lot of which had been fragile and unstable. The ethnic and nationwide tensions that had contributed to the outbreak of the warfare remained unresolved, and the legacy of the warfare continued to form European politics for many years to come back.
Conclusion:
The First World Conflict profoundly altered the political panorama of Europe. The warfare’s influence prolonged past the battlefield, reshaping the continent’s political boundaries, creating new nations, and dismantling previous empires. The Treaty of Versailles, whereas aiming to determine an enduring peace, inadvertently contributed to future conflicts by failing to deal with underlying tensions and imposing harsh phrases on defeated powers. The map of Europe throughout World Conflict I, and its subsequent redrawing, serves as a stark reminder of the devastating penalties of warfare and the enduring challenges of making a steady and simply worldwide order. The legacy of this era continues to form the political realities of Europe even as we speak, highlighting the enduring influence of this pivotal second in historical past.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into A Shifting Panorama: Europe’s Map Through the First World Conflict. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!