Mapping the Rise and Fall of Islamic Empires: A Geographic and Historic Survey
Associated Articles: Mapping the Rise and Fall of Islamic Empires: A Geographic and Historic Survey
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Mapping the Rise and Fall of Islamic Empires: A Geographic and Historic Survey. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mapping the Rise and Fall of Islamic Empires: A Geographic and Historic Survey

The Islamic world, an enormous and numerous tapestry of cultures and societies, has left an indelible mark on historical past. Understanding its trajectory requires inspecting its geographic footprint, charting the ebb and circulation of Islamic empires throughout centuries. This text explores the evolution of Islamic empires via a geographical lens, analyzing the important thing components contributing to their growth, consolidation, and eventual fragmentation. It is vital to notice that the time period "Islamic empire" is a broad generalization; the various political entities encompassed below this label assorted considerably of their governance, tradition, and interactions with surrounding societies.
The Early Caliphates: A Speedy Growth (Seventh-Tenth Centuries)
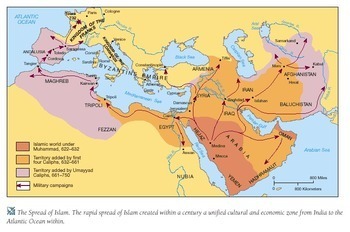
The preliminary growth of Islam, following the Prophet Muhammad’s dying in 632 CE, was remarkably swift. The Rashidun Caliphate (632-661 CE), guided by the primary 4 caliphs, noticed the conquest of huge territories inside a number of many years. Ranging from the Arabian Peninsula, the armies of the Rashidun Caliphate swept via Syria, Palestine, Egypt, and components of North Africa. Their army prowess, mixed with the relative weak point of the Byzantine and Sasanian empires (which had been exhausted by many years of struggle), facilitated this speedy growth. The map of the Islamic world at this stage is characterised by a core area in Arabia, radiating outwards to embody fertile crescent lands and the Nile valley.
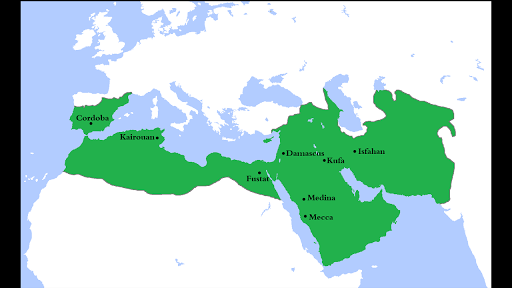
The Umayyad Caliphate (661-750 CE) continued this growth, pushing additional into North Africa, reaching the Atlantic coast by the early eighth century. The conquest of Sindh in modern-day Pakistan marked a major eastward push, establishing a foothold within the Indian subcontinent. The Umayyad Caliphate’s map is considerably bigger, showcasing an enormous territory stretching from the Iberian Peninsula (Al-Andalus) within the west to the Indus River within the east. Nevertheless, this huge empire confronted inside challenges, together with ethnic and spiritual tensions, which in the end led to its downfall.
The Abbasid Caliphate (750-1258 CE), which changed the Umayyads, initially maintained and expanded upon the prevailing territories. Baghdad, strategically positioned on the Tigris River, turned the brand new capital, remodeling into a middle of studying and tradition. Underneath the Abbasids, the Islamic world skilled a Golden Age, marked by important developments in science, arithmetic, philosophy, and literature. The Abbasid map reveals a considerably decentralized empire, with governors holding important energy in numerous provinces. Nevertheless, the empire’s vastness and inside divisions made it weak to fragmentation. The rise of unbiased dynasties and regional powers, such because the Tulunids in Egypt and the Tahirids in Khorasan, eroded the Caliph’s authority, resulting in a decline in centralized management.
Fragmentation and Regional Empires (Tenth-Sixteenth Centuries)
The disintegration of the Abbasid Caliphate didn’t signify the top of Islamic energy. As an alternative, it ushered in an period of regional empires, every with its personal distinct traits and geographic boundaries. The Fatimids in Egypt, the Seljuks in Persia and Anatolia, and the Khwarazmians in Central Asia had been among the many distinguished powers. The map of this era is characterised by a mosaic of unbiased states, continually vying for energy and territory. The Crusades (1096-1291 CE), a collection of non secular wars between Christians and Muslims, additional formed the geopolitical panorama of the japanese Mediterranean.
The rise of the Ottoman Empire (1299-1922 CE) marked a major turning level. Beginning as a small Anatolian beylik, the Ottomans steadily conquered huge territories, together with the Balkans, North Africa, and components of the Center East. By the Sixteenth century, the Ottoman Empire managed an enormous empire stretching from Vienna within the north to Yemen within the south, and from Algeria within the west to Iraq within the east. This empire’s map showcases a outstanding consolidation of energy, reflecting its army power and complex administrative system. The Ottomans’ management over key commerce routes and strategic places considerably impacted international commerce and politics.
Concurrently, different Islamic empires flourished. The Mughal Empire in India (1526-1857 CE) established a robust presence within the Indian subcontinent, leaving a long-lasting legacy on Indian tradition and structure. The Safavid Empire in Persia (1501-1736 CE) performed an important position in shaping the political and spiritual panorama of the area. The maps of those empires present a definite geographic distribution, reflecting their distinctive historic trajectories and political ambitions.
Colonialism and the Fashionable Period (18th Century – Current)
The 18th and nineteenth centuries witnessed the decline of many Islamic empires below the stress of European colonialism. The Ottoman Empire, as soon as a dominant drive, steadily misplaced territories to European powers. The Mughal Empire suffered the same destiny, ultimately being absorbed into British India. The map of the Islamic world throughout this era displays the numerous affect of European imperialism, with many areas falling below colonial rule.
The twentieth century noticed the rise of nationalism and independence actions throughout the Islamic world. Many former colonies gained independence, resulting in the redrawing of borders and the institution of recent nation-states. The map of the trendy Islamic world is a fancy patchwork of unbiased nations, reflecting the various ethnic, linguistic, and cultural identities throughout the broader Islamic neighborhood. Nevertheless, the legacy of colonialism, coupled with ongoing political and social challenges, continues to form the geopolitical panorama.
Conclusion:
Mapping the Islamic empires throughout historical past reveals a dynamic and complicated story of growth, consolidation, fragmentation, and resurgence. From the speedy conquests of the early caliphates to the huge empires of the Ottomans and Mughals, the geographic extent of Islamic rule has profoundly formed the political, cultural, and spiritual panorama of Eurasia and North Africa. Understanding the historic geography of those empires requires contemplating the interaction of army prowess, financial components, cultural change, and inside dynamics. The trendy Islamic world, though fragmented into quite a few unbiased states, stays a major international participant, reflecting the enduring legacy of its wealthy and numerous previous. Additional analysis into particular regional histories and detailed cartographic evaluation can present a richer and extra nuanced understanding of this complicated and interesting historic narrative. The maps themselves, whether or not historic or fashionable, should not simply static representations of territory; they’re dynamic instruments that permit us to hint the ebb and circulation of energy, the evolution of cultures, and the enduring affect of Islamic empires on the world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied invaluable insights into Mapping the Rise and Fall of Islamic Empires: A Geographic and Historic Survey. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!