Unpacking Southeastern Europe: A Geographic and Geopolitical Tapestry
Associated Articles: Unpacking Southeastern Europe: A Geographic and Geopolitical Tapestry
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Unpacking Southeastern Europe: A Geographic and Geopolitical Tapestry. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Unpacking Southeastern Europe: A Geographic and Geopolitical Tapestry
Southeastern Europe, a area typically missed in broader discussions of continental Europe, boasts a wealthy tapestry of historical past, tradition, and complicated geopolitical dynamics. Its borders are fluid, with various definitions relying on the context, however usually embody the Balkan Peninsula, elements of Greece, and typically extending to incorporate nations bordering the Black Sea. Understanding this area requires navigating its intricate geography, various ethnicities, and turbulent previous, all of which proceed to form its current and future.
A Various Panorama: Geography and its Affect
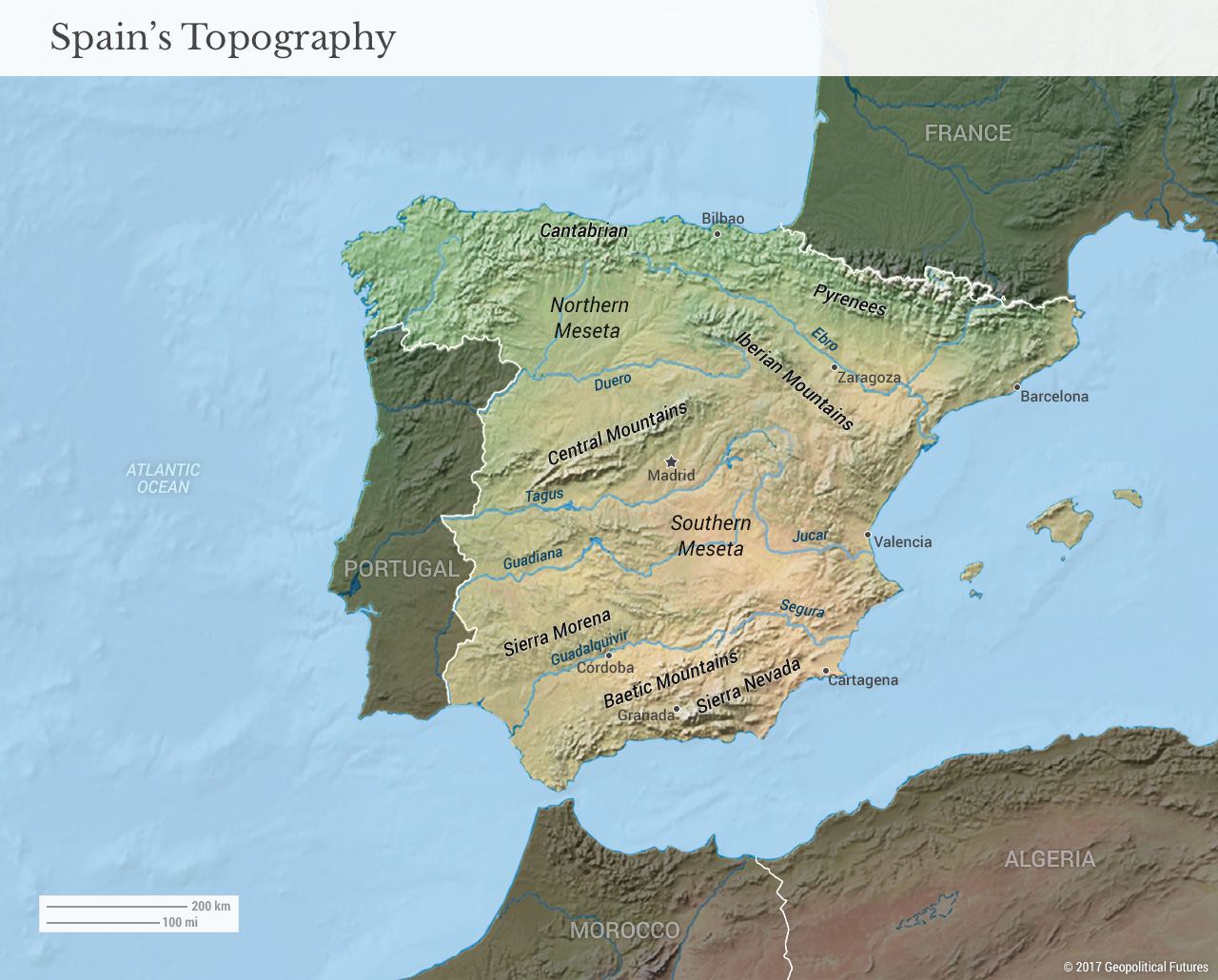
The geography of Southeastern Europe is as various as its inhabitants. Mountain ranges, such because the Dinaric Alps, Pindus Mountains, and Balkan Mountains, dominate the panorama, creating remoted valleys and hindering simple communication and transportation all through historical past. These pure boundaries have contributed to the event of distinct regional identities and cultures, typically separated by language, faith, and custom. The presence of quite a few rivers, together with the Danube, Sava, and Morava, has traditionally facilitated commerce and settlement, but in addition led to territorial disputes and strategic significance all through the centuries.
Coastal areas, notably alongside the Adriatic, Aegean, and Black Seas, have performed essential roles within the area’s historical past. Port cities like Dubrovnik, Cut up, Thessaloniki, and Constanța served as very important hubs for commerce, cultural trade, and the unfold of concepts, typically connecting Southeastern Europe to wider Mediterranean and Eurasian networks. The fertile plains of Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria have supported vital agricultural manufacturing, contributing to the financial vitality of the area. Nevertheless, the uneven distribution of assets and arable land has additionally been a supply of battle and financial disparity.
A Crucible of Cultures: Historic and Ethnic Complexity
Southeastern Europe’s historic expertise is marked by a posh interaction of empires and migrations. The area has been a crossroads of civilizations, with successive waves of Greeks, Romans, Slavs, Ottomans, and Austro-Hungarians leaving indelible imprints on its cultural panorama. This layered historical past is mirrored within the area’s structure, languages, religions, and traditions. The legacy of the Ottoman Empire, particularly, is pervasive, evident within the architectural kinds of many cities, the affect on delicacies and customs, and the enduring presence of Islam alongside Orthodox Christianity and Catholicism.
The ethnic range of Southeastern Europe is equally putting. Quite a few ethnic teams, together with Albanians, Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Greeks, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Romanians, Serbs, Slovenes, and others, coexist inside comparatively small geographic areas. This range, whereas enriching, has additionally been a supply of stress and battle. Centuries of overlapping empires and shifting borders have led to intricate patterns of ethnic intermingling and, at occasions, violent clashes over territory and nationwide identification. The legacy of those conflicts continues to form political relations and social dynamics inside the area.
Geopolitical Dynamics: A Area in Transition
The geopolitical panorama of Southeastern Europe is characterised by its strategic location and enduring tensions. The area’s proximity to the European Union and the Russian Federation locations it on the coronary heart of a posh geopolitical tug-of-war. The growth of the EU eastward has had a profound impression on the area, providing alternatives for financial improvement and political integration but in addition elevating considerations about sovereignty and nationwide identification.
The legacy of the Yugoslav Wars within the Nineteen Nineties continues to forged a protracted shadow. The disintegration of Yugoslavia led to widespread violence and ethnic cleaning, leaving deep scars on the area’s psyche. Whereas peace has largely returned, the unresolved problems with territorial disputes, minority rights, and historic grievances proceed to pose challenges to regional stability. The rise of nationalism and populism in a number of Southeastern European nations additionally presents a possible menace to regional cooperation and integration.
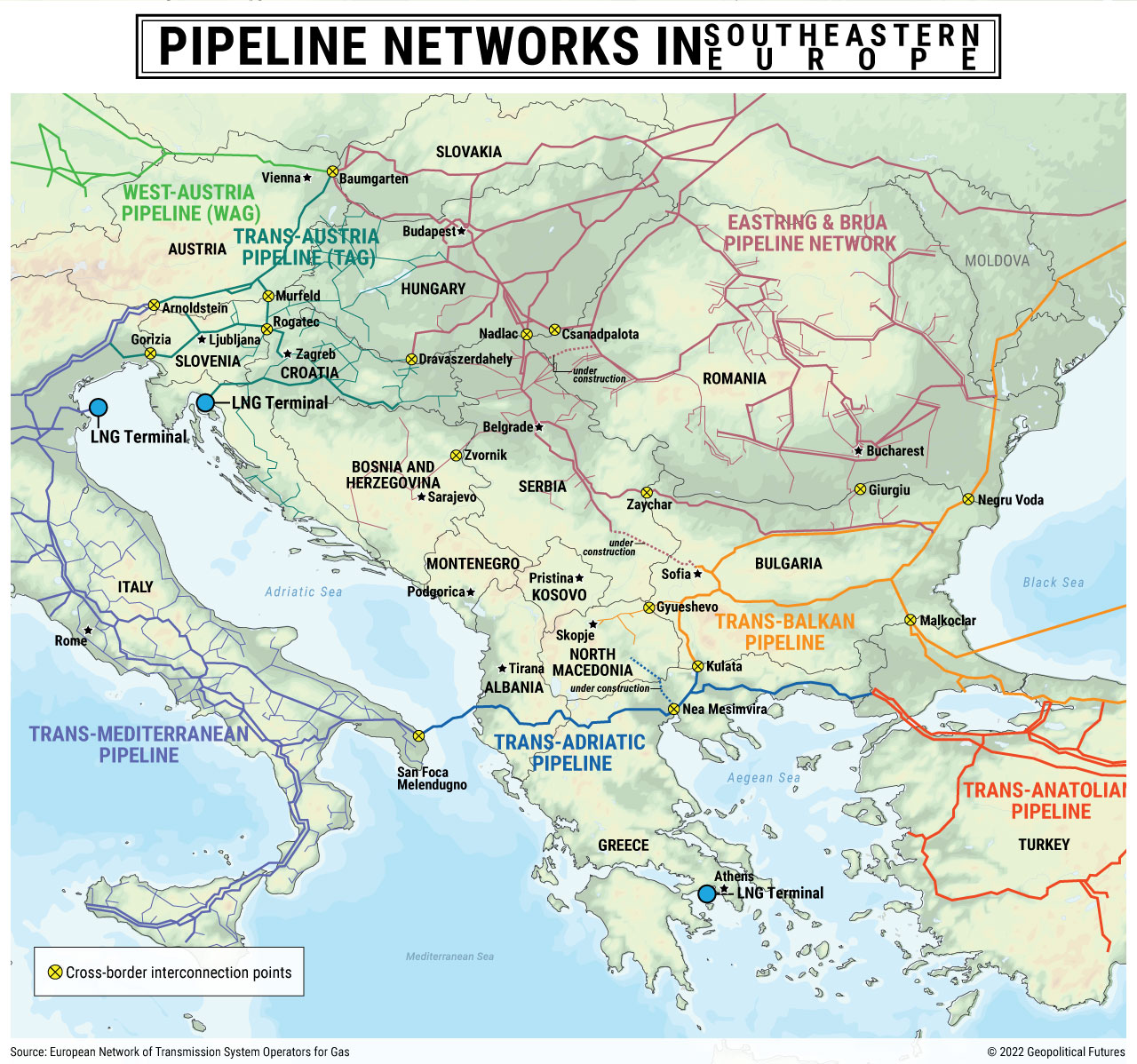
Moreover, the area’s power safety stays a important concern. Many Southeastern European nations rely closely on power imports, primarily from Russia. Diversifying power sources and decreasing dependence on a single provider are essential for enhancing power safety and selling financial independence. The event of regional power infrastructure, together with pipelines and interconnectors, is significant on this regard.
Challenges and Alternatives:
Southeastern Europe faces numerous vital challenges, together with:
- Financial disparities: Vital financial gaps exist between totally different nations and areas inside the area. Addressing these disparities requires focused investments in infrastructure, schooling, and human capital.
- Corruption: Corruption stays a widespread drawback in lots of Southeastern European nations, hindering financial improvement and undermining democratic establishments. Strengthening the rule of legislation and selling transparency are essential for tackling this problem.
- Demographic adjustments: Many Southeastern European nations face declining populations and getting older demographics. This poses challenges to financial progress and social welfare methods.
- Mind drain: The emigration of expert employees to different elements of Europe contributes to a lack of human capital and additional exacerbates financial challenges.
Regardless of these challenges, Southeastern Europe additionally presents vital alternatives:
- EU integration: Membership within the European Union gives the potential for financial progress, political stability, and enhanced regional cooperation.
- Tourism: The area’s wealthy cultural heritage and various landscapes provide vital potential for tourism improvement.
- Renewable power: Southeastern Europe has appreciable potential for growing renewable power sources, corresponding to hydropower, photo voltaic, and wind energy.
- Regional cooperation: Enhanced regional cooperation can foster financial improvement, handle frequent challenges, and promote stability.
Conclusion:
Southeastern Europe is a area of extraordinary complexity and dynamism. Its distinctive geography, various cultures, and turbulent historical past have formed its present-day challenges and alternatives. Navigating the intricate internet of geopolitical dynamics and addressing the legacy of previous conflicts are essential for guaranteeing the area’s future stability and prosperity. The trail ahead requires a dedication to regional cooperation, good governance, financial improvement, and the promotion of inclusive societies that remember range whereas fostering mutual understanding and respect. The way forward for Southeastern Europe hinges on its skill to beat its historic baggage and harness its appreciable potential for progress and integration inside the broader European and international context.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Unpacking Southeastern Europe: A Geographic and Geopolitical Tapestry. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!
